1 gprs operations, 1 introduction – Rainbow Electronics GM862-QUAD-PY User Manual
Page 6
Easy GPRS User Guide
80000ST10028 Rev. 4 - 16/07/08
Reproduction forbidden without Telit Communications S.p.A. written authorization - All Rights Reserved
page 6 of 63
1 GPRS Operations
1.1 Introduction
The General Packet Radio Services (GPRS) standard permits DATA transfers in a completely
different way with respect to previous point to point communications made with Circuit Switch Data
(CSD) GSM modems.
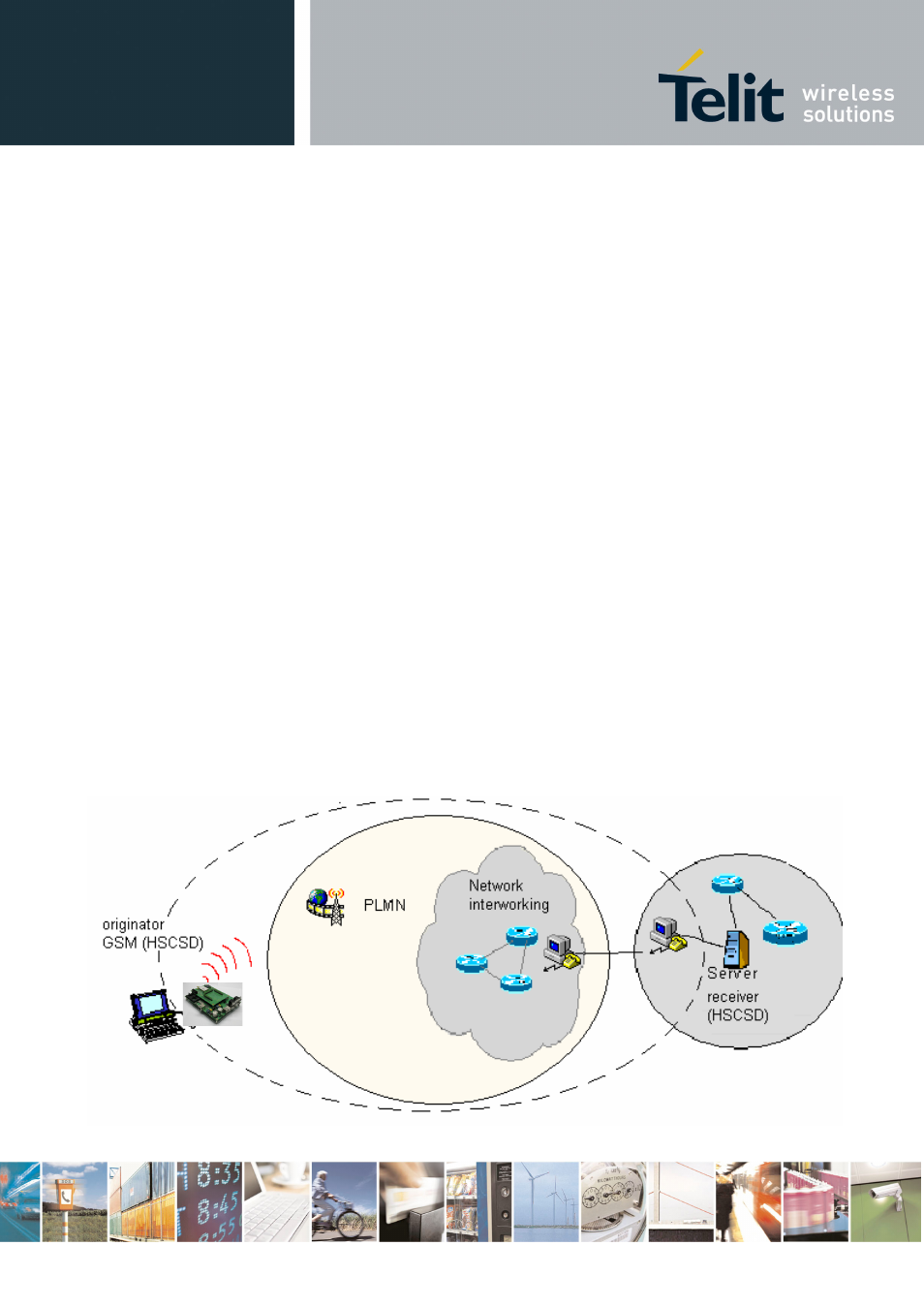
In CSD operations the modem establishes a connection with the other party (another modem) in such
a way that all the Network devices in between are transparent to the data exchanged, simulating a real
point to point connection, just as if the other party is directly connected with the controlling application
of the modem. The other party can be either an Internet Service Provider (ISP) or a private server, but
in any case, the arrival point must have a modem to connect to (Landline, ISDN or GSM CSD). The
connection establishment procedure defines a particular path where all the information exchanged
between the two peers flows and this path is reserved for exclusive use of these 2 peers for all the
time the connection is active.
This approach has the drawbacks of a long time to set-up the link between the two peers (up to a
minute) and a time counting bill which proceeds even if no data is exchanged because the path
resources are reserved anyway; furthermore the speed of the data transfer is limited to 14400 bps.
An example of this kind of operation is shown in the following picture, where the point to point
connection is between the two peers as if all the devices inside the dashed line are not present: CSD
interconnectivity
