Common operating faults – Tweco 7-5227 User Manual
Page 5
July 28, 2004
5
Manual 0-4647
7. Follow normal recommended cutting practices as provided
in the power supply operator's manual.
NOTE
When the shield cup is properly installed, there is
a slight gap between the shield cup and the torch
handle. Gas vents through this gap as part of nor-
mal operation. Do not attempt to force the shield
cup to close this gap. Forcing the shield cup against
the torch head can damage components.
8. The optional Standoff Guide allows the user to easily
adjust and maintain a consistent standoff height for
most applications.
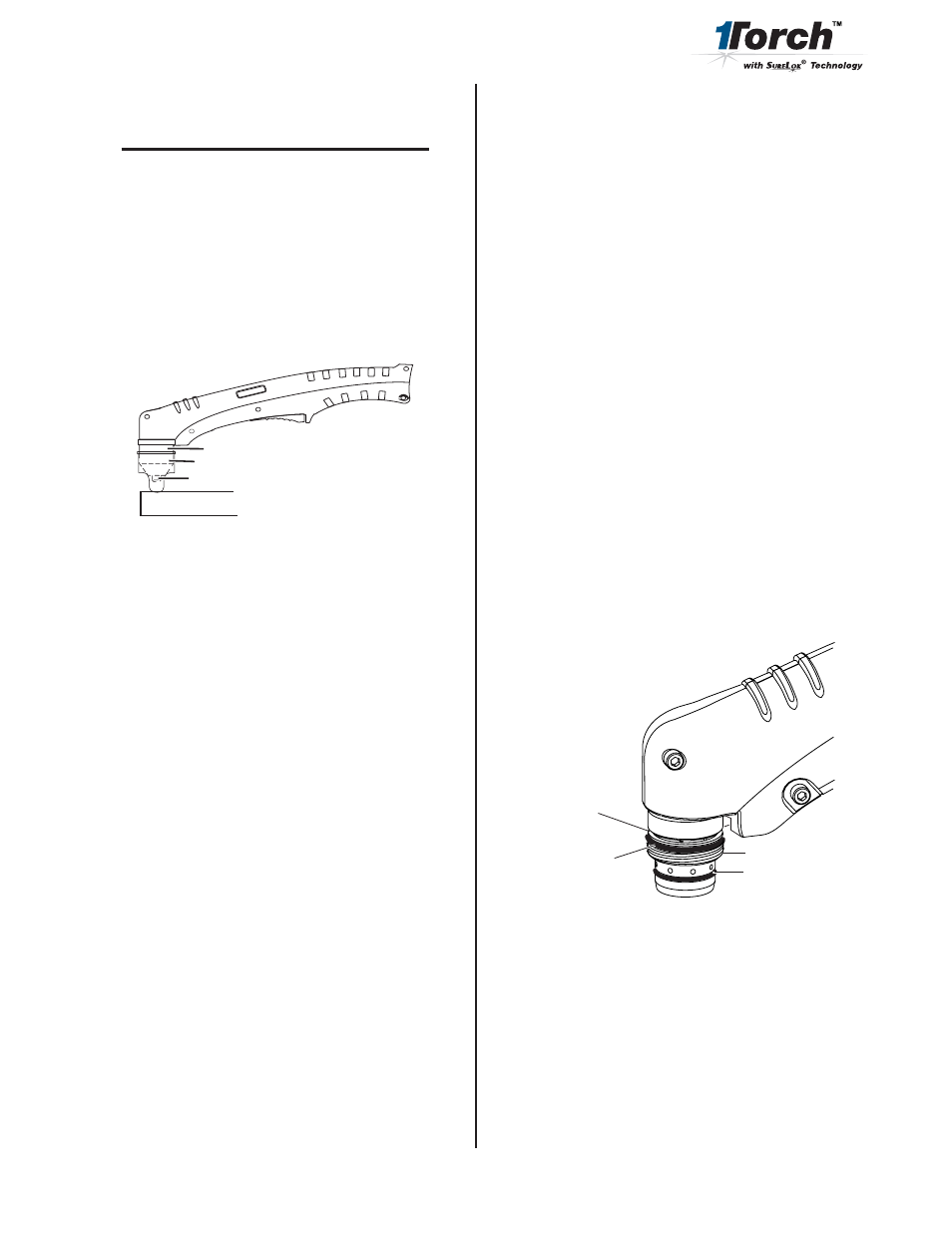
Art # A-04063
Shield Cup
Standoff Guide
Torch Tip
Workpiece
Common Operating Faults
The following are the more common cutting faults and the
possible causes:
1. Insufficient Penetration
a. Cutting speed too fast
b. Torch tilted too much
c. Metal too thick
d. Worn torch parts
e. Cutting current too low
f. Non-Genuine Thermal Dynamics Parts
2. Main Arc Extinguishes
a. Cutting speed too slow
b. Torch standoff too high from workpiece
c. Cutting current too high
d. Work cable disconnected
e. Worn torch parts
f.
Non-Genuine Thermal Dynamics Parts
3. Excessive Dross Formation
a. Cutting speed too slow
b. Torch standoff too high from workpiece
c. Worn torch parts
d. Improper cutting current
e. Non-Genuine Thermal Dynamics Parts
4. Short Torch Parts Life
a. Oil or moisture in air source
b. Exceeding system capability (material too thick)
c. Excessive pilot arc time
d. Gas pressure too low
e. Improperly assembled torch
f.
Non-Genuine Thermal Dynamics Parts
5. Difficult Starting
a. Worn torch consumables
b. Non - Genuine Thermal Dynamics Parts
6. Torch will not pilot when torch switch is activated
a. Upper O-ring on torch head is in wrong position
Lower O-Ring
Upper O-Ring
in Correct Groove
Upper Groove
with Vent Holes
Must Remain Open
Threads
Art # A-03640
