Rainbow Electronics MAX9671 User Manual
Page 15
MAX9670/MAX9671
Low-Power Audio/Video Switch with Audio
Volume Control for Dual SCART Connectors
______________________________________________________________________________________
15
Clickless Switching
The TV audio channel incorporates a zero-crossing
detect (ZCD) circuit that minimizes click noise due to
abrupt signal level changes that occur when switching
between audio signals at an arbitrary moment.
To implement the zero-crossing function when switch-
ing audio signals, set the ZCD bit high (Audio Control
register 00h, bit 6). Then set the mute bit high (Audio
Control register 00h, bit 0). Next, wait for a sufficient
period of time for the audio signal to cross zero. This
period is a function of the audio signal path’s low-fre-
quency 3dB corner (f
L3dB
). Thus, if f
L3dB
= 20Hz, the
time period to wait for a zero-crossing detect is 1/20Hz
or 50ms.
After the wait period, select a new audio source for the
TV audio channel by writing to bits 1 and 0 of TV Audio
Control register (01h). Finally, clear mute (Audio Control
register, 00h, bit 0), but leave ZCD (Audio Control reg-
ister 00h, bit 6) high. The MAX9670/MAX9671 switches
the signal out of mute at the next zero crossing. See
Tables 12 and 13.
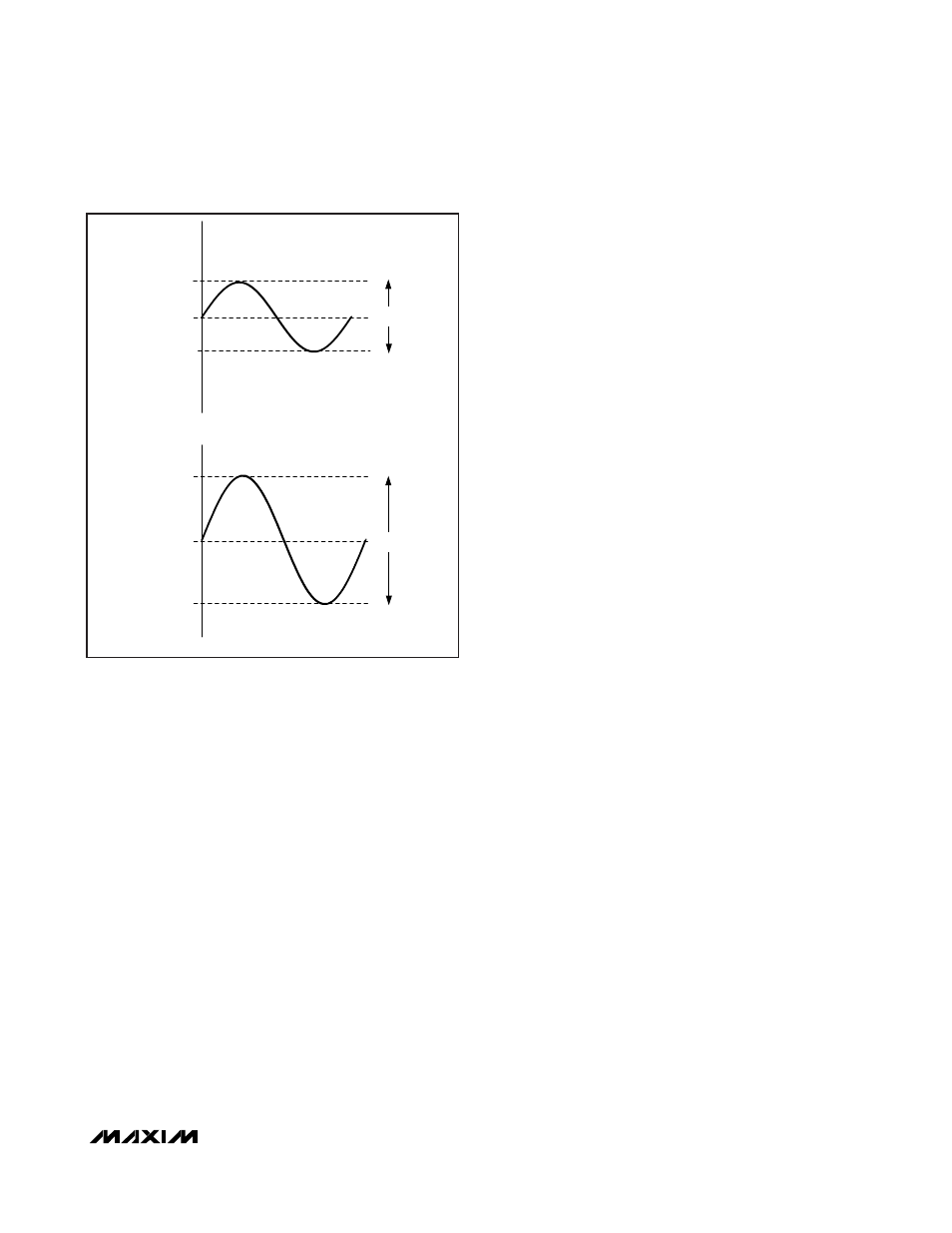
Audio Outputs
The MAX9670/MAX9671 audio output amplifiers feature
Maxim’s patented DirectDrive architecture, thereby
eliminating the need for output-coupling capacitors
required by conventional single-supply audio line dri-
vers. An internal charge pump inverts the positive sup-
ply (V
AUD
), creating a negative supply (CPVSS). The
audio output amplifiers operate from these bipolar sup-
plies with their outputs biased about audio ground
(Figure 2). The benefit of this audio ground bias is that
the amplifier outputs do not have a DC component. The
DC-blocking capacitors required with conventional
audio line drivers are unnecessary, conserving board
