Ncast presentation recorder reference manual – NCast PR-HD User Manual
Page 60
NCast Presentation Recorder Reference Manual
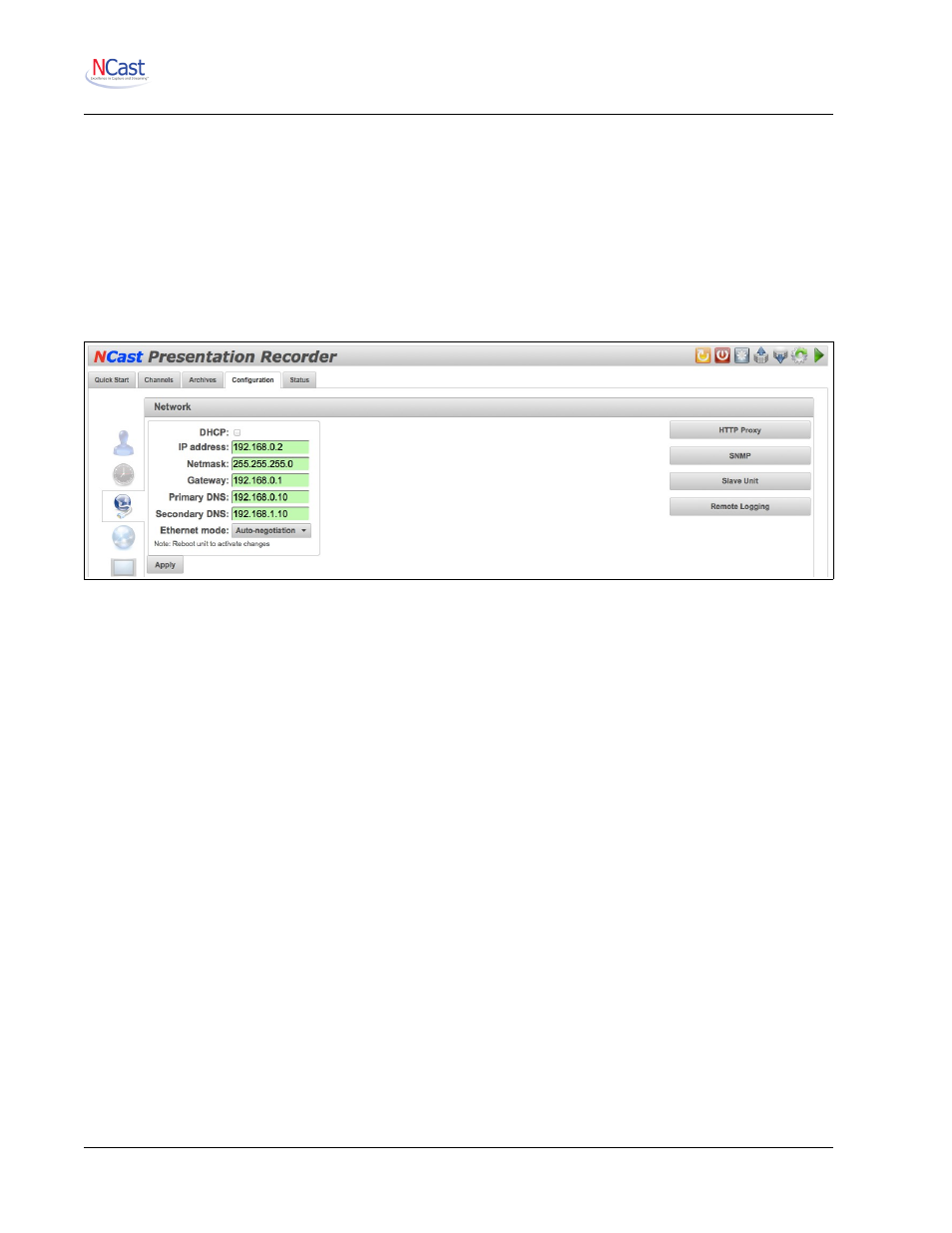
The following parameters may be configured on the Network page:
7.3.1. DHCP
If DHCP is enabled the unit will automatically receive an IP address from the network’s DHCP server. Some
networks require MAC address registration with the DHCP server before an IP address can be allocated.
The MAC address is on a label on the bottom of the chassis, and is also reported on the Network
Configuration page. If DHCP is disabled, a static IP address must be provided by the installer. Consult with
the IT staff or network management to obtain the IP address allocated for the unit.
7.3.2. IP Address
The static IP address to be used by the unit in numeric form (www.xxx.yyy.zzz). Not required if DHCP is
enabled.
7.3.3. Netmask
The IP netmask in use for this LAN segment (e.g. 255.255.255.0).
7.3.4. Gateway
The numeric IP address of the gateway host on this LAN segment (e.g. www.xxx.yyy.1).
7.3.5. Primary DNS
The numeric IP address of the primary Domain Name Server (DNS) for this LAN segment (e.g.
www.xxx.yyy.10). Domain name servers translate symbolic domain names to numeric IP addresses. Various
processes within the Presentation Recorder may, on occasion, require contact with a valid name server.
7.3.6. Secondary DNS
The numeric IP address of the secondary (or backup) Domain Name Server.
7.3.7. Ethernet Mode
Adjusts the hardware link level settings for the connection between the Presentation Recorder and its
network switch. Normally Auto-negotiation will be sufficient to establish the correct settings, but under special
circumstances the installer may wish to force the Ethernet hardware to assume a different configuration. The
link speed and full/half duplex settings are adjusted through use of the pulldown menu tab.
7.3.8. USB Stick Network Settings
An alternative way to configure network parameters for the unit is to edit a special text file on a USB memory
stick and to insert that memory stick into any USB slot in the unit during power-on. The operating software
looks for the presence of a USB memory and searches for the presence of a specially named file. If this file
is found, the network parameters are read from the file, installed into unit and used during the network boot
process. Once the unit has booted, the USB memory may be removed and is not required again. The
network settings from the file will be reflected as permanent entries shown on the Network Configuration
page.
NCast Corporation
Revision 2.2
Page 60
