A.1.2 network classes, Appendix – Asus SL6000 User Manual
Page 118
ASUS VPN ADSL Router
117
Appendix
Appendix
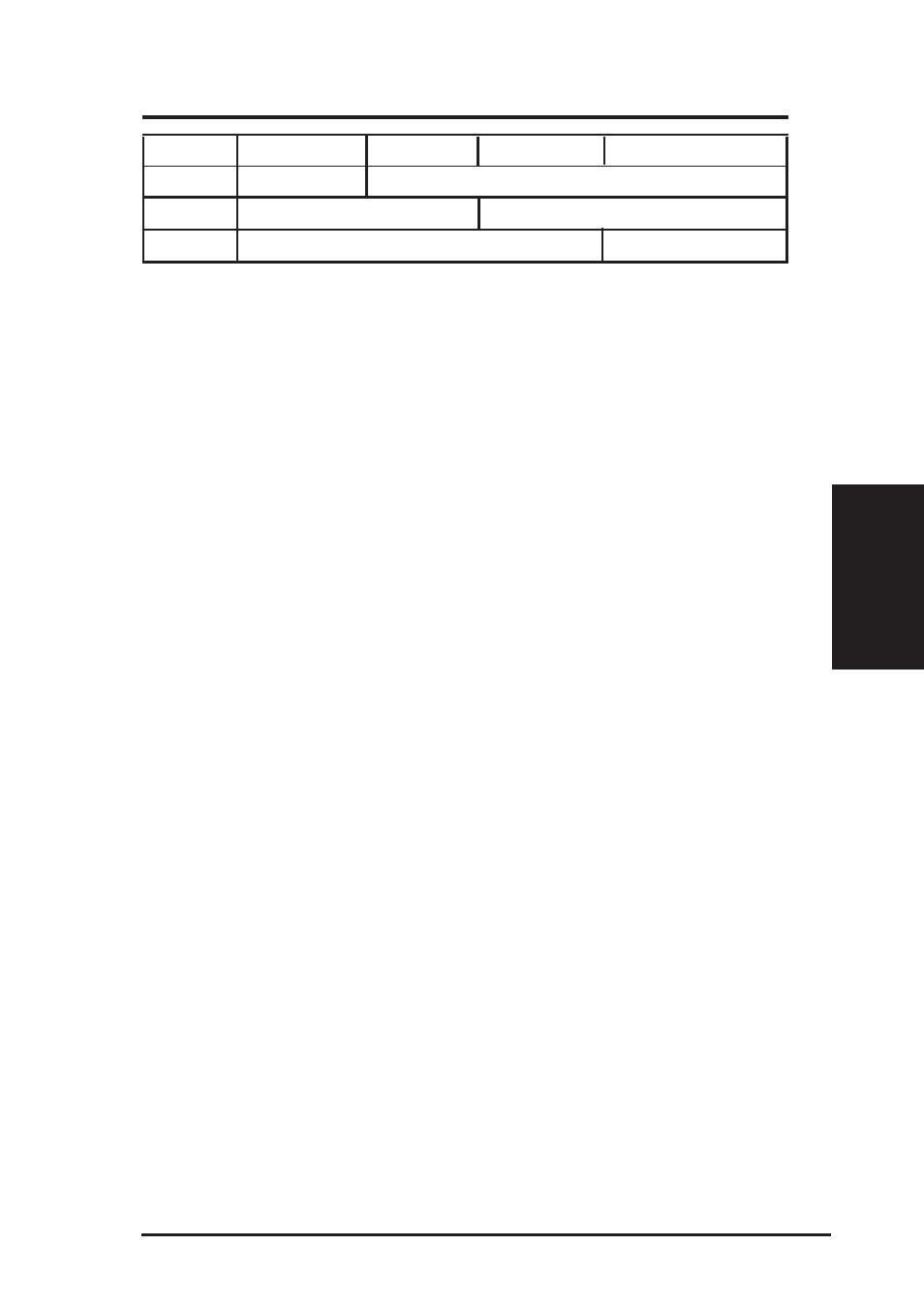
Field1
Field2
Field3
Field4
Class A
Network ID
Host ID
Class B
Network ID
Host ID
Class C
Network ID
Host ID
Table A.1. IP Address structure
Here are some examples of valid IP addresses:
Class A: 10.30.6.125 (network = 10, host = 30.6.125)
Class B: 129.88.16.49 (network = 129.88, host = 16.49)
Class C: 192.60.201.11 (network = 192.60.201, host = 11)
A.1.2 Network classes
The three commonly used network classes are A, B, and C. (There is also a
class D but it has a special use beyond the scope of this discussion.) These
classes have different uses and characteristics.
Class A networks are the Internet’s largest networks, each with room for over
16 million hosts. Up to 126 of these huge networks can exist, for a total of over
2 billion hosts. Because of their huge size, these networks are used for WANs
and by organizations at the infrastructure level of the Internet, such as your
ISP.
Class B networks are smaller but still quite large, each able to hold over 65,000
hosts. There can be up to 16,384 class B networks in existence. A class B
network might be appropriate for a large organization such as a business or
government agency.
Class C networks are the smallest, only able to hold 254 hosts at most, but the
total possible number of class C networks exceeds 2 million (2,097,152 to be
exact). LANs connected to the Internet are usually class C networks.
Some important notes regarding IP addresses:
•
The class can be determined easily from field1:
field1 = 1-126:
Class A
field1 = 128-191: Class B
field1 = 192-223: Class C
(field1 values not shown are reserved for special uses)
•
A host ID can have any value except all fields set to 0 or all fields set to
255, as those values are reserved for special uses.
