Gdop, Hdop, Pdop – Leica Geosystems GPS Basics User Manual
Page 17: Vdop, Dilution of precision, How gps works 4 5 6
17
GPS Basics -1.0.0en
How GPS works
4
5
6
4. Dilution of Precision
The Dilution of Precision (DOP) is a
measure of the strength of satellite
geometry and is related to the spacing
and position of the satellites in the sky.
The DOP can magnify the effect of
satellite ranging errors.
The principle can be best illustrated by
diagrams:
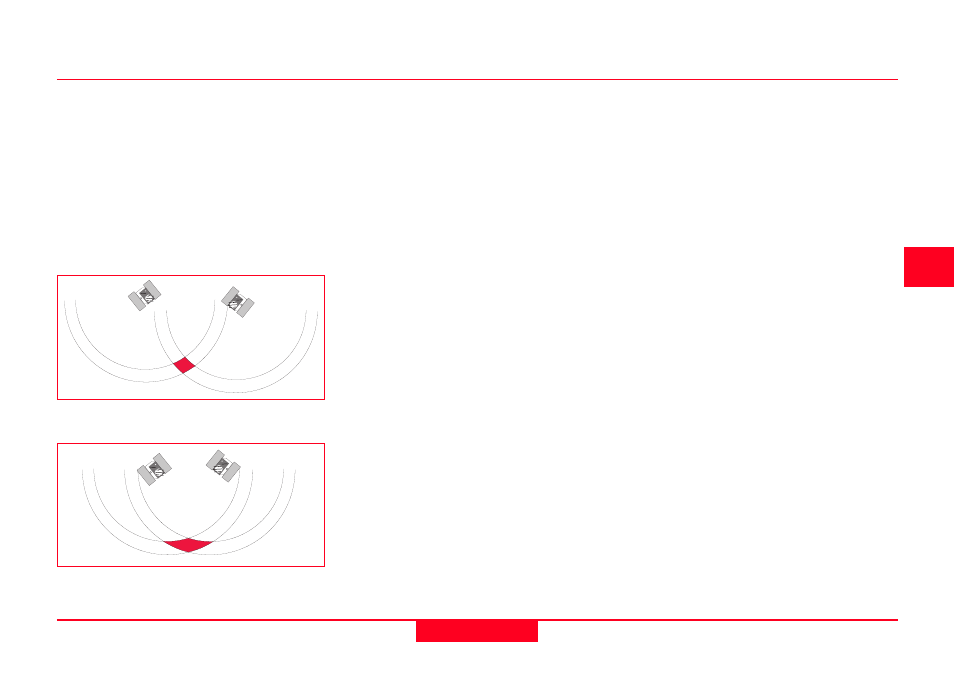
Well spaced satellites - low uncertainty
of position
The range to the satellite is affected by
range errors previously described. When
the satellites are well spaced, the
position can be determined as being
within the shaded area in the diagram
and the possible error margin is small.
When the satellites are close together,
the shaded area increases in size,
increasing the uncertainty of the posi-
tion.
Different types of Dilution of Precision or
DOP can be calculated depending on
the dimension.
VDOP Vertical Dilution of Precision.
Gives accuracy degradation in vertical
direction.
HDOP Horizontal Dilution of Precision.
Gives accuracy degradation in horizontal
direction.
PDOP Positional Dilution of Precision.
Gives accuracy degradation in 3D
position.
GDOP Geometric Dilution of Precision.
Gives accuracy degradation in 3D
position and time.
The most useful DOP to know is GDOP
since this is a combination of all the
factors. Some receivers do however
calculate PDOP or HDOP which do not
include the time component.
The best way of minimizing the effect of
GDOP is to observe as many satellites
as possible. Remember however, that
the signals from low elevation satellites
are generally influenced to a greater
degree by most error sources.
As a general guide, when surveying with
GPS it is best to observe satellites that
are 15° above the horizon. The most
accurate positions will generally be
computed when the GDOP is low,
(usually 8 or less).
Poorly spaced satellites - high
uncertainty of position
