Traffic shaping – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 50
41
NOTE:
Traffic policing supports policing the inbound traffic and the outbound traffic.
Traffic shaping
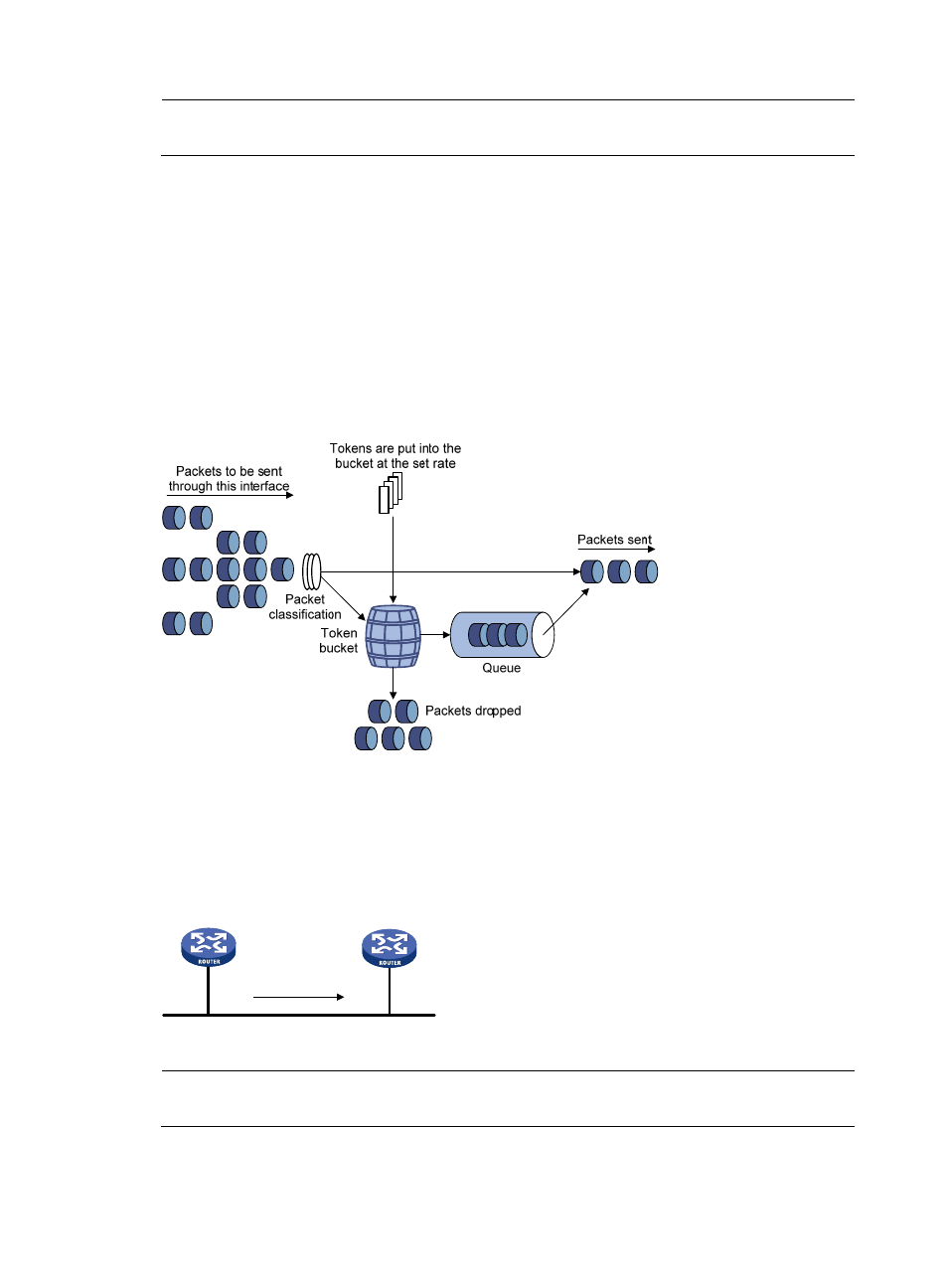
Traffic shaping limits the outbound traffic rate by buffering exceeding traffic. You can use traffic shaping
to adapt the traffic output rate on a device to the input traffic rate of its connected device to avoid packet
loss.
The difference between traffic policing and GTS is that packets to be dropped with traffic policing are
retained in a buffer or queue with GTS, as shown in
. When enough tokens are in the token
bucket, the buffered packets are sent at an even rate. Traffic shaping might result in additional delay and
traffic policing does not.
Figure 8 GTS
For example, in
, Router B performs traffic policing on packets from Router A and drops packets
exceeding the limit. To avoid packet loss, you can perform traffic shaping on the outgoing interface of
Router A so packets exceeding the limit are cached in Router A. Once resources are released, traffic
shaping takes out the cached packets and sends them out.
Figure 9 GTS application
NOTE:
Traffic shaping supports shaping only the outbound traffic.
Router A
Router B
Physical link
