Switching characteristics – Cypress CY7C028V User Manual
Page 7
CY7C027V/027VN/027AV/028V
CY7C037V/037AV/038V
Document #: 38-06078 Rev. *B
Page 7 of 18
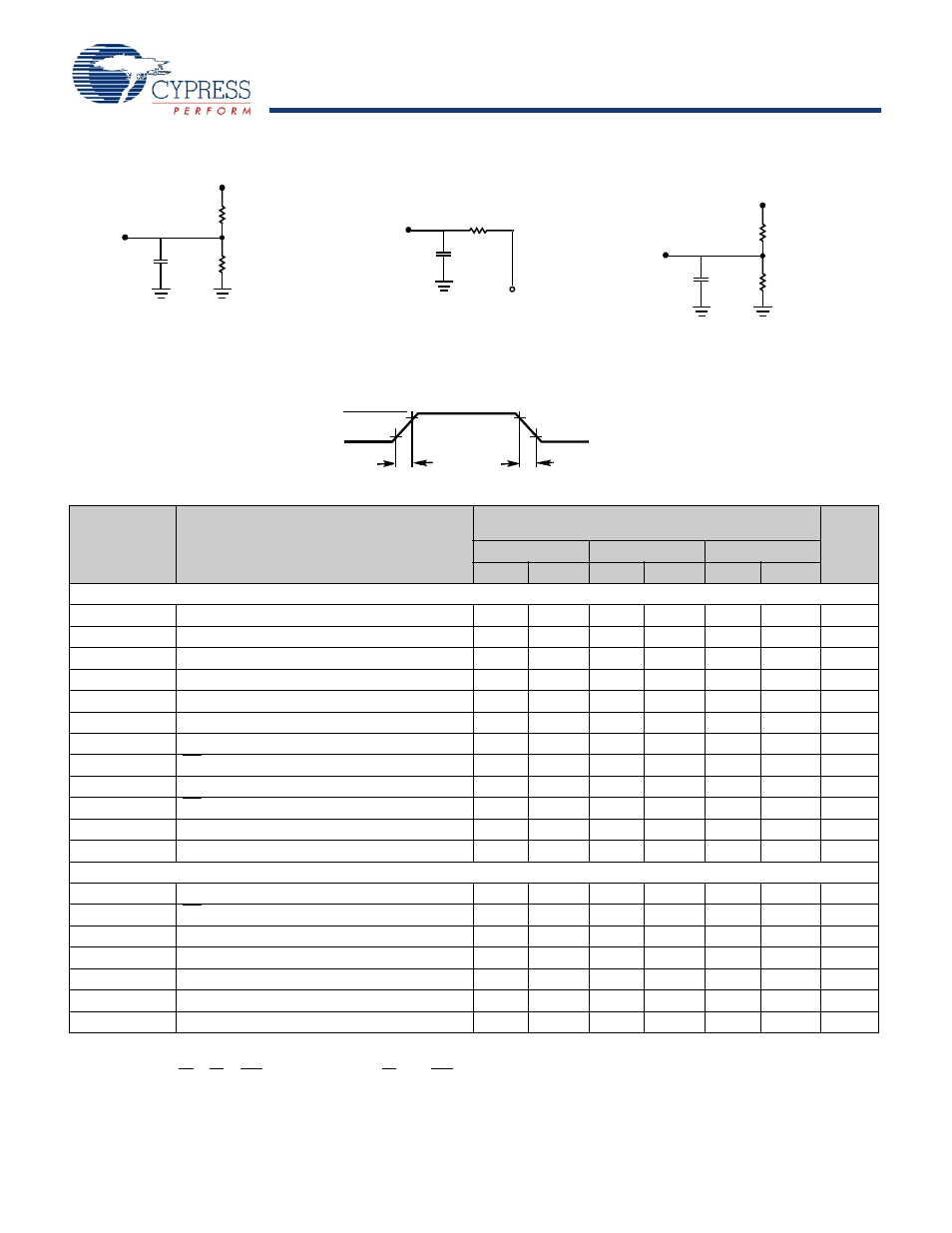
Figure 3. AC Test Loads and Waveforms
3.0V
GND
90%
90%
10%
3 ns
3 ns
10%
ALL INPUT PULSES
(a) Normal Load (Load 1)
R1 = 590
Ω
3.3V
OUTPUT
R2 = 435
Ω
C = 30 pF
V
TH
= 1.4V
OUTPUT
C = 30 pF
(b) Thévenin Equivalent (Load 1)
(c) Three-State Delay (Load 2)
R1 = 590
Ω
R2 = 435
Ω
3.3V
OUTPUT
C = 5 pF
R
TH
= 250
Ω
≤
≤
including scope and jig)
(Used for t
LZ
, t
HZ
, t
HZWE
, & t
LZWE
Switching Characteristics
Over the Operating Range
Parameter
Description
CY7C027V/027VN/027AV/028V/
CY7C037V/037AV/038V
Unit
-15
-20
-25
Min
Max
Min
Max
Min
Max
Read Cycle
t
RC
Read Cycle Time
15
20
25
ns
t
AA
Address to Data Valid
15
20
25
ns
t
OHA
Output Hold From Address Change
3
3
3
ns
t
ACE
CE LOW to Data Valid
15
20
25
ns
t
DOE
OE LOW to Data Valid
10
12
13
ns
t
LZOE
OE LOW to Low Z
3
3
3
ns
t
HZOE
OE HIGH to High Z
10
12
15
ns
t
LZCE
CE LOW to Low Z
3
3
3
ns
t
HZCE
CE HIGH to High Z
10
12
15
ns
t
PU
CE LOW to Power Up
0
0
0
ns
t
PD
CE HIGH to Power Down
15
20
25
ns
t
ABE
Byte Enable Access Time
15
20
25
ns
Write Cycle
t
WC
Write Cycle Time
15
20
25
ns
t
SCE
CE LOW to Write End
12
16
20
ns
t
AW
Address Valid to Write End
12
16
20
ns
t
HA
Address Hold From Write End
0
0
0
ns
t
SA
[7]
Address Setup to Write Start
0
0
0
ns
t
PWE
Write Pulse Width
12
17
22
ns
t
SD
Data Setup to Write End
10
12
15
ns
Notes
6. Test conditions assume signal transition time of 3 ns or less, timing reference levels of 1.5V, input pulse levels of 0 to 3.0V, and output loading of the specified I
OI
/I
OH
and 30 pF load capacitance.
7. To access RAM, CE=L, UB=L, SEM=H. To access semaphore, CE=H and SEM=L. Either condition must be valid for the entire t
SCE
time.
8. At any given temperature and voltage condition for any given device, t
HZCE
is less than t
LZCE
and t
HZOE
is less than t
LZOE
.
9. Test conditions used are Load 2.
10. This parameter is guaranteed by design, but it is not production tested. For information on port-to-port delay through RAM cells from writing port to reading port,
refer to
.
