Three typical l2tp tunneling modes – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 37
4
same tunnel ID but different session IDs are multiplexed to the same tunnel. The tunnel ID and session ID
in a header are the intended receiver’s, not those of the sender.
L2TP Tunneling Modes and Tunnel Establishment Process
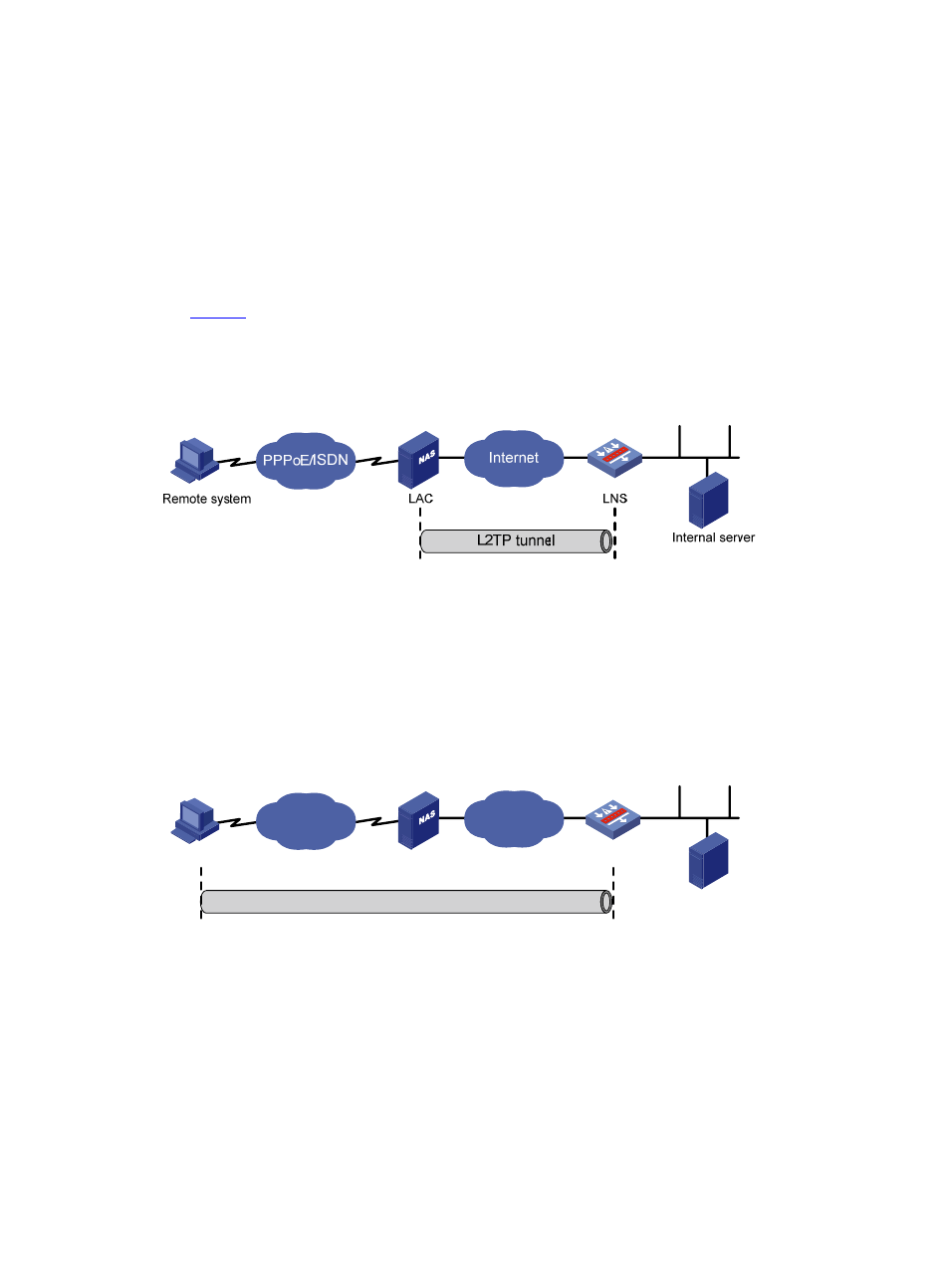
Three typical L2TP tunneling modes
There are three typical L2TP tunneling modes: NAS-initiated, client-initiated, and LAC-auto-initiated.
•
NAS-initiated
See
. In this mode, a remote system dials in to the LAC through a PPPoE/ISDN network, and the
LAC initiates a tunneling request to the LNS over the Internet. The LNS assigns a private IP address to the
remote system. Authentication and accounting of the remote system can be implemented on the LAC or
on the LNS.
Figure 4 NAS-initiated tunneling mode
•
Client-initiated
In this mode, after being permitted to access the Internet, a remote system running the L2TP client
application (LAC client) directly initiates a tunneling request to the LNS without any dedicated LAC device.
The LNS assigns the LAC client a private IP address.
In this mode, a LAC client needs a public network address to communicate with the LNS through the
Internet.
Figure 5 Client-initiated tunneling mode
PPPoE/ISDN
Internet
LAC client
LNS
Internal server
L2TP tunnel
•
LAC-auto-initiated
In NAS-initiated mode, a remote system must successfully dial in to the LAC through PPPoE or ISDN to
trigger the LAC to initiate a tunneling request to the LNS.
In LAC-auto-initiated mode, you can create a virtual PPP user and execute the l2tp-auto-client
enable command on the LAC. Then, the LAC automatically initiates a tunneling request to the LNS to
establish an L2TP tunnel for the virtual PPP user. Then, when a remote system accesses the internal
network, the LAC forwards data through the L2TP tunnel. In this mode, the connection between a remote
system and the LAC is not confined to a dial-up connection and can be any IP-based connection.
