2 hardware processing ras functions, 1 wdt circuit and hardware reset, 3 interrupt signals – Toshiba 2000 User Manual
Page 57
5.2
Hardware Processing RAS Functions
6F8C1111
37
5
5.2
Hardware Processing RAS Functions
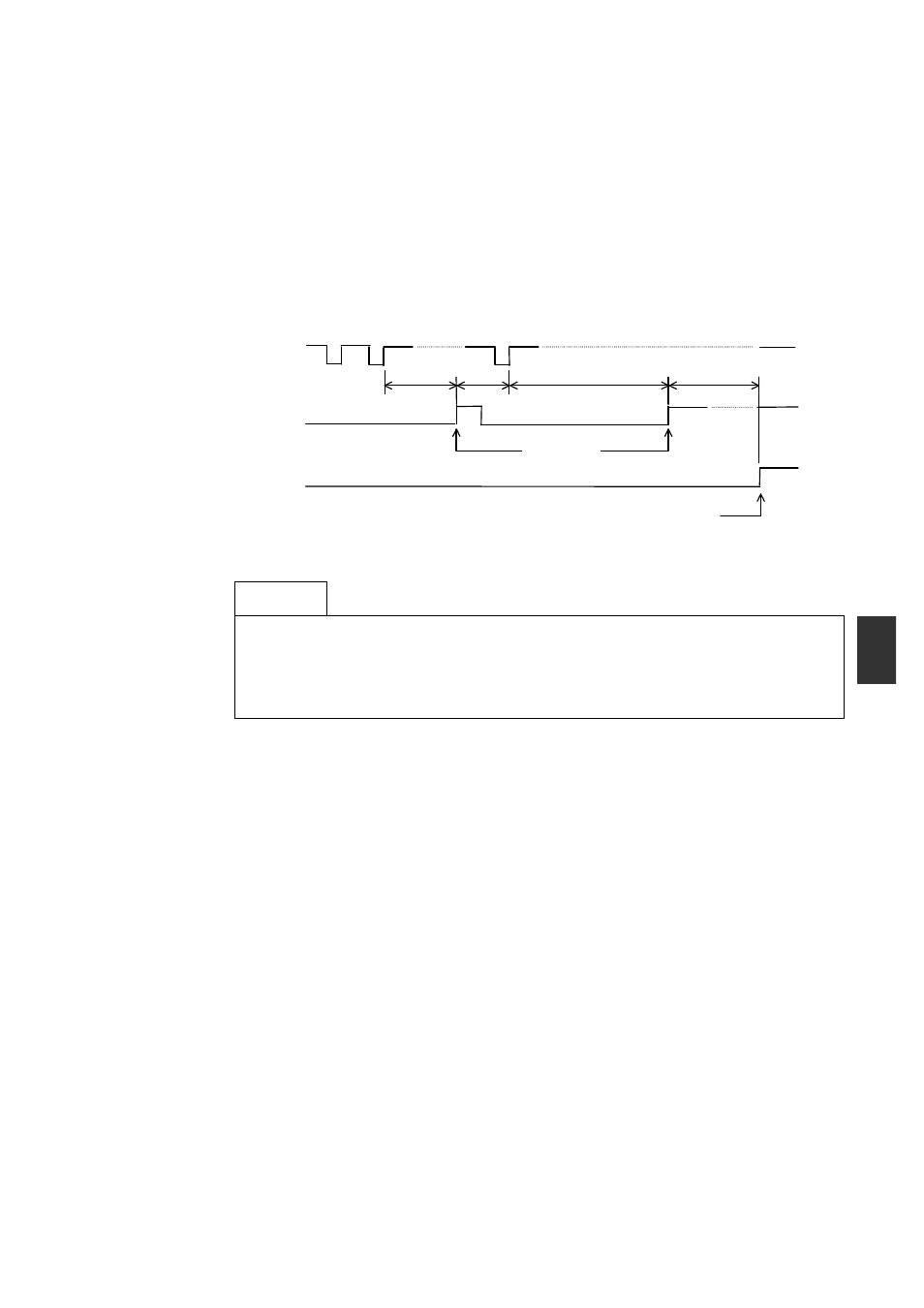
5.2.1 WDT Circuit and Hardware Reset
The WDT circuit issues an NMI to the main unit when the WDT counter is not reset within a
certain interval (WDT monitoring interval). The WDT monitoring interval can be set up to
500ms x 255 (approximately 2 minutes) in 500ms units.
If an NMI is not accepted within 500ms after a WDT timeout NMI is issued, the system is
reset by the hardware reset function.
Force reset because NMI (WDT) reset is not performed by CPU
WDT reset
NMI
request
Force reset
output
500ms*N
500ms*N
500ms
(recover because reset
within 500ms)
NMI issued
Important
• Do not enable the suspend function when using the WDT function. This may cause a
mal-function.
The suspend function is a power saving method and cannot be used together with
the WDT function.
5.2.2 RAS Memory
RAS memory is a 64K-byte battery backed non-volatile memory and is used to store NMI
events and RAS information. It is also used by the RAS support software to save shutdown
information.
RAS memory is designed to be accessed using the I/O space and does not use any
memory space.
RAS memory is backed up by the backup battery (Lithium battery) installed inside the main
unit.
5.2.3 Interrupt Signals
Interrupts detected by RAS board and sent to CPU are classified into NMI events and MI
events.
• Examples of NMI events are: WDT timeout, events requiring immediate action such as
power failure, system shutdown, and remote input for power control.
• An example of MI event is fan stop.
