Network configuration – Lindy Switch User Manual
Page 58
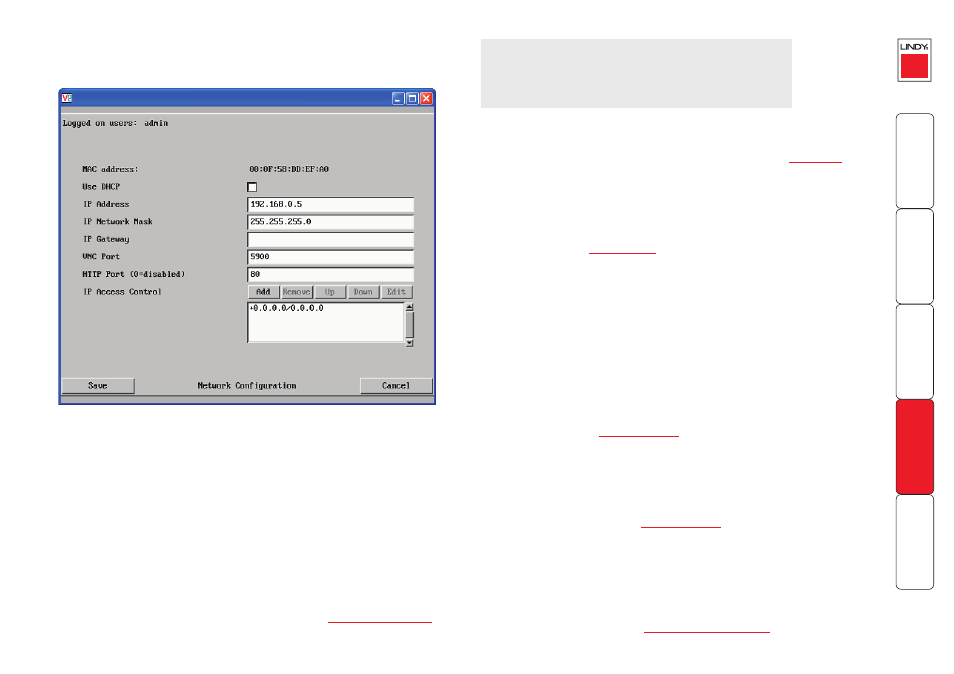
Network configuration
This page allows you to configure the various aspects of the IP port and its
relationship with the local network.
MAC address
Media Access Control address – this is the unique and unchangeable code that
was hard coded within your LINDY KVM IP unit when it was built. It consists of
six 2-digit hexadecimal (base 16) numbers separated by colons. A section of the
MAC address identifies the manufacturer, while the remainder is effectively the
unique electronic serial number of your particular unit.
Use DHCP
DHCP is an acronym for ‘Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol’. Its function is
particularly useful when connecting to medium size or larger networks, such as
the Internet. When this option is selected, your LINDY KVM IP will attempt to
locate a DHCP server on the network. If such a server is located, it will supply
three things to the LINDY KVM IP: an IP address, an IP network mask (also
known as a Subnet mask) and a Gateway address. These are not usually granted
permanently, but on a ‘lease’ basis for a fixed amount of time or for as long as
the LINDY KVM IP remains connected and switched on.
.
IP Address
This is the identity of the LINDY KVM IP within a network. The
can be thought of as the telephone number of the LINDY KVM IP. Unlike the
MAC address, the IP address can be altered to suit the network to which it is
connected. It can either be entered manually or configured automatically using
the DHCP option. When the DHCP option is enabled, this entry is greyed out.
IP Network Mask
Also often called the
, this value is used alongside the IP address
to help define a smaller collection (or subnet) of devices on a network. In this
way a distinction is made between locally connected devices and ones that are
reachable elsewhere, such as on the wider Internet. This process helps to reduce
overall traffic on the network and hence speed up connections in general.
IP Gateway
This is the address of the device that links the local network (to which the LINDY
KVM IP is connected) to another network such as the wider Internet. Usually
the actual gateway is a network switch or router and it will be used whenever a
required address lies outside the current network.
VNC Port
This is the logical link through which communications with a remote VNC viewer
will be channelled (see
). The default setting is 5900 which is
a widely recognised port number for use by VNC software. However, in certain
circumstances it may be advantageous to alter this number - see ‘Security issues
with ports’ for more details.
HTTP Port
This is the logical link through which communications with a remote web
browser will be channelled (see
). The default setting of 80 is an
established standard for web (HTTP – HyperText Transfer Protocol) traffic though
this can be changed to suit your local network requirements.
IP Access Control
This section allows you to optionally specify ranges of addresses which will or
won’t be granted access to the LINDY KVM IP. If this option is left unchanged,
then the default entry of ‘+0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0’ ensures that access from all IP
addresses will be permitted. See
for details.
To get here
1 Using VNC viewer or a browser, log on as the ‘admin’ user.
2 Click the ‘Configure’ button in the top right corner.
3 Click the ‘Network Configuration’ option.
