9 placement of data – IBM DS8000 User Manual
Page 121
Chapter 5. Virtualization concepts
99
This new virtualization concept provides for much more flexibility. Logical volumes can
dynamically be created and deleted. They can be grouped logically to simplify storage
management. Large LUNs and CKD volumes reduce the total number of volumes and this
also contributes to a reduction of the management effort.
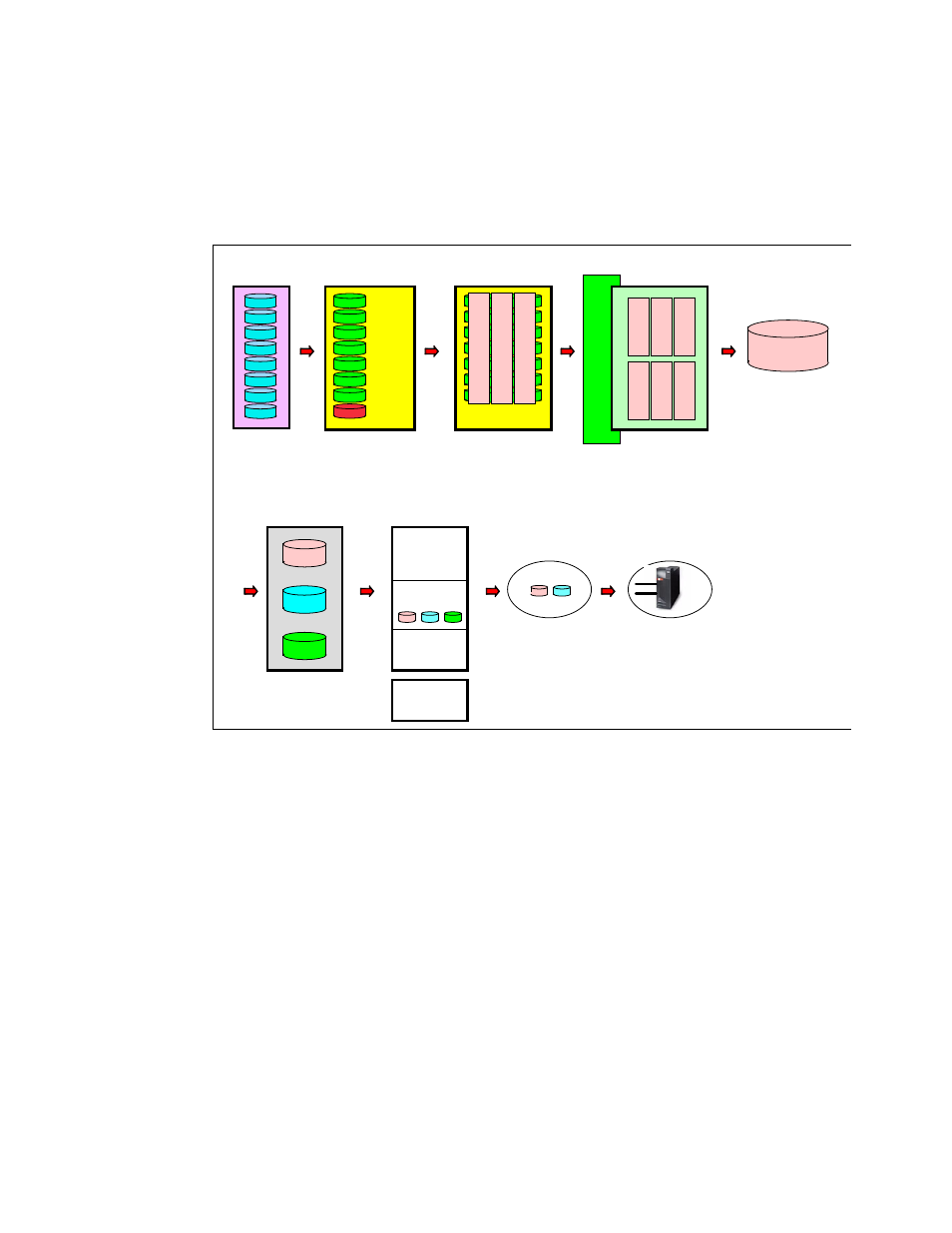
Figure 5-12 summarizes the virtualization hierarchy.
Figure 5-12 Virtualization hierarchy
5.3.9 Placement of data
As explained in the previous chapters, there are several options on how to create logical
volumes. You can select an extent pool that is owned by one server. There could be just one
extent pool per server or you could have several. The ranks of extent pools could come from
arrays on different device adapter pairs and different loops or from the same loop. Figure 5-13
on page 100 shows an optimal distribution of eight logical volumes within a DS8000. Of
course you could have more extent pools and ranks, but when you want to distribute your data
for optimal performance, you should make sure that you spread it across the two servers,
across different device adapter pairs, across the loops, and across several ranks.
If you use some kind of a logical volume manager (like LVM on AIX) on your host, you can
create a host logical volume from several DS8000 logical volumes (LUNs). You can select
LUNs from different DS8000 servers, device adapter pairs, and loops as shown in
Figure 5-13. By striping your host logical volume across the LUNs, you will get the best
performance for this LVM volume.
Se
rv
e
r0
Array
Site
RAID
Array
Spare
Data
Data
Data
Data
Data
Data
Parity
Rank
Type FB
1 GB FB
1 G
B
FB
1 G
B
FB
1 G
B
F
B
1 G
B
F
B
1 G
B
F
B
1 G
B
FB
1 GB FB
1 GB FB
Extent
Pool
Logical
Volume
LSS
FB
Address
Group
X'2x' FB
4096
addresses
LSS X'27'
X'3x' CKD
4096
addresses
Volume
Group
Host
Attachment
