Assembly instructions static measurements – Elenco SEE AMFM108CK User Manual
Page 21
-20-
SECTION 4
FIRST AM IF AMPLIFIER
Q8 BASE BIAS
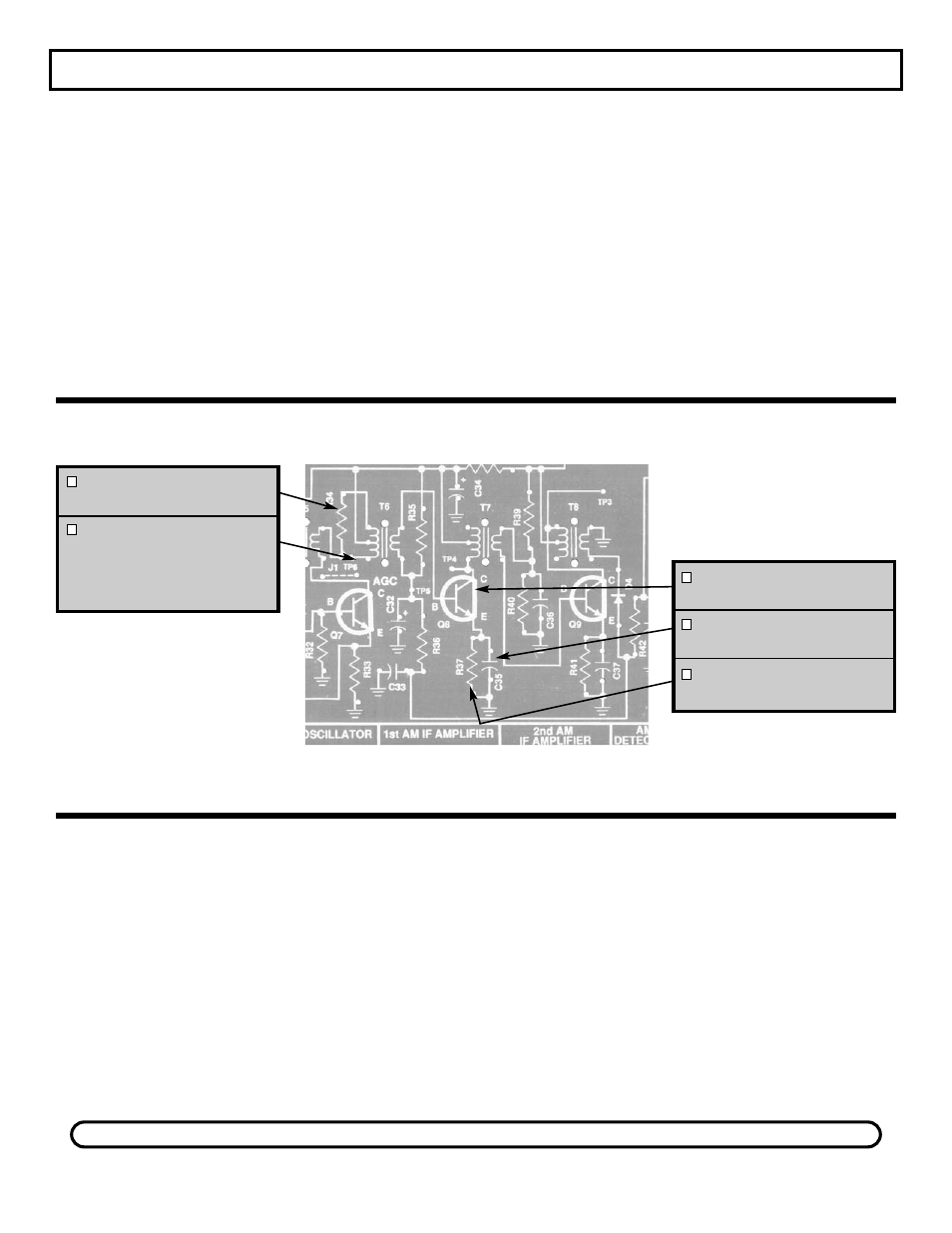
Connect your VOM to the circuit as shown in Figure 13.
Set your VOM to read 2 volts DC and turn the power
ON. The voltage at TP5 should be approximately 1.5
volts. If your circuit fails this test, check Q8 and R37.
Turn the power OFF.
Q8 CURRENT
Connect the positive lead of your VOM to the emitter
of Q8 and connect the negative lead to ground point
TP15. Turn the power ON. The voltage should be
approximately .8 volts. Since the current in Q8 is
equal to the current in R37, I(Q2) = .8/R37 or
approximately .8 milliamps. Turn the power OFF.
R34 - 1M
Ω
Resistor
(brown-black-green-gold)
TP6 - Test Point Pin
(see Figure A)
CAUTION: Test point must
not touch can of IF Coil.
Q8 - 2N3904 Transistor
(see Figure C)
C35 - .02
μ
F Discap (203)
or .022
μ
F Discap (223)
R37 - 1k
Ω
Resistor
(brown-black-red-gold)
The operation of the first IF amplifier is the same as
the second IF amplifier with one important difference.
The gain of the first IF amplifier decreases after the
AGC threshold is passed to keep the audio output
constant at the detector and prevent overload of the
second IF amplifier. This is accomplished by making
the voltage on the base of transistor Q8 lower as the
signal strength increases. Since the voltage from
base to emitter is fairly constant, the drop in voltage
at the base produces a similar drop in voltage at the
emitter of Q8. This drop lowers the voltage across
R37 and thus, reduces the DC current through R37.
Since all of the DC current from the emitter of Q8
must go through R37, the DC current in Q8 is
therefore lowered. When the DC current in a
transistor is lowered, its effective emitter resistance
increases. The AC gain of transistor Q8 is equal to
the AC collector load of Q8 divided by its effective
emitter resistance. Raising the value of the effective
emitter resistance, thus, lowers the AC gain of Q8.
ASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS
STATIC MEASUREMENTS
If you do not have an RF generator and oscilloscope, skip to Section 5.
