2 hp storageworks secure key manager, 1 overview, 2 cryptographic module specification – HP FIPS 140-2 User Manual
Page 6
Security Policy, version 1.0
January 31, 2008
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
Page 6 of 26
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
2 HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
2.1 Overview
HP provides a range of security products for banking, the Internet, and enterprise security applications. These
products use encryption technology—often embedded in hardware—to safeguard sensitive data, such as financial
transactions over private and public networks and to offload security processing from the server.
The HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager is a hardened server that provides security policy and key management
services to encrypting client devices and applications. After enrollment, clients, such as storage systems, application
servers and databases, make requests to the SKM for creation and management of cryptographic keys and related
metadata.
Client applications can access the SKM via its Key Management Service (KMS) server. Configuration and
management can be performed via web administration, Secure Shell (SSH), or serial console. Status-monitoring
interfaces include a dedicated FIPS status interface, a health check interface, and Simple Network Management
Protocol (SNMP).
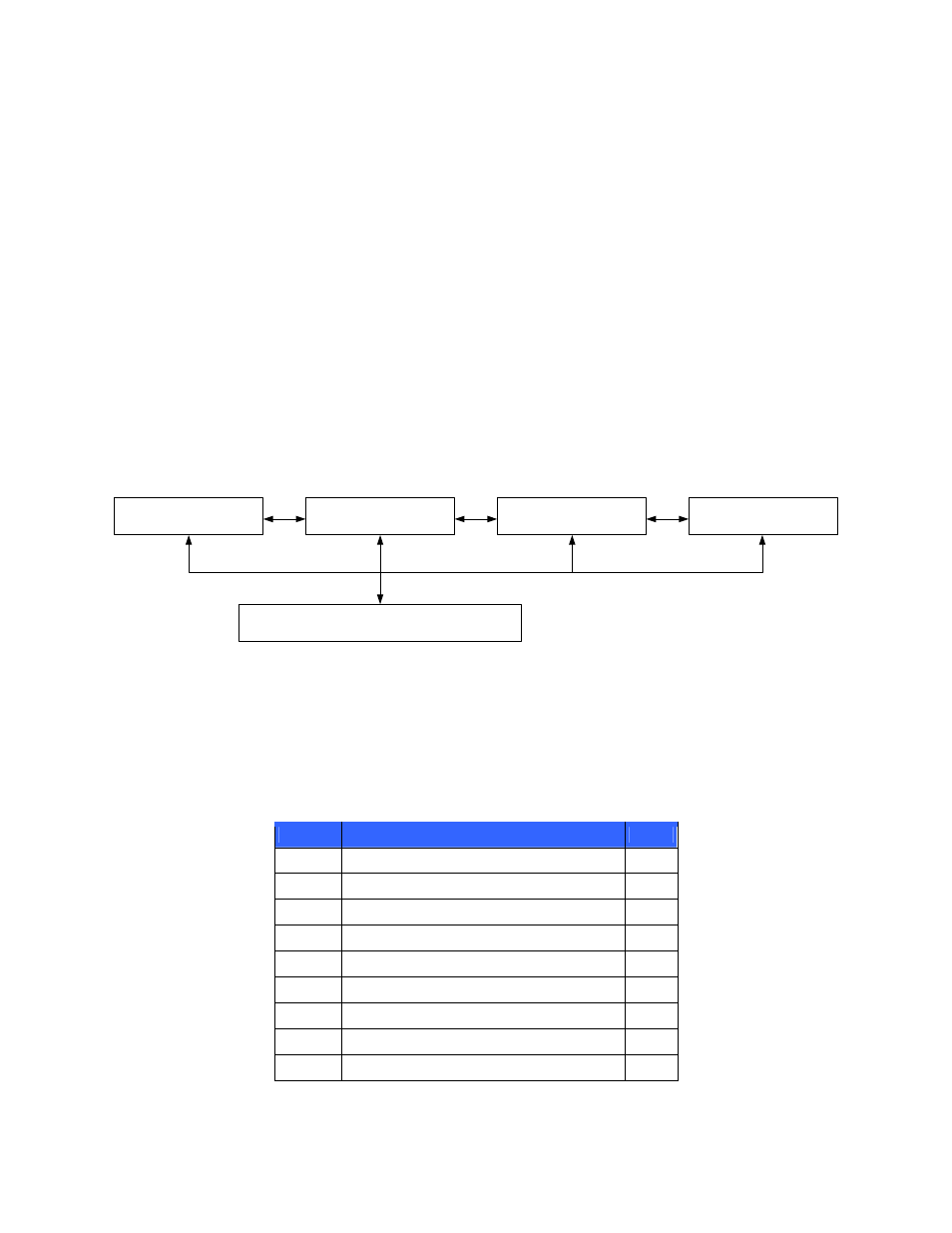
The deployment architecture of the HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager is shown in Figure 1 below.
Web Server
Application Server
Database
Storage System
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
Figure 1 – Deployment Architecture of the HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
2.2 Cryptographic Module Specification
The HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager is validated at FIPS 140-2 section levels shown in Table 1 – Security
Level per FIPS 140-2 Section.
Table 1 – Security Level per FIPS 140-2 Section
Section
Section Title
Level
1
Cryptographic Module Specification
3
2
Cryptographic Module Ports and Interfaces
2
3
Roles, Services, and Authentication
3
4
Finite State Model
2
5 Physical
Security
2
6 Operational
Environment
N/A
7
Cryptographic Key Management
2
8 EMI/EMC
2
9 Self-Tests
2
