Point to multi-point gre tunnel configuration, P2mp gre tunnel overview, Background – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 17
1
Point to Multi-Point GRE Tunnel Configuration
This chapter includes these sections:
•
•
•
Displaying and Maintaining P2MP GRE Tunnels
•
P2MP GRE Tunnel Configuration Examples
P2MP GRE Tunnel Overview
Background
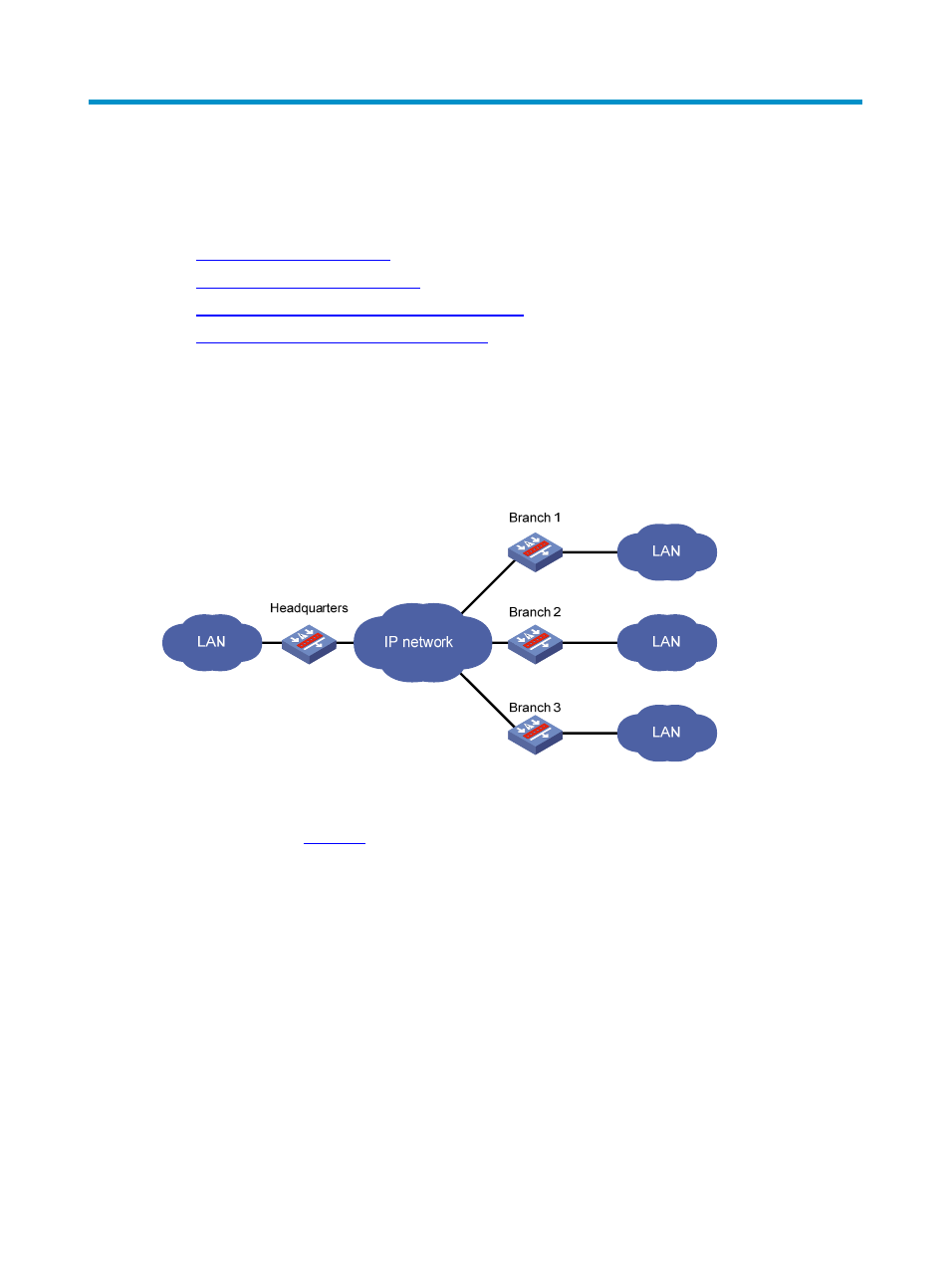
Figure 11 P2MP GRE tunnel application scenario
A traditional GRE tunnel is a point to point connection. To use traditional GRE tunnels on an enterprise
network as shown in
, you need to configure a P2P GRE tunnel between the headquarters and
each branch. When an enterprise has plenty of branches, the configuration workload is huge and,
adding new branches requires additional configurations on the headquarters node, burdening network
administrators. Besides, if branches dial in to the network through ADSL, the configurations on the
headquarters node is even complicated due to the indetermination of the public network addresses of the
branches.
Dynamic VPN technologies such as Dynamic Virtual Private Network (DVPN) can solve the problem
because they support dynamic learning of the mappings of public network addresses and private
network addresses and thereby can dynamically establish tunnels between the headquarters and the
branches and between the branches. However, there is no unified standard for implementation of
dynamic VPN at present. As a result, vendors use their proprietary protocols to implement dynamic VPN,
making it difficult for devices of different vendors to cooperate.
The P2MP GRE tunnel technology solves this problem. It is very applicable to enterprise networks with a
lot of branches. In a P2MP GRE tunnel application, you only need to configure the tunnel interface on the
headquarters node to work in P2MP GRE tunnel mode and that on each branch node to work in
