Rainbow Electronics MAX9796 User Manual
Page 15
Operating Modes
Fixed-Frequency Modulation
The MAX9796 features a fixed-frequency modulation
mode with a 1.1MHz switching frequency, set through
the I
2
C interface (Table 2). In fixed-frequency modula-
tion mode, the frequency spectrum of the Class D out-
put consists of the fundamental switching frequency
and its associated harmonics (see the Wideband
Output Spectrum Fixed-Frequency Mode graph in the
Typical Operating Characteristics
).
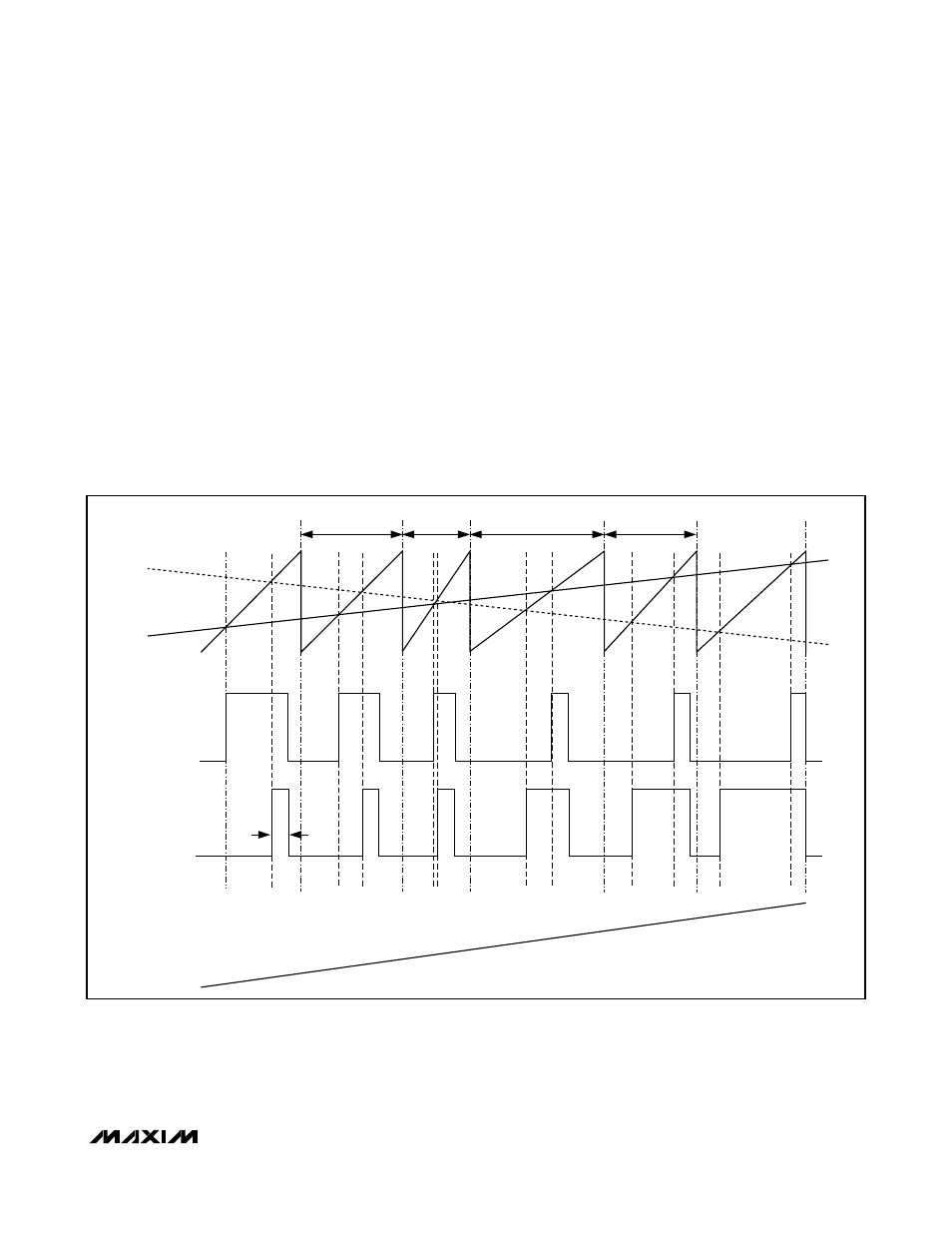
Spread-Spectrum Modulation
The MAX9796 features a unique, patented spread-
spectrum modulation that flattens the wideband spec-
tral components. Proprietary techniques ensure that the
cycle-to-cycle variation of the switching period does
not degrade audio reproduction or efficiency (see the
Typical Operating Characteristics
). Select the spread-
spectrum modulation mode through the I
2
C interface
(Table 2). In spread-spectrum modulation mode, the
switching frequency varies randomly by ±30kHz
around the center frequency (1.16MHz). The modula-
tion scheme remains the same, but the period of the
sawtooth waveform changes from cycle to cycle
(Figure 2). Instead of a large amount of spectral energy
present at multiples of the switching frequency, the
energy is now spread over a bandwidth that increases
with frequency. Above a few megahertz, the wideband
spectrum looks like white noise for EMI purposes (see
Figure 3).
MAX9796
2.3W, High-Power Class D Audio Subsystem
with DirectDrive Headphone Amplifiers
______________________________________________________________________________________
15
V
OUT+
- V
OUT-
t
SW
t
SW
t
SW
t
SW
V
IN-
V
IN+
OUT+
OUT-
t
ON(MIN)
Figure 2. Output with an Input Signal Applied (Spread-Spectrum Modulation Mode)