space, reducing system cost, and improving frequency
response.
Conventional single-supply audio line drivers have their
outputs biased about a nominal DC voltage (typically
half the supply) for maximum dynamic range. Large
coupling capacitors are needed to block this DC bias.
Clicks and pops are created when the coupling capaci-
tors are charged during power-up and discharged dur-
ing power-down.
The MAX9670/MAX9671 features a low-noise charge
pump that requires only two small ceramic capacitors.
The 580kHz switching frequency is well beyond the
audio range and does not interfere with audio signals.
The switch drivers feature a controlled switching speed
that minimizes noise generated by turn-on and turn-off
transients.
The SCART standard specifies 2V
RMS
as the full-scale
for audio signals. As the audio circuits process
0.5V
RMS
full-scale audio signals internal to the
MAX9670/MAX9671, the gain-of-4 output amplifiers
restore the audio signals to a full-scale of 2V
RMS
.
To select which audio input source is routed to the TV
SCART connector, write to bits 1 and 0 of the TV Audio
Control register (01h). To select which audio input
source is routed to the VCR SCART connector, write to
bits 3 and 2 of the TV Audio Control register (01h). The
power-on default is for the TV and VCR audio outputs to
be muted (the inputs of the output amplifiers are con-
nected to audio ground). See Tables 10 and 13.
Volume Control
Volume control is programmable from -62dB to 0dB in
2dB steps through I
2
C interface. The block consists of
a resistive ladder network to generate 31 2dB volume
control steps, a unity gain buffer to isolate the input
from the resistive ladder, switches (MPLx and MNLx)
that select 1 of 32 nodes on the resistive ladder, and
logic to decode the the I
2
C volume control value. See
Table 12.
+V
DD
-V
DD
GND
V
OUT
CONVENTIONAL DRIVER-BIASING SCHEME
DirectDrive BIASING SCHEME
V
DD
/2
V
DD
V
DD
GND
2V
DD
Figure 2. Conventional Driver Output Waveform vs. MAX9670/
MAX9671 Output Waveform.
