Ospf vpn extension, Ospf multi-instance on pe – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 69
6
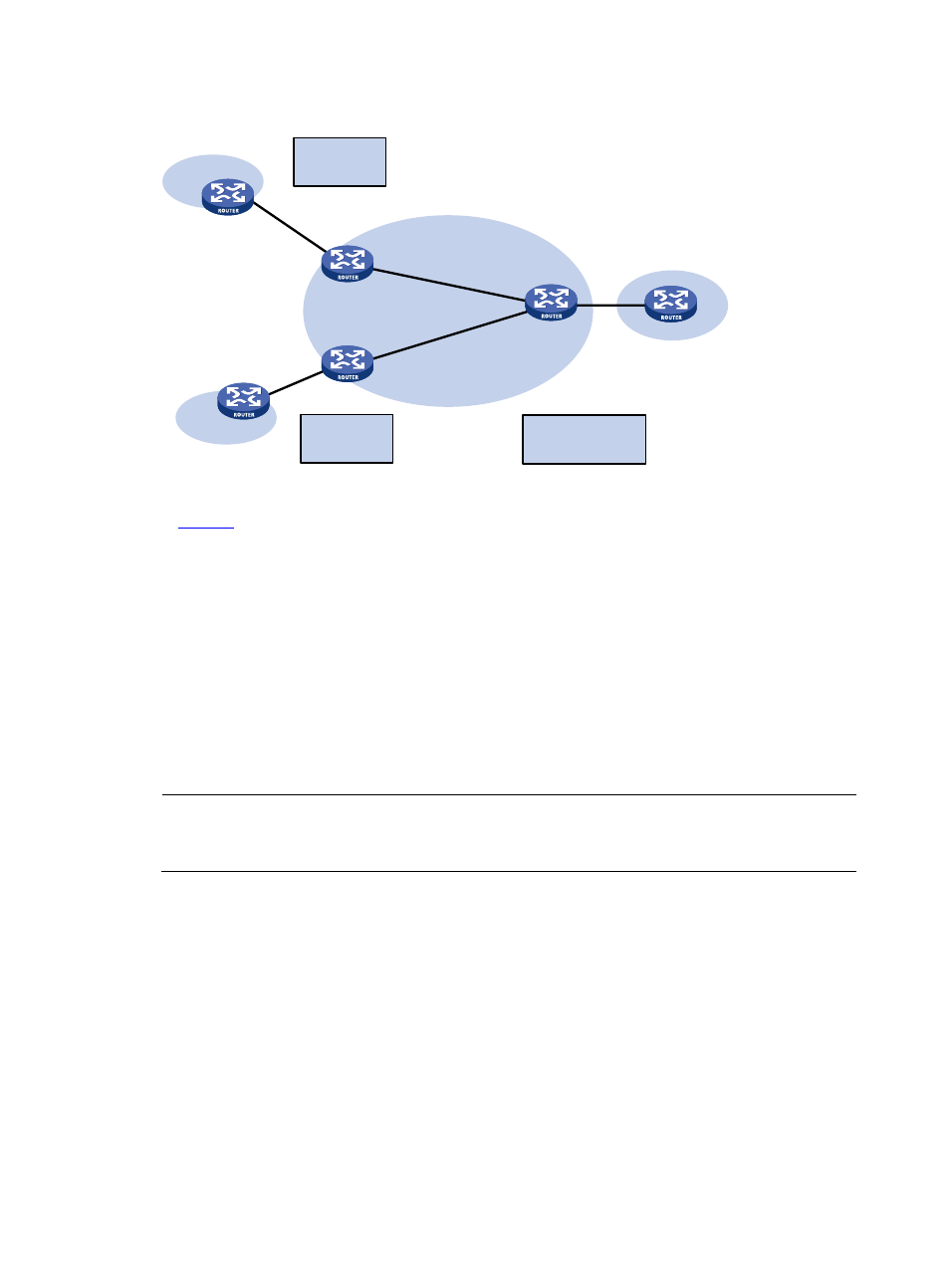
Figure 4 Network diagram for extranet networking scheme
CE
CE
PE 1
PE 3
Site 2
Site 1
Site 3
VPN 1
VPN 1
VPN 2
VPN 1:
Import:100:1
Export:100:1
CE
VPN 2:
Import:200:1
Export:200:1
PE 2
VPN 1:
Import:100:1,200:1
Export:100:1,200:1
In
, VPN 1 and VPN 2 can access Site 3 of VPN 1.
•
PE 3 can receive the VPN-IPv4 routes advertised by PE 1 and PE 2.
•
PE 1 and PE 2 can receive the VPN-IPv4 routes advertised by PE 3.
•
Based on the above, Site 1 and Site 3 of VPN 1 can communicate with each other, and Site 2 of
VPN 2 and Site 3 of VPN 1 can communicate with each other.
•
PE 3 advertises neither the VPN-IPv4 routes received from PE 1 to PE 2, nor the VPN-IPv4 routes
received from PE 2 to PE 1 (that is, routes learned from an IBGP neighbor will not be advertised to
any other IBGP neighbor). Therefore, Site 1 of VPN 1 and Site 2 of VPN 2 cannot communicate
with each other.
OSPF VPN Extension
NOTE:
This section focuses on the OSPF VPN extension. For more information about OSPF, see
OSPF
Configuration in the IP Routing Volume.
OSPF multi-instance on PE
OSPF is a prevalent IGP protocol. In many cases, VPN clients are connected through BGP peers, and the
clients often run OSPF. Running OSPF between PEs and CEs can simplify the configuration and
management of the CEs, because the CEs only need to support OSPF. In addition, if the customers
require L3VPN services through conventional OSPF backbone, using OSPF between PEs and CEs can
simplify the transition.
For OSPF to run between CEs and PEs, the PEs must support multiple OSPF instances. Each OSPF
instance must correspond to a VPN instance and have its own interface and routing table.
The following describes details of OSPF configuration between PEs and CEs.
1.
Configuration of OSPF areas between PEs and CEs
The OSPF area between a PE and a CE can be either a non-backbone area or a backbone area.
