Helmert, Helmert transformation, Geodetic aspects – Leica Geosystems GPS Basics User Manual
Page 32: Gps basics -1.0.0en
32
GPS Basics -1.0.0en
Geodetic Aspects
Helmert Transformations
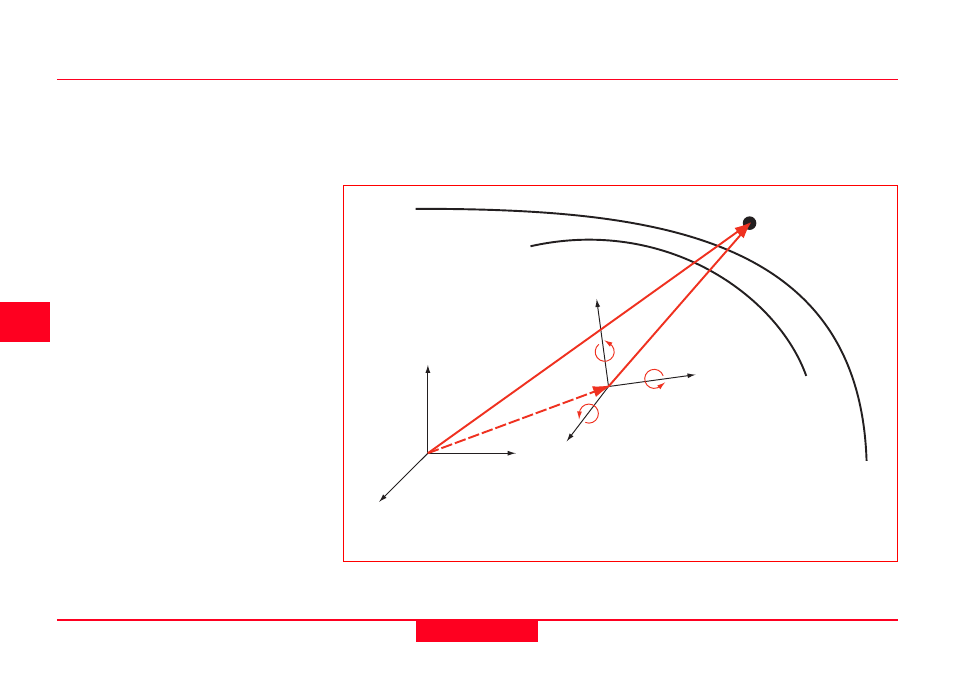
The Helmert 7 parameter transformation
offers a mathematically correct transfor-
mation. This maintains the accuracy of
the GPS measurements and local
coordinates.
Experience has shown that it is common
for GPS surveys to be measured to a
much higher accuracy than older surveys
measured with traditional optical
instruments.
In the vast majority of cases, the previ-
ously measured points will not be as
accurate as the new points measured
with GPS. This may create non-homoge-
neity in the network.
When transforming a point between
coordinate systems, it is best to think of
the origin from which the coordinates are
derived as changing and not the surface
on which it lies.
In order to transform a coordinate from
one system to another, the origins and
axes of the ellipsoid must be known
relative to each other. From this informa-
tion, the shift in space in X, Y and Z from
one origin to the other can be deter-
mined, followed by any rotation about the
X, Y and Z axes and any change in scale
between the two ellipsoids.
X
S
Y
S
Z
S
X
L
Y
L
Z
L
M
Y
M
Z
M
X
P
T
P
S
P
L
P
S
P
L
T
M
X
, M
Y
, M
Z
Local
Ellipsoid
WGS84
Ellipsoid
= Position in WGS84
= Position in Local System
= Resultant Vector from shift of origin in X, Y and Z
= Rotation angles
7 parameter Helmert transformation
