Applications information, Table 10. global control register, Table 11. global control register configurations – Rainbow Electronics MAX9796 User Manual
Page 24
Applications Information
Class D Filterless Operation
Traditional Class D amplifiers require an output filter to
recover the audio signal from the amplifier’s PWM out-
put. The filters add cost, increase the solution size of
the amplifier, and can decrease efficiency. The tradi-
tional PWM scheme uses large differential output
swings (2 x V
DD(P-P)
) and causes large ripple currents.
Any parasitic resistance in the filter components results
in a loss of power, lowering the efficiency.
The MAX9796 does not require an output filter. The
device relies on the inherent inductance of the speaker
coil and the natural filtering of both the speaker and the
human ear to recover the audio component of the
square-wave output. Eliminating the output filter results
in a smaller, less costly, more efficient solution.
Because the switching frequency of the MAX9796
speaker output is well beyond the bandwidth of most
speakers, voice coil movement due to the square-wave
frequency is very small. Although this movement is
small, a speaker not designed to handle the additional
power may be damaged. For optimum results, use a
speaker with a series inductance >10µH. Typical 8Ω
speakers, for portable audio applications, exhibit series
inductances in the range of 20µH to 100µH.
Input Amplifier
Differential Input
The MAX9796 features a programmable differential
input structure, making it compatible with many
CODECs, and offering improved noise immunity over a
single-ended input amplifier. In devices such as cellu-
lar phones, high-frequency signals from the RF trans-
mitter can be picked up by the amplifier’s input traces.
The signals appear at the amplifier’s inputs as com-
mon-mode noise. A differential input amplifier amplifies
the difference of the two inputs and any signal common
to both is cancelled.
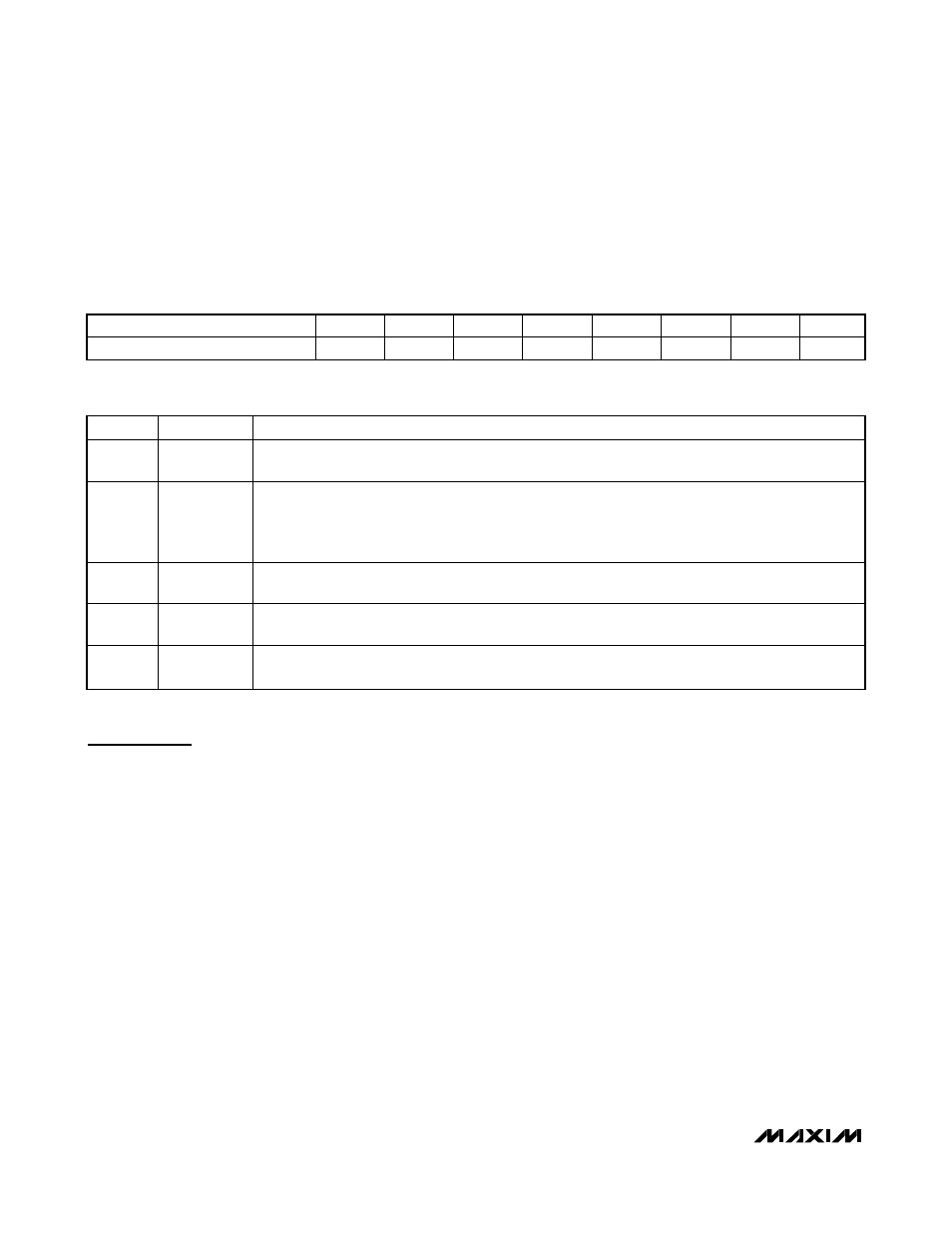
Global Control Register
The Global Control Register is used for global configu-
rations, those affecting all inputs and outputs. The bits
in the Control Register affect the inputs and outputs as
shown in Table 11.
B7
B6
B5
B4
B3
B2
B1
B0
Global Control Register
1
0
1
SHDN
IN+6dB
MUTE
SSM
MONO
Table 10. Global Control Register
BIT
NAME
FUNCTION
B4
SHDN
1 = Normal operation.
0 = Low-power shutdown mode. I
2
C settings are saved.
B3
IN+6dB
1 = All input signals are boosted by 6dB.
0 = All input signals are passed unamplified.
This bit does not affect INA if the INA+20dB bit (B4 of the Input Mode Control Register) is set to 1, in
which case INA is boosted by 20dB.
B2
MUTE
1 = Mute all outputs.
0 = All outputs are active.
B1
SSM
1 = Spread-spectrum Class D modulation.
0 = Fixed-frequency Class D modulation.
B0
MONO
1 = Speaker outputs L+R in modes 7, 8, 12, and 13 (see Table 9).
0 = Speaker outputs L in modes 7, 8, 12, and 13 (see Table 9).
Table 11. Global Control Register Configurations
MAX9796
2.3W, High-Power Class D Audio Subsystem
with DirectDrive Headphone Amplifiers
24
______________________________________________________________________________________
