Measurement Computing CIO-DAS16/M1/16 User Manual
Page 19
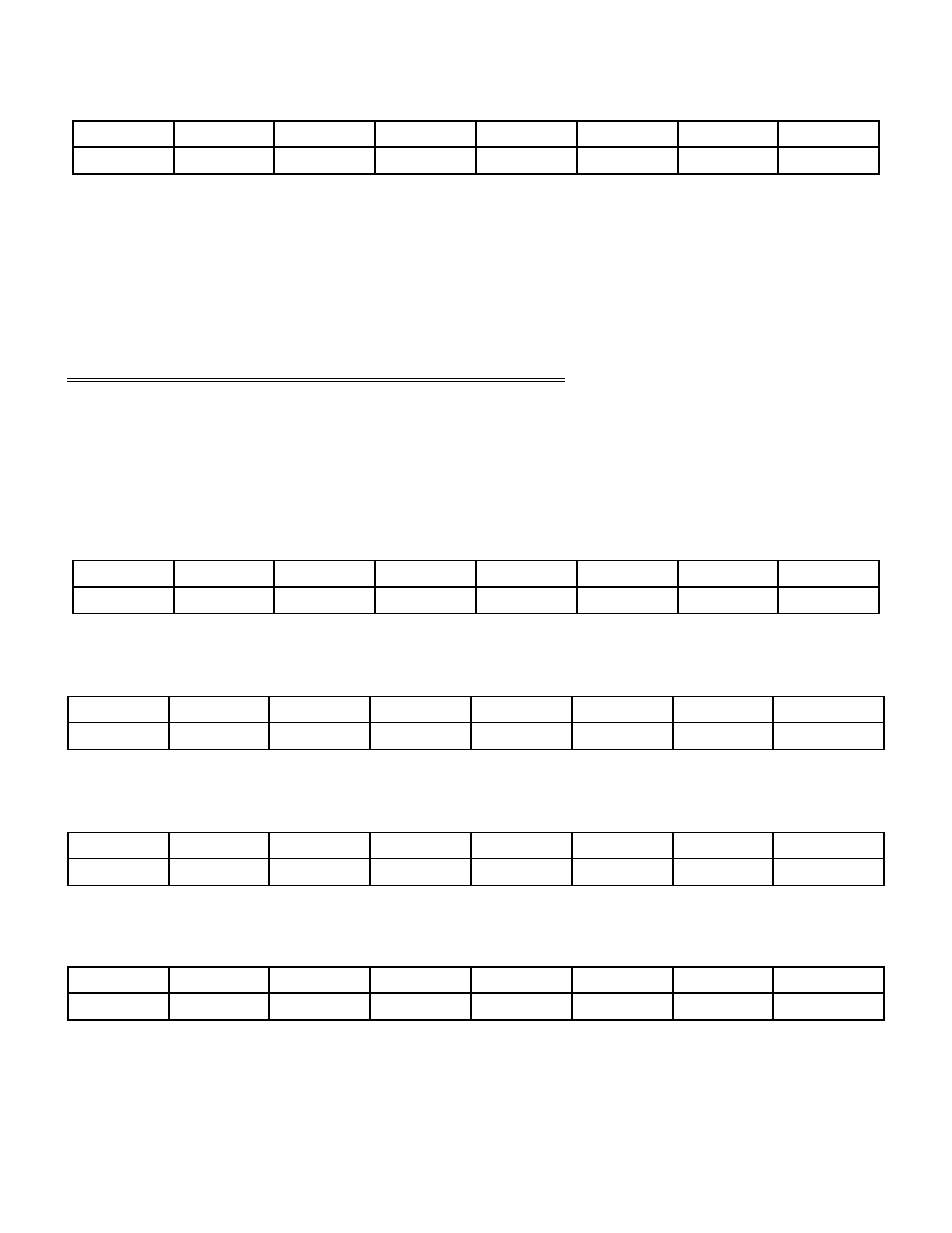
6.9.4
8254 CONTROL REGISTER
BASE + Fh
Example, 30Fh, 783 decimal
WRITE ONLY
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
0
1
3
2
4
5
6
7
The control register is used to set the operating Modes of 8254 Counters 0, 1, and 2. A counter is configured by
writing the correct Mode information to the Control Register, then the proper count data must be written to the
specific Counter Register.
The Counters on the 82C54 are 16-bit devices. Since the interface to the 82C54 is only eight bits wide, Count data is
written to the Counter Register as two successive bytes. First the low byte is written, then the high byte. The Control
Register is eight bits wide. Further information can be obtained on the 82C54 data sheet, available from Intel or
Harris.
5.10 82C55 DIGITAL I/O DATA AND CONTROL REGISTERS
The 82C55 Digital I/O port is at Register BASE +400h to follow the register configuration of the CIO-DAS1600
family.
5.10.1 8255 PORT A DATA
BASE + 400h
Example, 700h, 1792 decimal
READ/WRITE
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
0
1
3
2
4
5
6
7
5.10.2 8255 PORT B DATA
BASE + 401h
Example, 701 hex, 1793 decimal
READ/WRITE
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
0
1
3
2
4
5
6
7
5.10.3 8255 PORT C DATA
BASE + 402h
Example, 702h, 1794 decimal
READ/WRITE
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
0
1
3
2
4
5
6
7
5.10.4 8255 CONTROL REGISTER
BASE + 403h
Example, 703h, 1795 decimal
WRITE ONLY
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
0
1
3
2
4
5
6
7
The control register is used to set the operating Modes of 8255 Ports A, B, and C. A port is configured by writing the
correct Mode information to the Control Register, then the proper data must be written to the specific digital output
register or read from the specific input register. Further information can be obtained on the 8255 data sheet, available
from Intel or Harris.
15
