5switch configuration and spanning tree, Switch configuration and spanning tree -10, Figure 13. switch configuration menu -10 – CANOGA PERKINS 9135 SNMP Managed 10/100/1000 Ethernet Switch User Manual
Page 26
EdgeAccess Universal Chassis System
Model 9135 10/100/1000
3-10
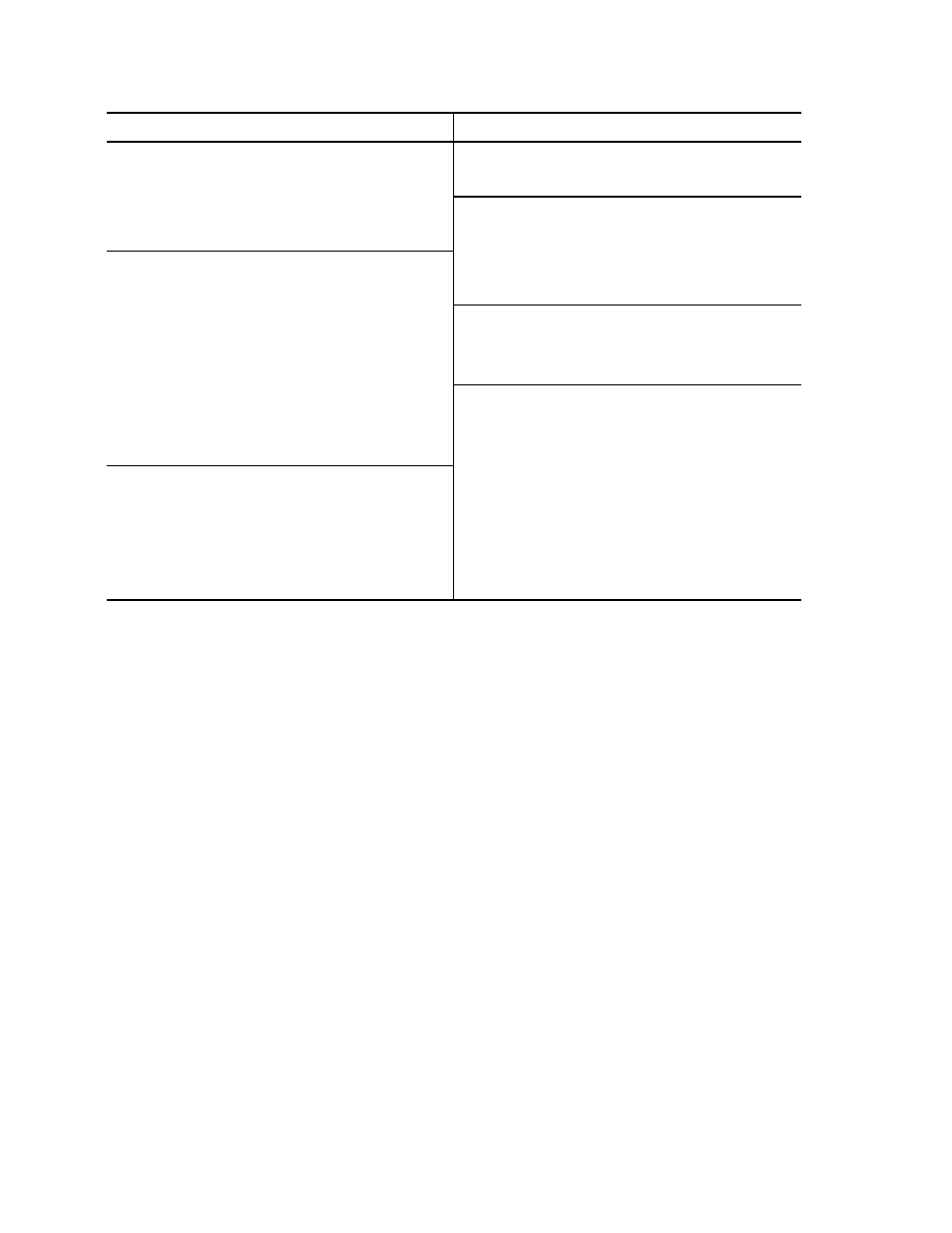
Menu and Selection
Minimum Access
Menu and Selection
Minimum Access
Host Table / SNMP Settings Menu
Port n Details Menu
Read Community
Supervisor
Clear Counters
User
Write Community
Supervisor
Traps Log Menu
Send Alert Traps
Supervisor
View Previous Page
User
SLIP Port Settings Menu
View Next Page
User
Interface
Supervisor
Clear the log
Supervisor
Init Modem at Startup
Supervisor
Fdb Log Menu
Modem Init String
Supervisor
View Previous Page
User
Password Enable
Supervisor
View Next Page
User
SLIP Password
Supervisor
Ping Menu
SLIP IP Address
Supervisor
Ping Address
User
SLIP Subnet Mask
Supervisor
Ping Count
User
SLIP Port Setup Menu
Start Pinging
User
Baud Rate
Supervisor
Parity
Supervisor
Stop Bits
Supervisor
Flow Control
Supervisor
3.5
Switch Configuration and Spanning Tree
The Switch Configuration menu offers one option, Spanning Tree; see Figure 13.
Switch Configuration
1.
Spanning Tree
2.
Main Menu
Figure 13. Switch Configuration Menu
Ethernet bridges or switches use the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), an algorithm that creates a logical
topology that connects all network segments and ensures only one path between any two stations.
When STP is enabled, the 9135 monitors the incoming data packets and periodically sends Bridge
Protocol Data Units (BPDU). STP monitors the incoming BPDUs to detect any loops. If the same
BPDU arrives on two ports, STP blocks one port to remove the loop. Because this tree-like structure
spans all nodes in the network, it is called Spanning Tree. Figure 14 shows a typical STP application.
