3 overview of noise reduction, Overview of noise reduction – Kenwood 50 MHZ ALL MODE TRANSCEIVER TS-590S User Manual
Page 37
4 DSP
TS-590S
31
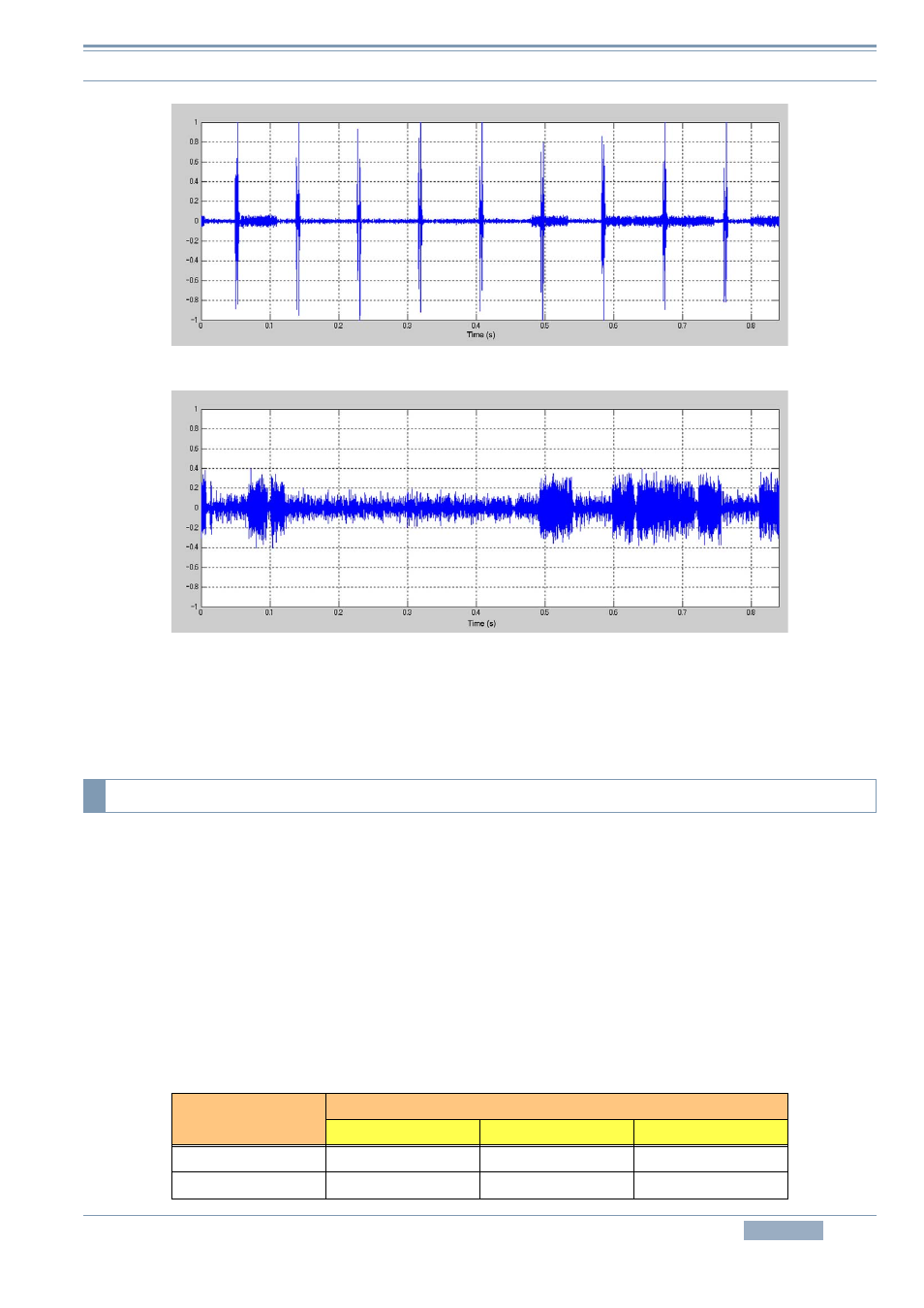
Figure 4-11 NB2: Inactive
Figure 4-12 NB2: Active
However, depending on the nature of the pulse noise, the noise blanker cannot suppress the noise
effectively. In such a case, by using other methods such as noise reduction in conjunction, the
reception conditions may be improved.
There are two methods available for noise reduction on TS-590S: NR1 and NR2. You can select the
noise reduction that is more effective depending on the operation mode and reception conditions.
NR1 has different algorithms that operate according to the operation mode: in voice modes (SSB, FM
and AM), a newly developed noise reduction method featuring audio signals based on spectral
subtraction is used. In non-voice modes (CW and FSK), noise reduction is based on a line enhancer
using an adaptive filter that emphasizes the periodic signal. The noise reduction is automatically
switched over when an operation mode is selected.
On the other hand, NR2 employs what is known as SPAC (speech processing by auto correlation) to
piece together only the periodic components detected from the RX signal and to produce the result as
audio output. Table 4-1 provides the relationship between the RX modes and NR algorithms used.
Table 4-1 Reception Modes and NR Algorithms Used
4.6.3 Overview of Noise Reduction
Noise Reduction
Receive Mode
SSB/ SSB DATA
FM/ AM
CW/ FSK
NR1
Spectral subtraction
Spectral subtraction
Line enhancer
NR2
SPAC
SPAC
SPAC
