2 the lambert projection, Lambert, Standard parallel – Leica Geosystems GPS Basics User Manual
Page 37: Geodetic aspects
37
GPS Basics -1.0.0en
Geodetic Aspects
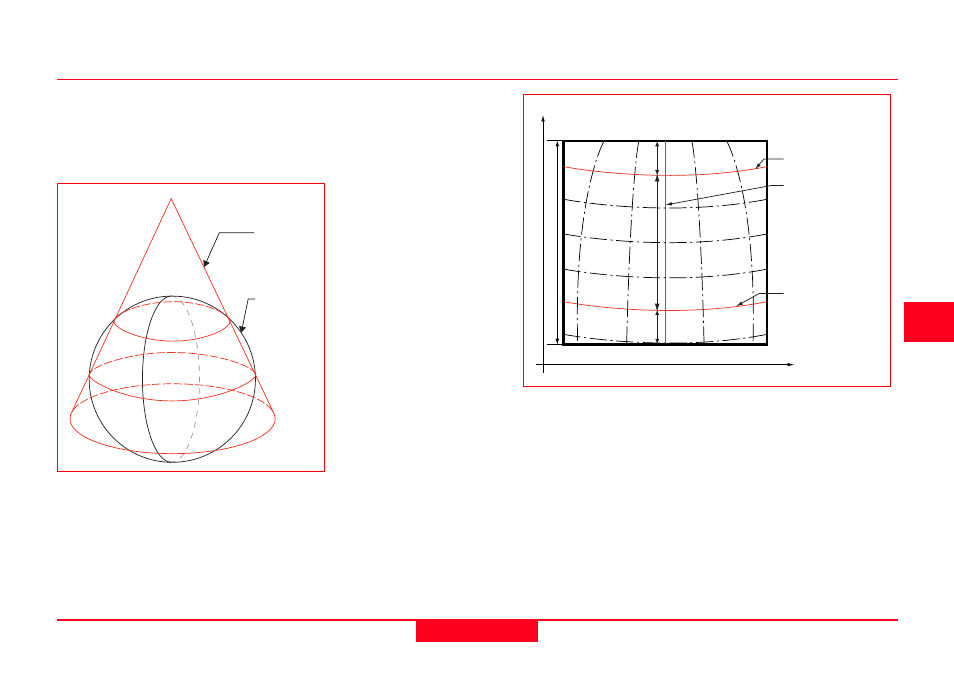
4.6.2 The Lambert Projection
The Lambert Projection is also a
conformal projection based on a cone
that intersects the spheroid. It is ideal for
small, circular countries, islands and
polar regions.
0
N
E
Features of the Lambert Projection
Cone
Latitude of 1st Standard
Parallel
Latitude of 2nd Stand-
ard Parallel
The False Easting and
False Northing are
defined in order that the
origin of the grid projec-
tion can be in the lower
left hand corner as
convention dictates. This
does away with the need
for negative coordinates.
The Latitude of Origin
defines the latitude of the
origin of the projection.
The Central Meridian
defines the direction of
grid north and the
longitude of the centre of
the projection.
The Latitude of 1st
Standard Parallel
defines the latitude at
which the cone first cuts
the spheroid. This also
defines where the
Spheroid
The Lambert Projection
The Lambert projection is defined by:
False Easting and Northing
Latitude of origin
Central Meridian
influence of scale in the north-south direction is zero.
The Latitude of 2nd Standard Parallel defines the
second latitude at which the cone cuts the pyramid. The
influence of scale will also be zero at this point.
The scale is too small between the standard parallels
and too large outside them, being defined by the
latitudes of the Standard Parallels at which it is zero.
Scale in the east-west direction does not vary.
Zone Width
1/6 Zone
Width
2/3 Zone Width
1/6 Zone
Width
Standard Parallel
Central Meridian
Standard Parallel
