HP FIPS 140-2 User Manual
Page 16
Security Policy, version 1.0
January 31, 2008
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
Page 16 of 26
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
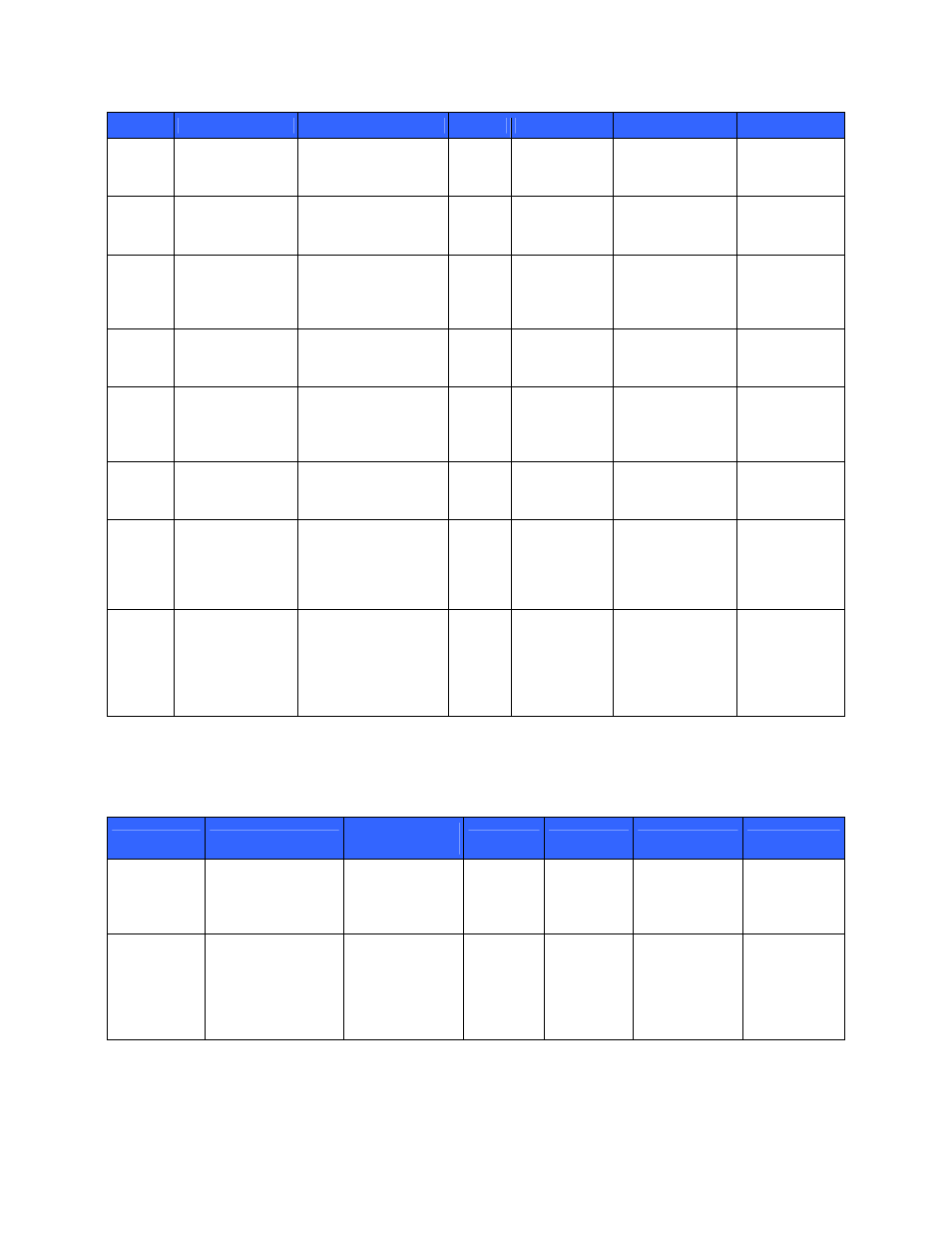
Key
Key Type
Generation / Input
Output
Storage
Zeroization
Use
DH
public
param
1024-bit Diffie-
Hellman public
parameters
Generated by ANSI
X9.31 DRNG during
session initialization
In
plaintext
In volatile
memory
Upon session
termination
Negotiate SSH
Ks and SSH
Khmac
DH
private
param
1024-bit Diffie-
Hellman private
parameters
Generated by ANSI
X9.31 DRNG during
session initialization
Never
In volatile
memory
Upon session
termination
Negotiate SSH
Ks and SSH
Khmac
Kdsa
public
1024-bit DSA
public keys
Generated by ANSI
X9.31 DRNG during
first-time initialization
In
plaintext
In non-volatile
memory
At operator delete
or zeroize request
Verify the
signature of the
server’s
message.
Kdsa
private
1024-bit DSA
private keys
Generated by ANSI
X9.31 DRNG during
first-time initialization
Never In
non-volatile
memory
At operator delete
or zeroize request
Sign the
server’s
message.
Krsa
public
1024-bit RSA
public keys
Generated by ANSI
X9.31 DRNG during
first-time initialization
In
plaintext
In non-volatile
memory
At operator delete
or zeroize request
Verify the
signature of the
server’s
message.
Krsa
private
1024-bit RSA
private keys
Generated by ANSI
X9.31 DRNG during
first-time initialization
Never In
non-volatile
memory
At operator delete
or zeroize request
Sign the
server’s
message.
SSH Ks
SSH session
168-bit 3DES key,
128-, 192-, 256-bit
AES key
Diffie-Hellman key
agreement
Never In
volatile
memory
Upon session
termination or
when a new Ks is
generated (after a
certain timeout)
Encrypt and
decrypt data
SSH
Khmac
SSH session 512-
bit HMAC key
Diffie-Hellman key
agreement
Never In
volatile
memory
Upon session
termination or
when a new
Khmac is
generated (after a
certain timeout)
Authenticate
data
Notice that SSH version 2 is explicitly accepted for use in FIPS mode, according to section 7.1 of the NIST FIPS
140-2 Implementation Guidance.
Table 12 – List of Cryptographic Keys, Cryptographic Key Components, and CSPs for TLS
Key
Key Type
Generation /
Input
Output
Storage
Zeroization
Use
Pre-MS TLS
pre-master
secret
Input in
encrypted form
from client
Never In
volatile
memory
Upon session
termination
Derive MS
MS
TLS master secret
Derived from Pre-
MS using FIPS
Approved key
derivation
function
Never In
volatile
memory
Upon session
termination
Derive TLS Ks
and TLS
Khmac
