External sram, Crystal oscillator – Digilent Cerebot Plus Board User Manual
Page 6
Digilent Cerebot Plus Reference Manual
Digilent, Inc.
www.digilentinc.com
page 6 of 13
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved. Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
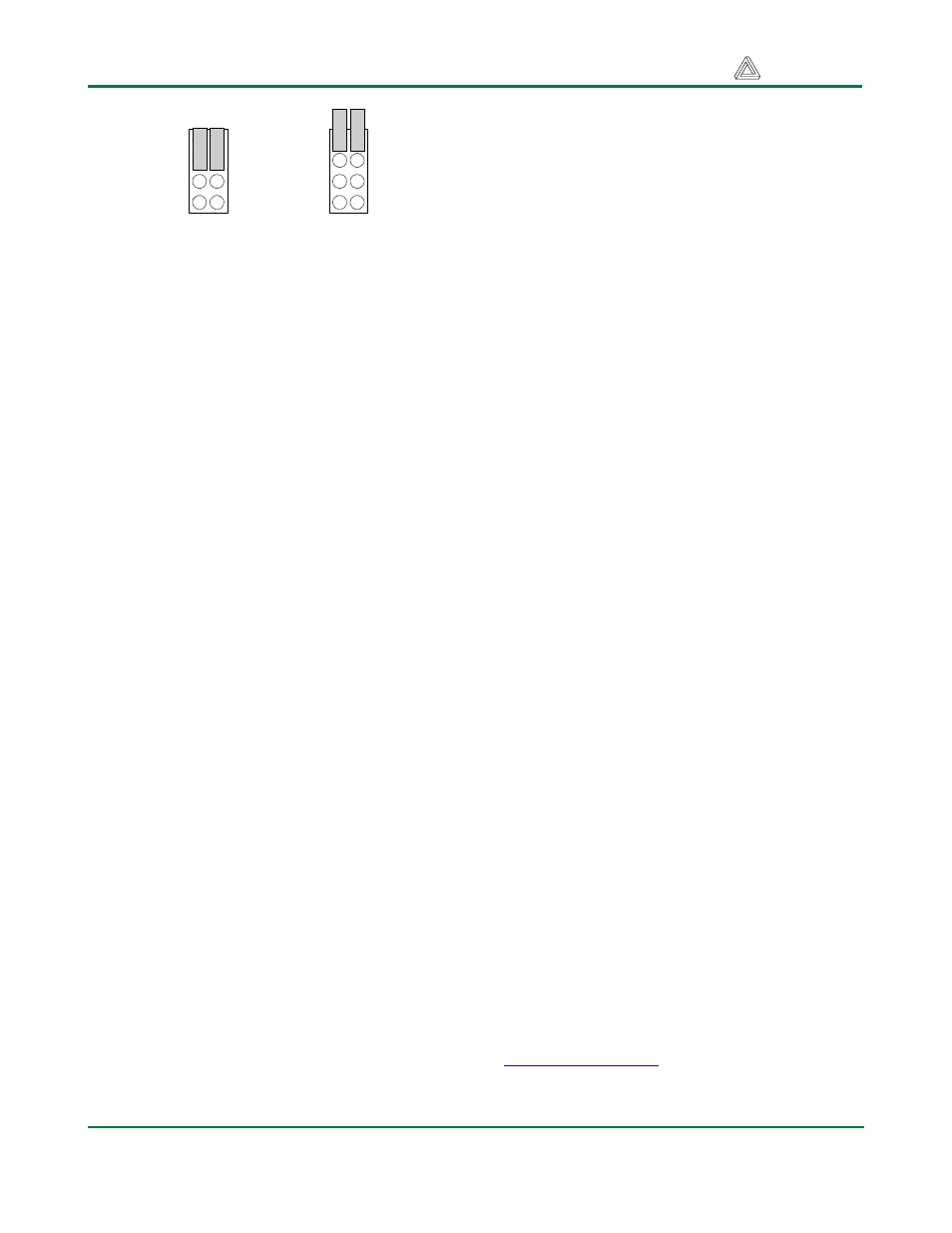
S
C
L
S
D
A
TW I-1
TW I-2
S
C
L
S
D
A
TW I-1
TW I-2
Pull-ups
Enabled
Pull-ups
Disabled
Jumper Settings for TWI Pull-Up Resistors
Connectors J4 and J5 are provided for daisy-
chaining power along with the TWI signals.
These can be use to pass power from the
Cerebot Plus to other devices on the TWI bus.
Either of these connectors could also be used
to provide power to the Cerebot Plus from
some other board on the TWI bus.
External SRAM
The ATmega2560 microcontroller has 8KB of
internal data memory and provision for up to
56KB of external expansion memory.
The Cerebot Plus contains a 128KB external
SRAM, providing two pages of 56KB each.
Before this memory is accessible, the external
memory interface must be enabled. See the
ATmega2560 data sheet for information on
how to enable the external memory interface.
I/O pin PG3 (port G, bit 3) is connected to the
high order address line on the external
memory. To access both pages of the external
memory, configure pin PG3 as an output and
set this pin low to access the lower page and
set this pin high to access the upper page. This
line is pulled low on the board, so that the
lower page will be accessed by default if PG3
is not used.
Although there are two pages of 64KB each in
the external memory, the lower 8KB of memory
addresses access the internal memory and so
the lower 8KB of each external memory page
are not accessible.
Crystal Oscillator
The ATmega2560 microcontroller supports
numerous clock source options for the main
processor operating clock. The Cerebot Plus
has an 8MHz oscillator crystal for use with the
crystal oscillator option. The Cerebot Plus
comes from the factory with the external crystal
oscillator source selected.
The ATmega2560 microcontroller also
provides an internal RC oscillator that operates
at a nominal frequency of 8MHz. This internal
oscillator has a frequency variability of
approximately 2-3%, which is suitable for many
applications. There is also a “Divide clock by 8”
option that can be selected via a fuse bit to
divide the processor clock by 8.
The RC oscillator’s nominal frequency
assumes operation at 5V. The Cerebot Plus
normally operates at 3.3V. See the oscillator
frequency vs. supply voltage chart in the
ATmega2560 data sheet to determine the
nominal frequency at 3.3V.
Although the Cerebot Plus will normally be
operated using the 8MHz crystal oscillator, the
internal oscillator can be selected to operate
the board at a lower frequency if desired. The
clock source to be used by the board is chosen
using the fuse settings in the in-system
programmer.
When changing the clock source fuse settings,
it is extremely important to ensure that the
clock source chosen actually exists on the
board (i.e., only choose the crystal oscillator or
internal oscillator). The ATmega2560 internal
in-system-programming state machine
operates from the selected clock source and if
an unavailable clock source is selected, the
board may no longer be programmable.
In some cases, it is possible to recover the
board if an improper clock source is chosen,
but not always. There is an applications note
“Cerebot Clock Source Fix” (available from
www.digilentinc.com
) that explains the
procedure for recovering a board that has had
an improper clock source programmed.
