Overview of wep parameters – NETGEAR MR814 v3 User Manual
Page 142
Reference Manual for the MR814 v3 Cable/DSL Wireless Router
D-6
Wireless Networking Basics
202-10039-01
5.
The station connects to the network.
If the decrypted text does not match the original challenge text (i.e., the access point and station do
not share the same WEP Key), then the access point will refuse to authenticate the station and the
station will be unable to communicate with either the 802.11b network or Ethernet network.
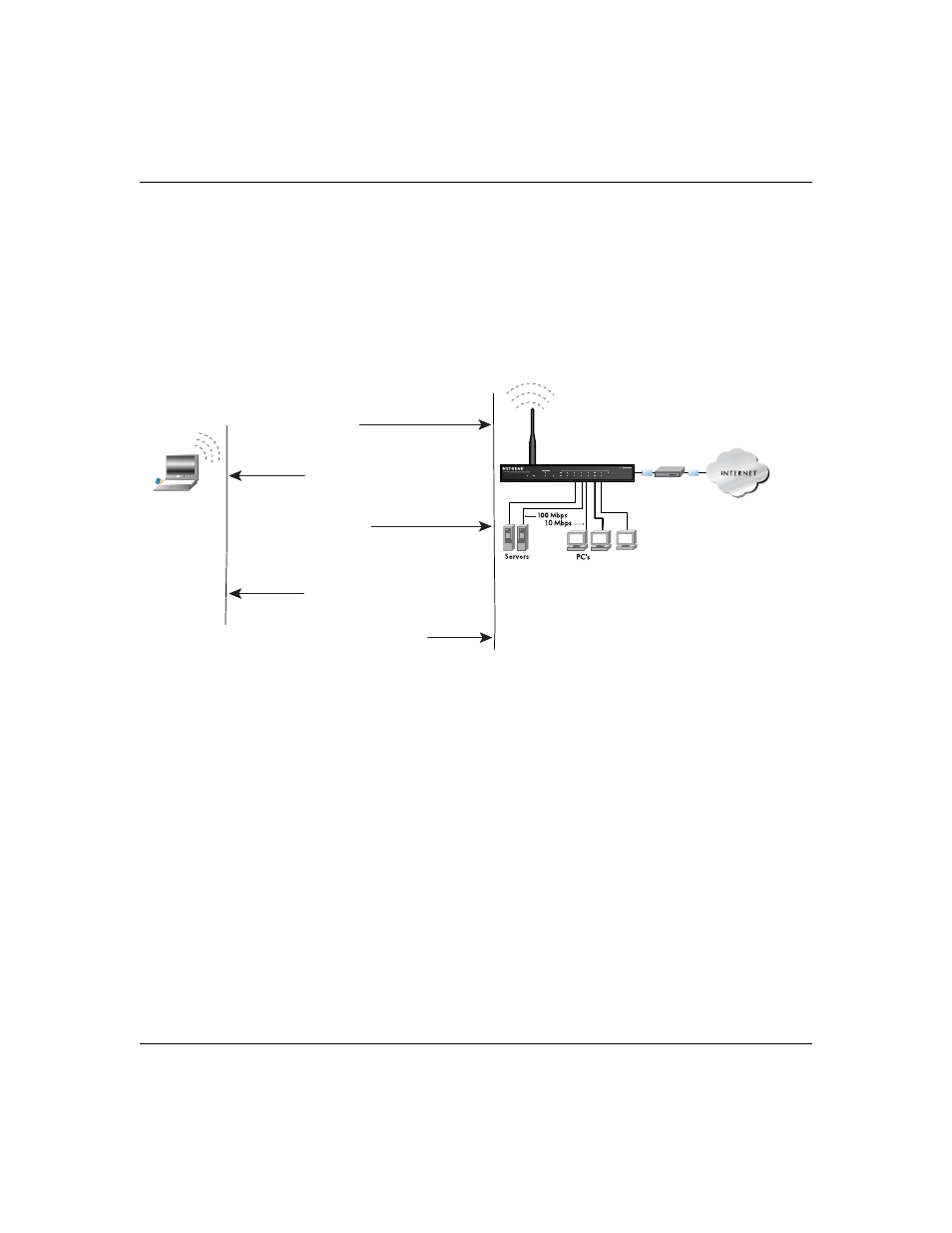
This process is illustrated in below.
Figure 8-2: 802.11b shared key authentication
Overview of WEP Parameters
Before enabling WEP on an 802.11b network, you must first consider what type of encryption you
require and the key size you want to use. Typically, there are three WEP Encryption options
available for 802.11b products:
1. Do Not Use WEP: The 802.11b network does not encrypt data. For authentication purposes, the
network uses Open System Authentication.
2. Use WEP for Encryption: A transmitting 802.11b device encrypts the data portion of every
packet it sends using a configured WEP Key. The receiving 802.11b device decrypts the data using
the same WEP Key. For authentication purposes, the 802.11b network uses Open System
Authentication.
I N TER N ET
LO C A L
ACT
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
LNK
LNK/ACT
100
Cable/DSL
ProSafe Wireless VPN Security Firewall
MODEL
FVM318
PWR
TEST
W LA N
Enable
Access Point
1) Authentication
request sent to AP
2) AP sends challenge text
3) Client encrypts
challenge text and
sends it back to AP
4) AP decrypts, and if correct,
authenticates client
5) Client connects to network
802.11b Authentication
Shared Key Steps
Cable or
DLS modem
Client
attempting
to connect
