Figure 3-3, Table 3-2 – Verilink M1-3 (880-503136-001) Product Manual User Manual
Page 34
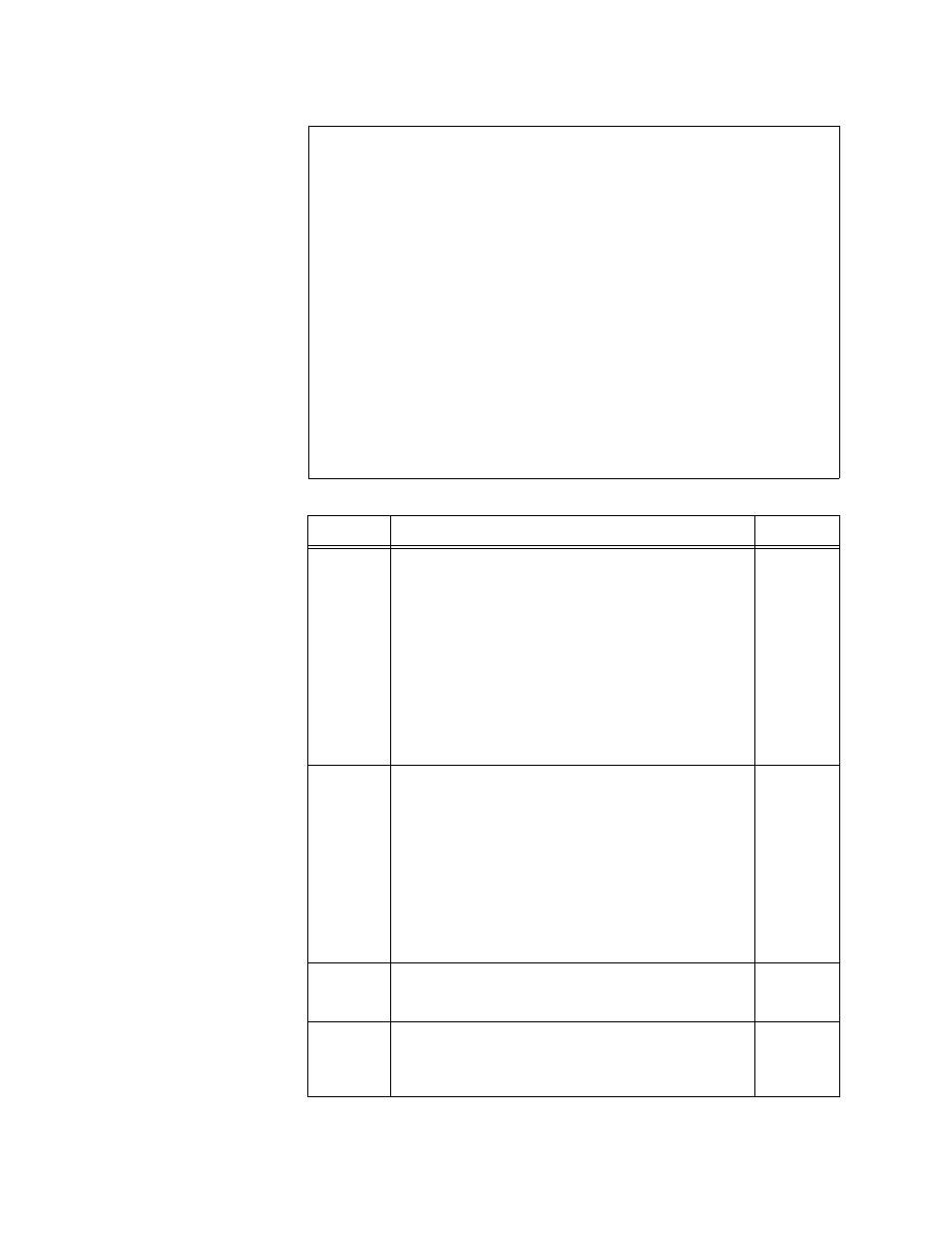
M1-3 Configuration Options
3-4
Verilink M1-3 User Manual
Figure 3-3
M1-3 DS3 Port Configuration Menu
Table 3-2 M1-3 DS3 Port Configuration Menu Options
Command
Description
Option
M
Line Type—must match what the telco assigns.
• C-bit—In the DS3 C-bit parity format the C-bits are
available to provide in-service, end-to-end path
performance monitoring of the DS3 signal, and in-
band data links. C-bit line type is available when
all multiplexing occurs within one mux, as in the
M1-3.
• M1-3—Asynchronous framing format that uses all
21 DS3 C-bits for bit stuffing. The standard M1-3
format cannot provide end-to-end parity
information. Use this format if the DS3 is split by
your telco to multiple far-end locations.
C-Bit
M1-3
H
Coding Type—displays the line options. This option
is carrier-specific when operating on a standard T3
network.
• Bipolar—A T-carrier line-coding system. This
system alternates the polarity of consecutive ones
bits. This is the normal option.
• Unipolar—A signal stream in which all one bits are
the same polarity. Intended for use with fiber
optics networks.
NOTE: Only bipolar is currently supported.
Bipolar
Unipolar
R
Performance Control—enables/disables
performance control. This option is usually enabled
for DS3 except during initialization.
Enable
Disable
C
Far End Control (FEAC)—enables or disables node
control at the far end using a DS3 C-bit subframe.
This channel is also used to initiate loopbacks at the
far-end terminal from the near-end terminal.
Enable
Disable
-- M1-3 DS3 PORT CONFIGURATION MENU --
-- M1-3 DS3 PORT CONFIGURATION MENU --
-- M1-3 DS3 PORT CONFIGURATION MENU --
-- M1-3 DS3 PORT CONFIGURATION MENU --
M) line type M13
M) line type M13
M) line type M13
M) line type M13
H) coding type Bipolar
H) coding type Bipolar
H) coding type Bipolar
H) coding type Bipolar
R) performance control On
R) performance control On
R) performance control On
R) performance control On
C) FEAC Enabled
C) FEAC Enabled
C) FEAC Enabled
C) FEAC Enabled
D) clock Network
D) clock Network
D) clock Network
D) clock Network
I) inband control Enabled
I) inband control Enabled
I) inband control Enabled
I) inband control Enabled
B) line build out Normal Cable
B) line build out Normal Cable
B) line build out Normal Cable
B) line build out Normal Cable
E) equipment id ten bytes
E) equipment id ten bytes
E) equipment id ten bytes
E) equipment id ten bytes
L) location id allows 11
L) location id allows 11
L) location id allows 11
L) location id allows 11
F) frame id ten bytes
F) frame id ten bytes
F) frame id ten bytes
F) frame id ten bytes
U) unit id unit06
U) unit id unit06
U) unit id unit06
U) unit id unit06
A) facility id up to thirty eight bytes
A) facility id up to thirty eight bytes
A) facility id up to thirty eight bytes
A) facility id up to thirty eight bytes
P) port id 38 character field!
P) port id 38 character field!
P) port id 38 character field!
P) port id 38 character field!
G) test Signal id 38 bytes here too
G) test Signal id 38 bytes here too
G) test Signal id 38 bytes here too
G) test Signal id 38 bytes here too
X) exit this menu
X) exit this menu
X) exit this menu
X) exit this menu
