Casio EA-200 User Manual
Page 29
20020601
English
Activity: Operating the Equipment
Activity: Operating the Equipment
Measurement
Measurement
2-8-2
55555555555555555555555
5555555555555555555555
55555
Other Things To Do
55555
í Analyzing Do-Re-Mi
u Record the notes Do, Re, and Mi, and then record the peaks of their frequency distribu-
tions. These are called “frequency components.”
u Study the relationship of the frequency components included in the single-note frequency
distribution.
u Study the relationship of the highest peaks of different notes.
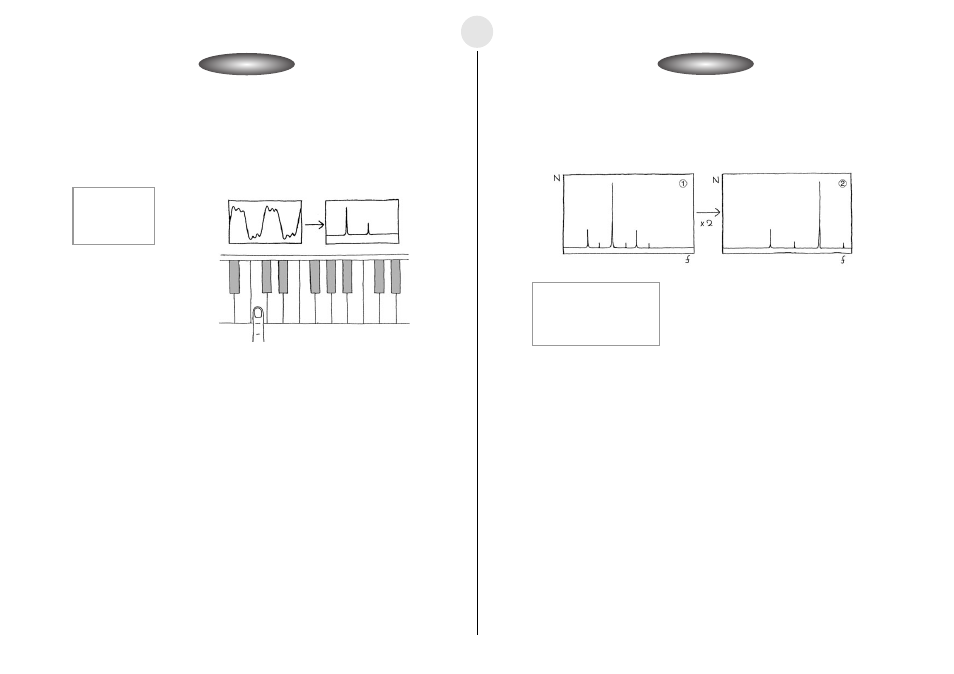
í Octaves
u Record Do in two adjoining octaves, and make a note of its frequency components.
u On the EA-200, double the frequency of the lower Do to synthesize the higher Do, and
then compare the result with the corresponding note played on the piano.
í Consonant Notes
u The sound at a frequency ratio of 1:1 is the original sound, and the sound at 2:1 is called
an “octave.” Two notes such as these are said to possess “absolute consonance.” Play the
same note in two different octaves to see what absolute consonance sounds like.
u Sounds at the frequency ratios 3:2 and 4:3 possess “perfect consonance,” sounds at 5:3
and 5:4 possess “medial consonance,” and sounds at 6:5 and 8:5 possess “imperfect
consonance” Predict the consonance of Do-Re-Mi from their frequencies, and then
actually play the notes on the piano.
u Using the EA-200’s frequency conversion function, create and produce consonant notes.
Next, play the same notes on the piano for comparison.
í Electronic Sound
u Use the EA-200 to record Do played using a piano timbre on the computer MIDI sound
source, and check its frequency components. Next, compare this with the frequency
component of Do played on the acoustic piano.
í Calculator Operation
u Record the sound on the EA-200, perform FFT analysis, and view the frequency.
u Find the applicable program in the Program Library (P.2-16-2), input it into your calculator,
and then run it.
u Use the EA-200 frequency conversion function to create synthesized sounds.
u Consider why notes synthesized on the EA-200 are different from those produced
by the piano.
u In many cases, physical properties become evident by studying frequency
components. Consider why this is so.
u Consider what noise is by checking its frequency components.
1
Waveform
2
Frequency
Distribution
3
Peak
1
Before Conversion
2
After Conversion
f
(Hz)
: Frequency
N
(counts) : Number of Counts
u Find the applicable program (Natural Frequency and Sound) in the Program Library
(P.2-16-2) , input it into your calculator, and then run it to use FFT graph (1
,
2)
.
1
2
3
3
