Texas Instruments THUNDER TNETX3270 User Manual
Page 21
TNETX3270
ThunderSWITCH
24/3 ETHERNET
SWITCH
WITH 24 10-MBIT/S PORTS AND 3 10-/100-MBIT/S PORTS
SPWS043B – NOVEMBER 1997 – REVISED APRIL 1999
21
POST OFFICE BOX 655303
•
DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
frame format on the NM port (continued)
TPID (Tag Protocol Identifier)
TCI (Tag Control Information)
Destination
Address
Source
Address
TPID
TCI
Length/Type
FCS
(CRC-32)
Data
Reserved
7
5
4
3
6
2nd
TCI
Byte
Odd Parity Bits
Reserved
Source
Port
Byte 1
Byte 2
CRC
Type
802.1Q header
1st
TCI
Byte
1st
TPID
Byte
2
1
0
7
5
4
3
6
2
1
0
1 0 0 0 0
0
0
0
1
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Priority cfi
VLAN ID
6 Bytes
6 Bytes
2 Bytes
2 Bytes
46–1517 Bytes
2 Bytes
4 Bytes
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 6
5
4 3 2 1 0 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
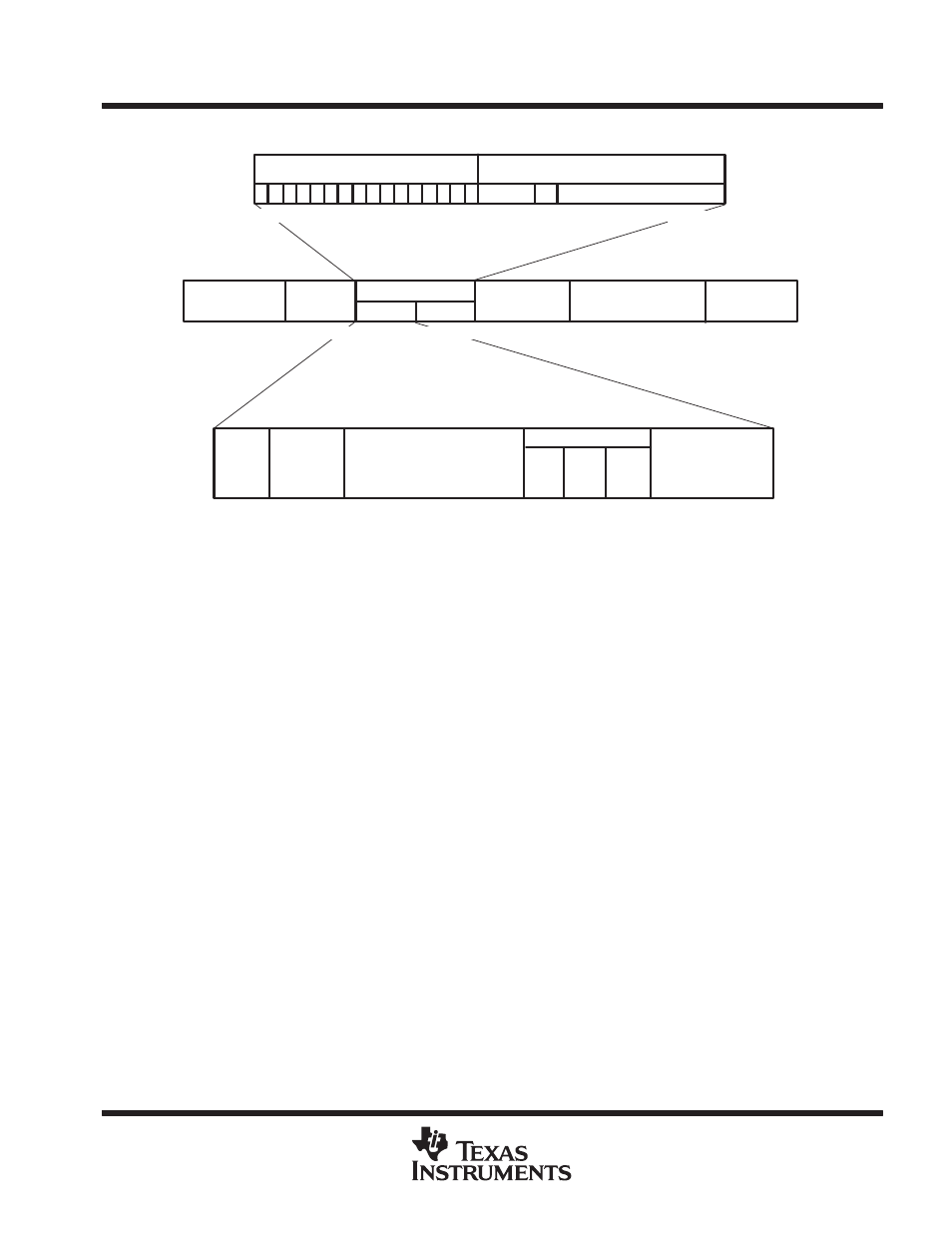
Figure 2. NM Frame Format
Any device reading frames out of the NM port must expect frames to be in the format shown in Figure 2.
Frames received into the switch on the NM port also must conform to this format, with the following caveats:
D
crc = 0
in NMRxcontrol
When the host provides a frame containing valid CRC it also must provide in the TPID field valid header
parity protection and indicate via the crctype bit which type of CRC the frame contains [i.e., including the
header (crctype = 0), or excluding the header (crctype = 1)]. If crctype indicates that the header is included,
as for NM port transmissions, this pretends that IEEE Std 802.1Q TPID of 81–00 (ethertype constant) is
present in the TPID field. If a CRC error or parity error is detected, the frame is discarded.
When
crctype indicates that the header is included, the NM port regenerates CRC to exclude the header
during the reception process (this converts the frame into the required internal frame format).
D
crc = 1
in NMRxcontrol
If the switch is asked to generate a CRC word for the frame, the values in the TPID field are ignored by the
NM port. The switch inserts header parity protection. It replaces the final four bytes of the frame with the
calculated CRC (the values in the final four bytes provided are don’t care).
In either case, the NM port inserts its own port number into the source port field in the least significant bits of
the first TPID byte, sets the crctype bit to 0, and also sets the reserved bits to 0.
Frames received from the host via the NM port must contain a valid IEEE Std 802.1Q VLAN ID in the third and
fourth bytes, following the source address (the NM port does not have a PortxQtag register for inserting a VLAN
tag if none is provided and does not have an
rxacc bit). Frames that do not contain a VLAN tag are incorrectly
routed. They also can be corrupted at the transmission port(s). The header-stripping process does not verify
that the two bytes after the source address are a valid IEEE Std 802.1Q TPID because there is a valid header
under all other circumstances.
