Write protect (wp) pin, Memory access, Read sequence (read) – Cypress CY14B101Q3 User Manual
Page 10: Write sequence (write), Table 7
PRELIMINARY
CY14B101Q1
CY14B101Q2
CY14B101Q3
Document #: 001-50091 Rev. *A
Page 10 of 22
Write Protect (WP) Pin
The write protect pin (WP) is used to provide hardware write
protection. WP pin enables all normal read and write operations
when held HIGH. When the WP pin is brought LOW and WPEN
bit is “1”, all write operations to the status register are inhibited.
The hardware write protection function is blocked when the
WPEN bit is “0”. This enables the user to install the device in a
system with the WP pin tied to ground, and still write to the status
register.
WP pin can be used along with WPEN and Block Protect bits
(BP1 and BP0) of the status register to inhibit writes to memory.
When WP pin is LOW and WPEN is set to “1”, any modifications
to status register are disabled. Therefore, the memory is
protected by setting the BP0 and BP1 bits and the WP pin inhibits
any modification of the status register bits, providing hardware
write protection.
Note WP going LOW when CS is still LOW has no effect on any
of the ongoing write operations to the status register.
Note CY14B101Q2 does not have WP pin and therefore does
not provide hardware write protection.
summarizes all the protection features of this device
Memory Access
All memory accesses are done using the READ and WRITE
instructions. These instructions cannot be used while a STORE
or RECALL cycle is in progress. A STORE cycle in progress is
indicated by the RDY bit of the status register and the HSB pin.
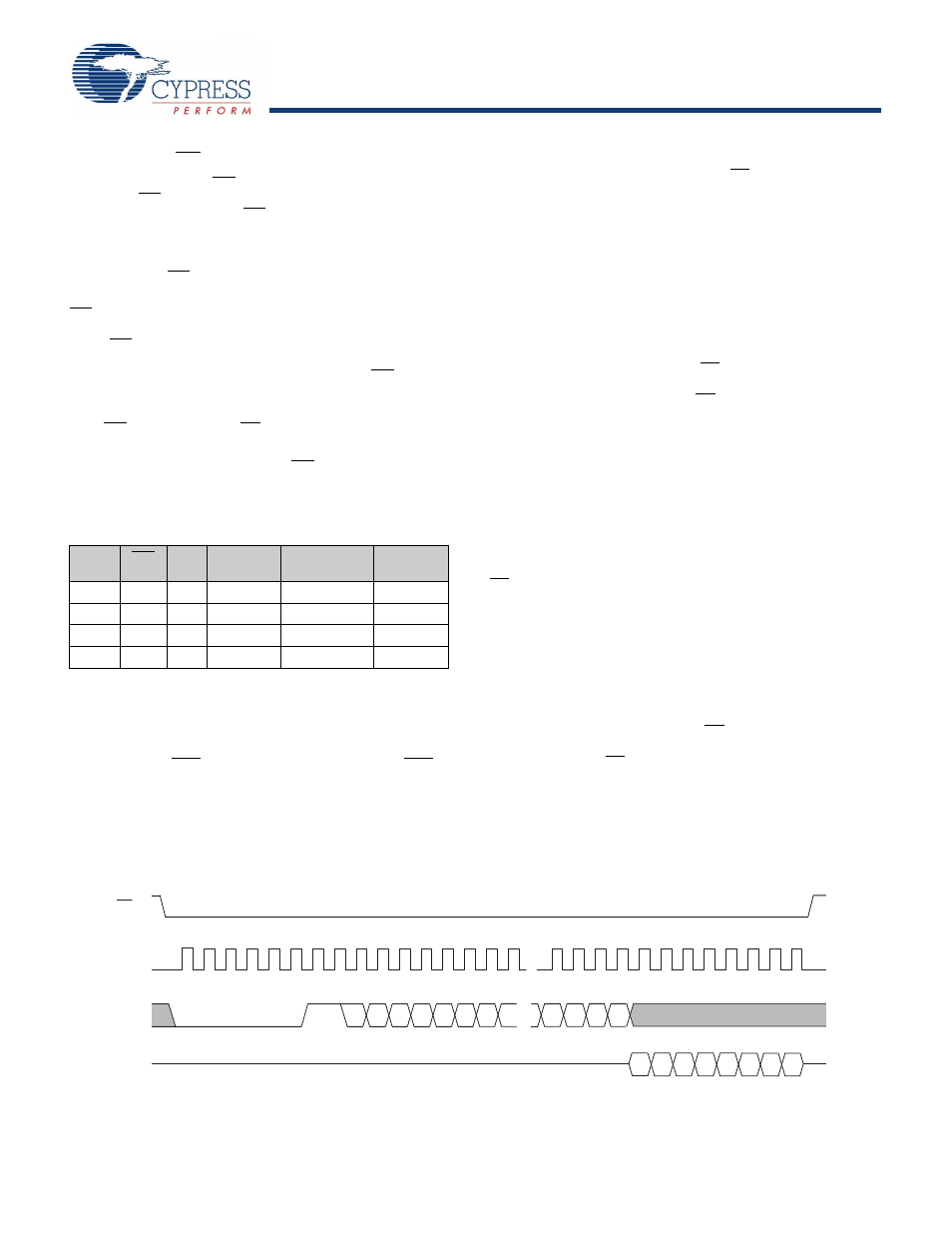
Read Sequence (READ)
The read operations on this device are performed by giving the
instruction on Serial Input pin (SI) and reading the output on
Serial Output (SO) pin. The following sequence needs to be
followed for a read operation: After the CS line is pulled LOW to
select a device, the read opcode is transmitted through the SI
line followed by three bytes of address. The Most Significant
address byte contains A16 in bit 0 and other bits as ‘don’t cares’.
Address bits A15 to A0 are sent in the following two address
bytes. After the last address bit is transmitted on the SI pin, the
data (D7-D0) at the specific address is shifted out on the SO line
on the falling edge of SCK. Any other data on SI line after the last
address bit is ignored.
