Customer billing mainframe, Area imc, Stargate – Sony Ericsson LBI-38965 User Manual
Page 11
LBI-38965
11
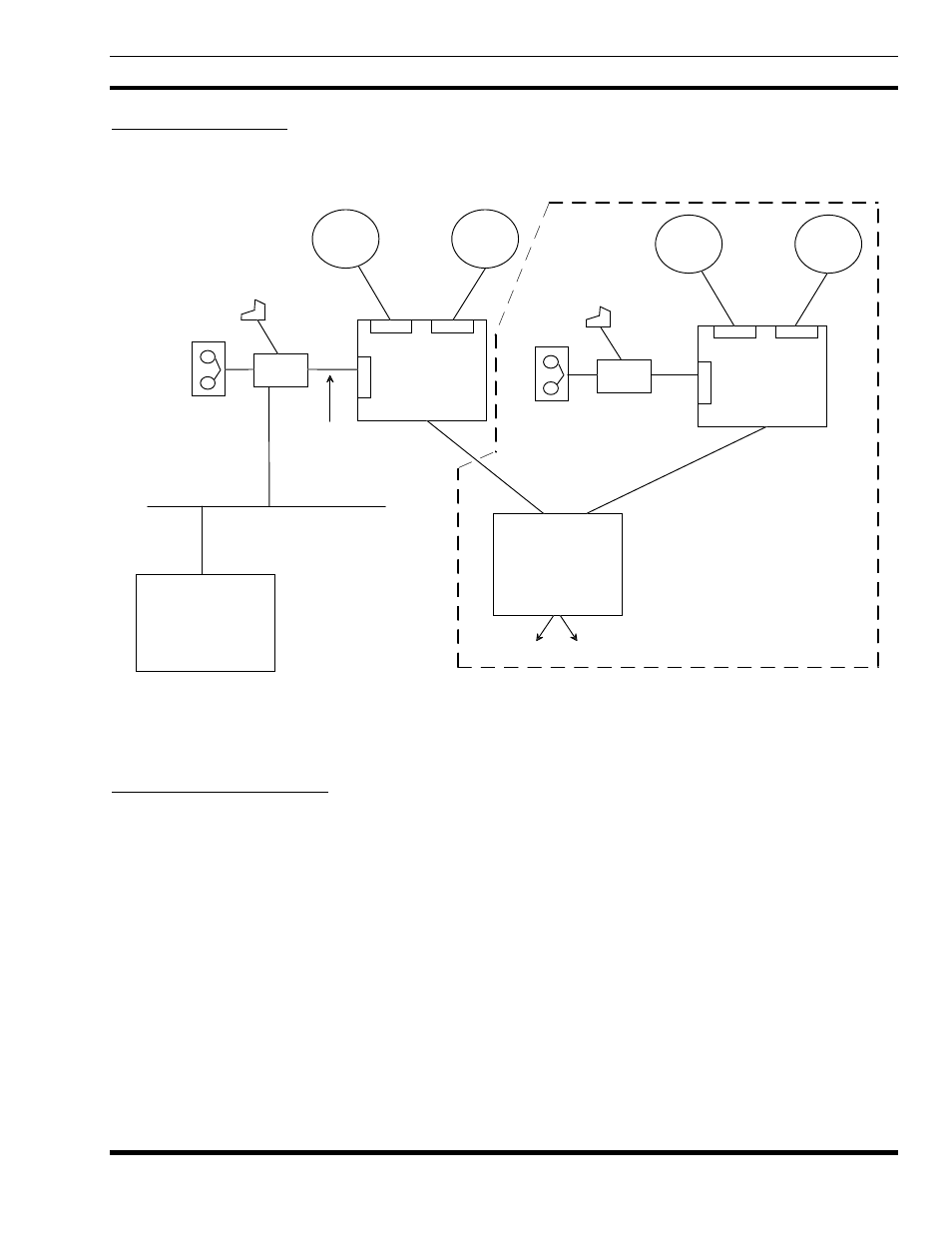
3.2.2. Billing Architecture
The EDACS billing system architecture is shown in Figure 3. Each IMC is connected to a BCU/CAL via a high-speed
serial communications link using HDLC protocol.
Figure 3 - Billing Architecture
3.2.3. BCU Operation Overview
Each RF system sends all call information to the IMC via the downlink. This is true for single-channel autonomous
trunking (SCAT), Conventional Network Interface (CNI), basic EDACS, and RF systems operating in failsoft mode.
All call activity information messages received by the IMC are collected by the Central Activity Module (CAM), where
each call message is time stamped. These messages, called raw activity records (RARs), are then passed via the high-speed
serial link to the BCU/CAL.
If activity logging is enabled, the BCU first archives a copy of each RAR received. The BCU then examines each RAR
and uses the time stamp values to determine the length of each call. The actual billing algorithm is quite complex and
depends on the BCU's keeping a memory of outstanding calls. The output of the billing algorithm is stored to a regular disk
file as a series of call detail records (CDR). Activity logging of RARs is a diagnostic capability not required for normal BCU
functionality. RAR activity logging consumes disk space and can result in degraded system throughput. Although the feature
is provided, its use is strongly discouraged for most users.
The CDR format is compatible with Cincinnati Bell Information System’s (CBIS) Cellware billing software.
Console
Terminal
Terminal
Console
High-Speed
HDLC Link
DAT (Optional)
DAT (Optional)
Customer
Billing
Mainframe
TCP/IP WAN
BCU
RF
System
RF
System
RF
System
Area
IMC
MIM
MIM
C
A
M
Downlink
BCU
C
A
M
Area
IMC
MIM
MIM
StarGate
To other IMCs
RF
System
Ethernet
The dotted lines enclose one optional setup for a StarGate (multi-node) billing architecture.
