The system hid lamp and ecg – OSRAM POWERTRONIC PT-FIT I ECG for HID lamps, with cable clamp User Manual
Page 6
THE SYSTEM HID LAMP AND ECG
1.2.1. Product range
POWERTRONIC
®
ECGs are available in a variety of
wattages. For indoor applications, the PTi and PT-FIT
control gear (POWERTRONIC
®
indoor) have been devel-
oped for operation of HCI and HQI lamps. For this area
of application there are ECGs available that are capable
of being connected to one or two lamps. PTo control
gear (POWERTRONIC
®
outdoor) have been developed
for outdoor operation of HCI, HQI and NAV lamps.
1.2.2. Operating principle
In POWERTRONIC
®
ECGs for high-pressure discharge
lamps, all functions for lamp ignition, lamp operation,
including monitoring and lamp shutdown are controlled
by a single device.
In order to achieve optimal lamp operation, POWERTRONIC
®
ECGs convert the sinusoidal alternating voltage from the
mains supply into a square-wave voltage with an operating
frequency of between 100 and 240 Hz. For optimal lamp
ignition, up to 4.5 kV is supplied by the ECG. But that will
not allow the restrike of hot lamps.
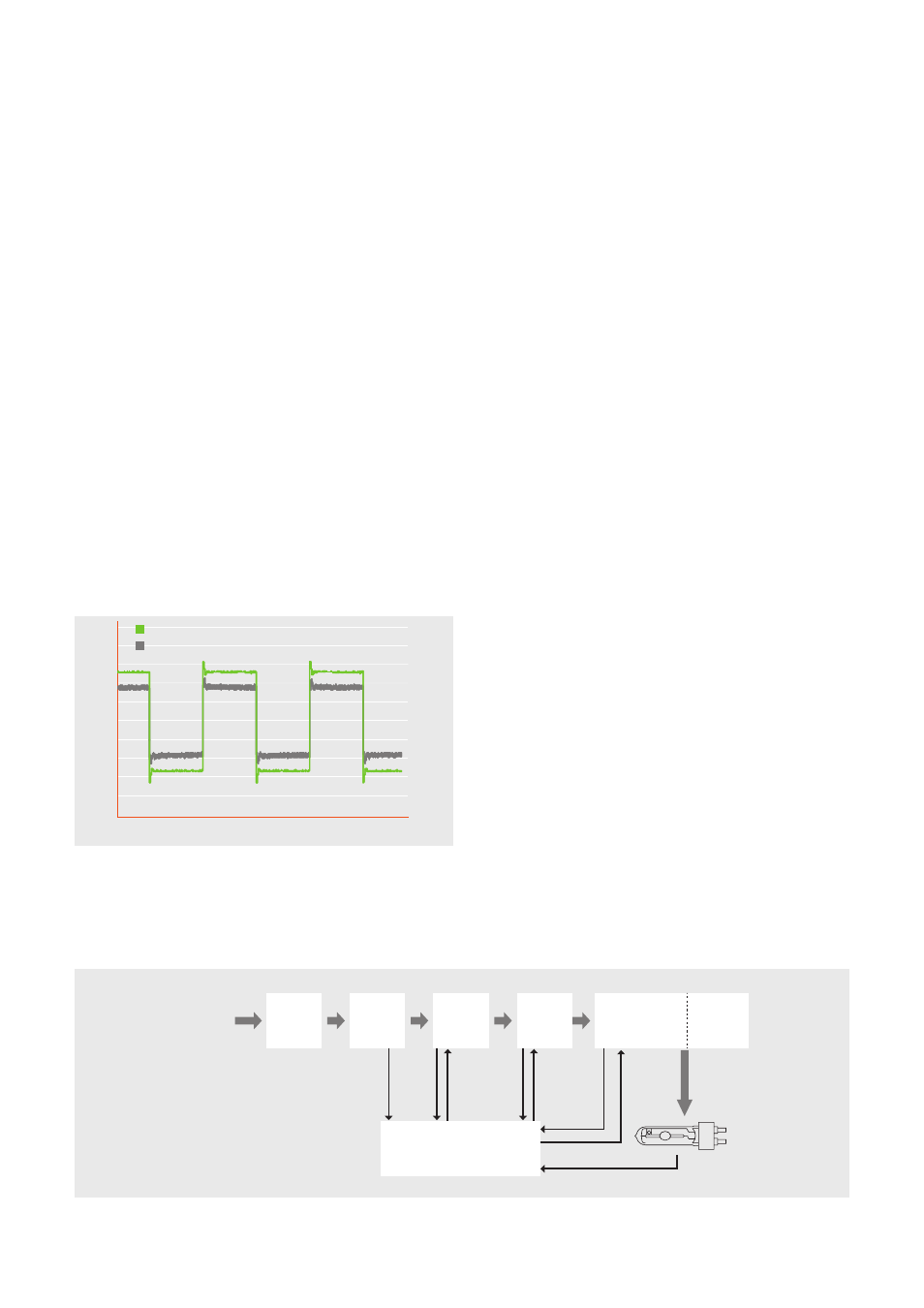
The following diagram shows the current and voltage
curves at the output end of a 150-W POWERTRONIC
®
square wave ECG:
Figure 2: 150 W POWERTRONIC
®
square-wave ECG
Figure 3: Block diagram of a square-wave ECG with half-bridge topology
6
1.2.3. Benefi ts of the intelligent POWERTRONIC
®
ECG
The following list shows the main benefi ts of using an
intelligent OSRAM POWERTRONIC
®
ECG:
• Compact and lightweight
• Long service life of ECG at maximum permissible
temperatures
• Good thermal behavior: High t
a
and t
c
temperatures for
best possible ECG performance, even in luminaires
where heat is a critical factor
• Micro-controller for fully digital lamp control, intelligent
ignition management and safe shutdown at the end of
the lamp life
• Power reduction control and reversible shutdown of the
ECG in cases of unsuitably high ambient temperature
for maximum light comfort
• Versions with cable clamp, with easy-to-install, two- piece
cable clamp (applies to indoor ECGs).
• PCB models for installation with the smallest possible
footprint and/or for thermally critical applications
(applies to ECGs for indoors use)
• 3DIM function (DALI
®
, StepDIM and AstroDIM) for PTo
(outdoor ECGs)
• Lightning strike protection up to 10 kV (for outdoor ECGs)
1.2.4. Advantages of electronic control gear over
conventional gear
In the past, HID lamps were operated almost exclusively
using conventional, ferromagnetic control gear. These
conventional devices are increasingly being replaced by
electronic control gear.
The following table offers an overview of the characteristic
properties of high-intensity discharge lamps and at the
same time shows the substantial advantages of using
electronic control gear for operating such lamps over
using CCG.
In the comparison between CCG and ECG, the perfor-
mance of the CCG is used as the reference, with a value
of 100. This is also due to the fact that the parameters
used to characterize lamps are largely fi xed using CCGs
as a reference.
The following block diagram shows the outline structure of
a classic square-wave ECG in half-bridge topology.
6
7
8
9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
-120
-2.4
-160
-3.2
-200
-4.0
-40
-0.8
-80
-1.6
0
0
40
0.8
120
2.4
80
1.6
160
3.2
200
4.0
Volta
ge (V)
Current (A)
Time (ms)
Voltage
Current
Mains
input
EMC
fi lter
Recti-
fi er
Buck
converter
Half-bridge
inverter
Ignition
Control
unit
PFC
