Table 1-2. calculating hankel singular values – National Instruments NI MATRIXx Xmath User Manual
Page 16
Chapter 1
Introduction
© National Instruments Corporation
1-9
•
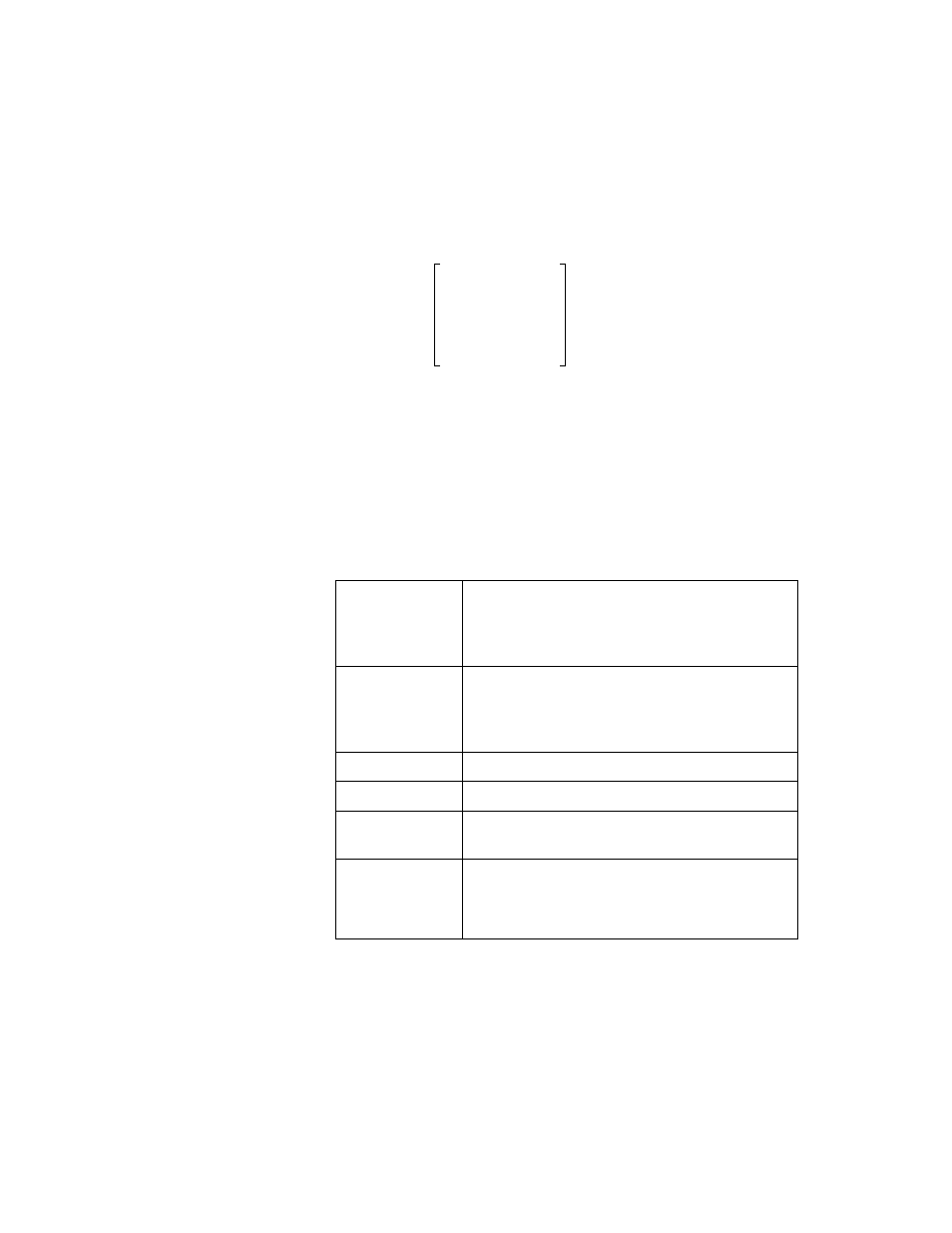
Suppose the transfer-function matrix corresponds to a discrete-time
system, with state variable dimension n. Then the infinite Hankel
matrix,
has for its singular values the n nonzero Hankel singular values,
together with an infinite number of zero singular values.
The Hankel singular values of a (stable) all pass system (or all pass matrix)
are all 1.
Slightly different procedures are used for calculating the Hankel singular
values (and so-called weighted Hankel singular values) in the various
functions. These procedures are summarized in Table 1-2.
Table 1-2. Calculating Hankel Singular Values
(balance( ))
For a discussion of the balancing algorithm, refer to
the
Internally Balanced Realizations
Hankel singular values are given by
diag(R
1/2
) = HSV
balmoore( )
For a discussion of the balancing algorithm, refer to
the
Internally Balanced Realizations
matrix S
H
yields the Hankel singular values through
diag(SH)
hankelsv( )
real(sqrt(eig(p*q)))
ophank( )
Calls
hankelsv( )
redschur( )
Computes a Schur decomposition of P*Q and then
takes the square roots of the diagonal entries
bst( )
mulhank( )
wtbalance( )
fracred( )
Same as
redschur( )
except either P or Q can be
a weighted grammian
H
CB
CAB CA
2
B
CAB CA
2
B
CA
2
B
=
