Parity – LSI MegaRAID Express 500 User Manual
Page 25
Chapter 2 Introduction to RAID
11
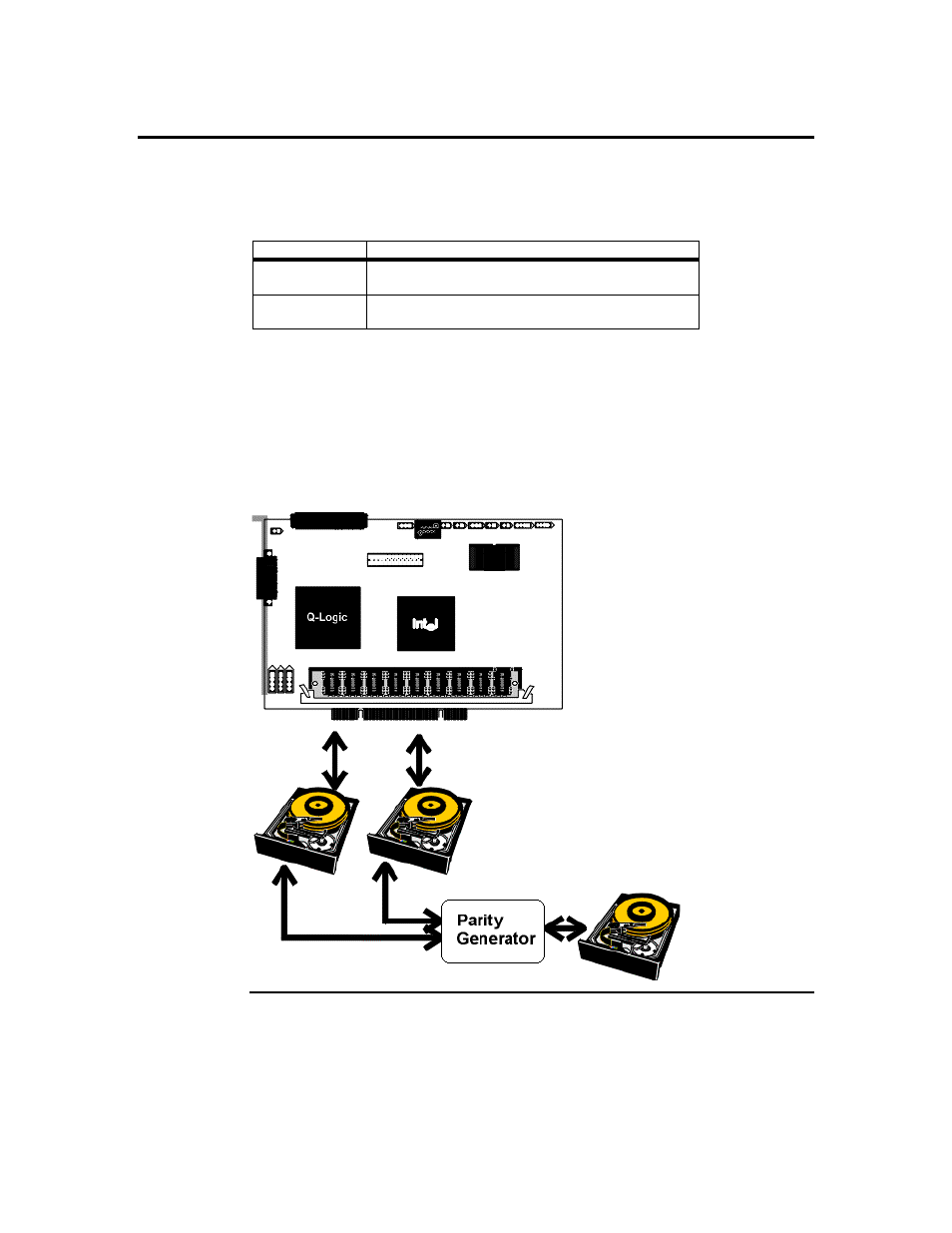
Parity
Parity generates a set of redundancy data from two or more parent data sets. The
redundancy data can be used to reconstruct one of the parent data sets. Parity data does
not fully duplicate the parent data sets. In RAID, this method is applied to entire drives or
stripes across all disk drives in an array. The types of parity are:
Type
Description
Dedicated Parity
The parity of the data on two or more disk drives is
stored on an additional disk.
Distributed
Parity
The parity data is distributed across all drives in the
system.
If a single disk drive fails, it can be rebuilt from the parity and the data on the remaining
drives.
RAID level 3 combines dedicated parity with disk striping. The parity disk in RAID 3 is
the last logical drive in a RAID set.
RAID level 5 combines distributed parity with disk striping. Parity provides redundancy
for one drive failure without duplicating the contents of entire disk drives, but parity
generation can slow the write process. A dedicated parity scheme during normal
read/write operations is shown below:
