Dell PowerEdge 6400 User Manual
Page 37
These COM ports have the following I/O address settings:
COM1: 3F8h
COM2: 2F8h
COM3: 3E8h
COM4: 2E8h
For example, if you add an internal modem card with a port configured as COM1, the system then sees logical COM1 as the address on the
modem card. It automatically remaps the integrated serial port that was designated as COM1 to COM3, which shares the COM1 IRQ setting.
(Note that when you have two COM ports sharing an IRQ setting, you can use either port as necessary but you may not be able to use them both at
the same time.) If you install one or more expansion cards with serial ports designated as COM1 and COM3, the corresponding integrated serial
port is disabled.
Before adding a card that remaps the COM ports, check the documentation that came with your software to make sure that the software can be
mapped to the new COM port designation.
To avoid autoconfiguration, you may be able to reset jumpers on the expansion card so that the card's port designation changes to the next
available COM number, leaving the designation for the integrated port as is. Alternatively, you can disable the integrated ports through the System
Setup program. The documentation for your expansion card should provide the card's default I/O address and allowable IRQ settings. It should also
provide instructions for readdressing the port and changing the IRQ setting, if necessary.
The integrated parallel port has autoconfiguration capability through the System Setup program; that is, if you set the parallel port to its automatic
configuration and add an expansion card containing a port configured as LPT1 (IRQ7, I/O address 378h), the system automatically remaps the
integrated parallel port to its secondary address (IRQ5, I/O address 278h). If the secondary port address is already being used, the integrated
parallel port is turned off.
For general information on how your operating system handles serial and parallel ports and for more detailed command procedures, see your
operating system documentation.
Serial Port Connectors
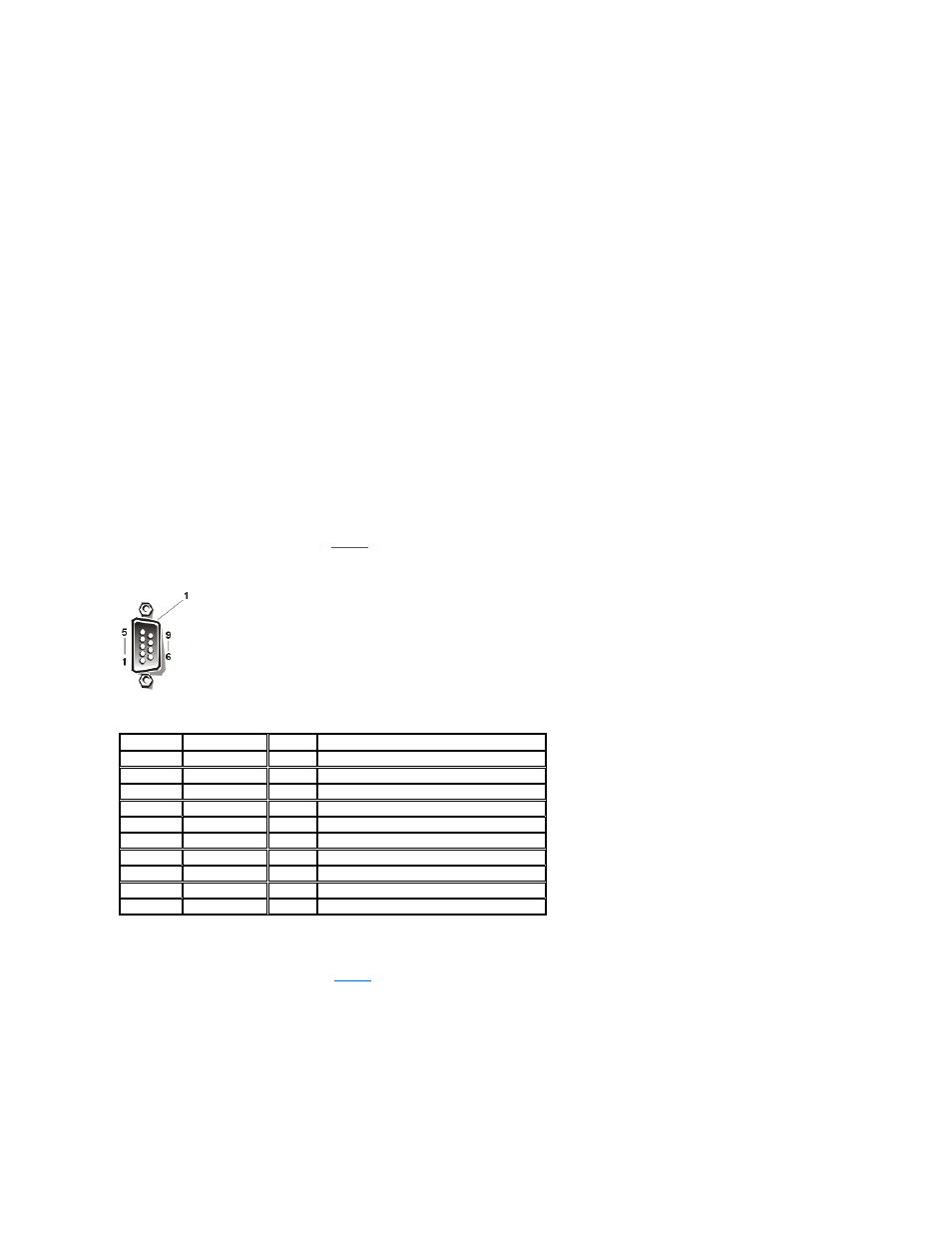
If you reconfigure your hardware, you may need pin number and signal information for the serial port connectors. Figure 2 illustrates the pin
numbers for the serial port connectors, and
defines the pin assignments and interface signals for the serial port connectors.
Figure 2. Pin Numbers for the Serial Port Connectors
Table 1. Pin Assignments for the Serial Port Connectors
Parallel Port Connector
If you reconfigure your hardware, you may need pin number and signal information for the parallel port connector. Figure 3 illustrates the pin
numbers for the parallel port connector, and
defines the pin assignments and interface signals for the parallel port connector.
Figure 3. Pin Numbers for the Parallel Port Connector
1 Shell
Pin
Signal
I/O
Definition
1
DCD
I
Data carrier detect
2
SIN
I
Serial input
3
SOUT
O
Serial output
4
DTR
O
Data terminal ready
5
GND
N/A
Signal ground
6
DSR
I
Data set ready
7
RTS
O
Request to send
8
CTS
I
Clear to send
9
RI
I
Ring indicator
Shell
N/A
N/A
Chassis ground
