Netconfig scope, Netconfig — instruction manual 8 introduction – Grass Valley NetConfig Network Configuration Application v.2.0.12 User Manual
Page 8
NetConfig — Instruction Manual
8
Introduction
NetConfig Scope
The NetConfig application uses a client-server model. The NetConfig
application acts as the server and sends out Requests to client devices,
which send Responses.
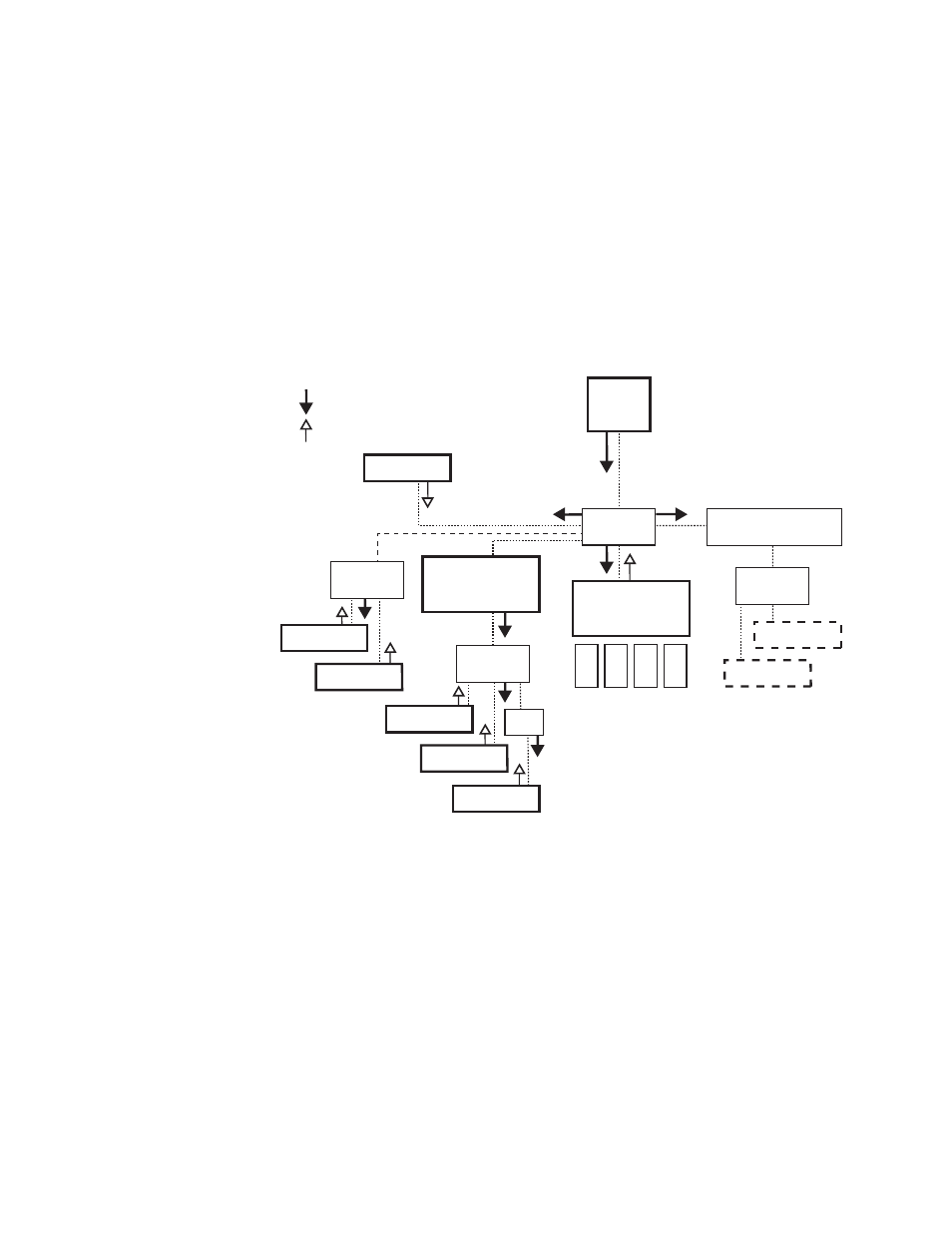
The NetConfig discovery process employs Ethernet broadcast messages.
This process works only when the NetConfig-enabled devices are on the
same LAN; that is, either connected directly, or connected via a hub or
switch. Broadcast messages do not normally propagate through router
gateways, so devices on a WAN are not normally discovered (see
Figure 1. Network Topology and Broadcast Messages
Hub
8190_01_
r0
Control Panel
Control Panel
Control Panel
Control Panel
Control Panel
Control Panel
Control Panel
Control Panel
Ethernet
Switch
Ethernet Router
(default Gateway address)
Boa
rd 1
Boa
rd 2
Boa
rd 3
Boa
rd 4
Ethernet
Switch
Uplink
Broadcast Message
Response Message
Encore
Controller
with Relay Agent
8900 Modular
Frame
with Net Card
Ethernet
Switch
Ethernet
Switch
NetConfig
PC
Via Uplink or
Relay Agent all
Control Panels
are on the same
Network and respond
to NetConfig.
NetConfig sends
Broadcast Discovery
messages and sees
devices that respond.
Router may or may not
be configured with
IP Helper to pass
Broadcast messages.
Net Card in
Modular Frame
responds and
relays Board
statuses to
NetConfig
Control Panels are
NOT seen by NetConfig
unless default Gateway
Router is using IP Helper.
Note
We generally recommend using unmanaged switches, instead of hubs, on
networks. A hub may be used with a single device to extend beyond the
Ethernet 100 meter limit. We do not recommend attaching multiple devices
to a hub since this commonly introduces Ethernet message collisions that
can affect overall system performance.
On some routers, IP Helper can be enabled to propagate broadcast mes-
sages. These messages are then sent as subnet broadcasts for a particular
port. If a device is configured on a subnet that matches IP Helper, then it
will receive and respond to broadcast messages. However, if the device is
completely unconfigured or misconfigured, it will not receive the broadcast
message even if IP Helper is enabled.
