Hanna Instruments HI 504 User Manual
Page 25
49
48
An hysteresis will eliminate the possibility of continuous se-
quences ‘energizing/de-energizing’ of the alarm relay when
the measured value is close to the alarm setpoint. The hyster-
esis amplitude is 0.2 pH for pH and 30 mV for ORP.
Moreover the alarm signal is generated only after an user
selectable time period (alarm mask) has elapsed since the
controlled value has overtaken one alarm threshold. This
additional feature will avoid fake or temporary alarm condi-
tions.
Note
If the power supply is interrupted, the relay is de-energized as
if in alarm condition to alert the operator.
In addition to the user-selectable alarm relays, the meter is
equipped with the Fail Safe alarm feature.
The Fail Safe feature protects the process against critical
errors arising from power interruptions, surges and human
errors. This sophisticated yet easy-to-use system resolves these
predicaments on two fronts: hardware and software. To elimi-
nate problems of blackout and line failure, the alarm function
operates in a “Normally Closed” state and hence alarm is
triggered if the wires are tripped, or when the power is down.
This is an important feature since with most meters the alarm
terminals close only when an abnormal situation arises, how-
ever, due to line interruption, no alarm is sounded, causing
extensive damage. On the other hand, software is employed
to set off the alarm in abnormal circumstances, for example, if
the dosing terminals are closed for too long a period. In both
cases, the red LED will also provide a visual warning signal.
The Fail Safe mode is accomplished by connecting the exter-
nal alarm circuit between the FS•C (Normally Open) and
the COM terminals. This way, an alarm will warn the user
when pH goes over the alarm thresholds, the power breaks
down and in case of a broken wire between the process meter
pH or mV value. Read the system time delay Tx on the time axis.
4. The deviation, Ti and Td can be calculated from the following:
• Deviation = Tx * max. slope (pH or mV)
• Ti = Tx / 0.4 (minutes)
• Td = Tx * 0.4 (minutes).
5. Set the above parameters and restart the system with the
controller in the loop. If the response has too much over-
shoot or is oscillating, then the system can be fine-tuned
slightly increasing or decreasing the PID parameters one
at a time.
Example:
the chart recording in the figure
aside was obtained continuously
dosing an alkaline solution to a
weak acid solution in a tank. The
initial settings will be:
Max. slope = 3 pH/5 mins = 0.6
pH/min
Time delay = Tx = approx. 7 mins
Deviation = Tx * 0.6 = 4.2 pH
Ti = Tx / 0.4 = 17.5 mins
Td = Tx * 0.4 = 2.8 mins
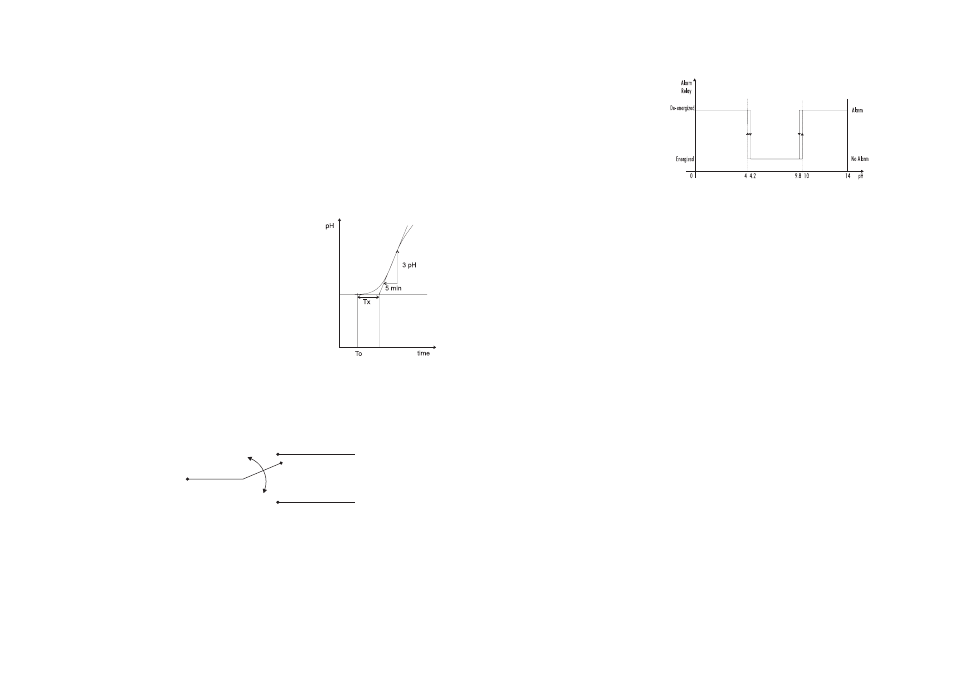
ALARM RELAY
The alarm relay functions in the following manner:
During normal operation (no alarm condition) the alarm re-
lay is energized; during an alarm condition or power failure
the relay will be de-energized. As long as a separate battery
power system is used an alarm will sound.
Example:
High alarm set at 10 pH
Low alarm set at 4 pH
FS•O = NC (Normally Closed)
De-energized Relay
COM
FS•C = NO (Normally Open)
Energized Relay