CY14B101Q1/CY14B101Q2/CY14B101Q3 allows reads to be
performed in bursts through SPI which can be used to read
consecutive addresses without issuing a new READ instruction.
If only one byte is to be read, the CS line must be driven HIGH
after one byte of data comes out. However, the read sequence
may be continued by holding the CS line LOW and the address
is automatically incremented and data continues to shift out on
SO pin. When the last data memory address (0x1FFFF) is
reached, the address rolls over to 0x0000 and the device
continues to read.
Write Sequence (WRITE)
The write operations on this device are performed through the
Serial Input (SI) pin. To perform a write operation, if the device is
write disabled, then the device must first be write enabled
through the WREN instruction. When the writes are enabled
(WEN = ‘1’), WRITE instruction is issued after the falling edge of
CS. A WRITE instruction constitutes transmitting the WRITE
opcode on SI line followed by 3 bytes address sequence and the
data (D7-D0) which is to be written. The Most Significant address
byte contains A16 in bit 0 with other bits being ‘don’t cares’.
Address bits A15 to A0 are sent in the following two address
bytes.
CY14B101Q1/CY14B101Q2/CY14B101Q3 enables writes to be
performed in bursts through SPI which can be used to write
consecutive addresses without issuing a new WRITE instruction.
If only one byte is to be written, the CS line must be driven HIGH
after the D0 (LSB of data) is transmitted. However, if more bytes
are to be written, CS line must be held LOW and address is
incremented automatically. The following bytes on the SI line are
treated as data bytes and written in the successive addresses.
When the last data memory address (0x1FFFF) is reached, the
address rolls over to 0x0000 and the device continues to write.
The WEN bit is reset to “0” on completion of a WRITE sequence.
Table 7. Write Protection Operation
WPEN
WP
WEN Protected
Blocks
Unprotected
Blocks
Status
Register
X
X
0
Protected
Protected
Protected
0
X
1
Protected
Writable
Writable
1
LOW
1
Protected
Writable
Protected
1
HIGH
1
Protected
Writable
Writable
Figure 11. Read Instruction Timing
~ ~
CS
SCK
SO
0 1 2 3 4 5
6 7
0
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
20 21 22 23 0 1 2 3 4 5
6 7
MSB
LSB
Data
SI
~ ~
Op-Code
0 0 0 0 0 0 1
0 0 0 0 0
0
1
0
A16
A3
A1
A2
A0
17-bit Address
MSB
LSB
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
