Connection examples, Circuit status, Operating principle – Rockwell Automation 22А PowerFlex DriveGuard Safe-Off User Manual - Series B User Manual
Page 20: Fault detection
20
Rockwell Automation Publication PFLEX-UM003B-EN-P - July 2012
Description of Operation
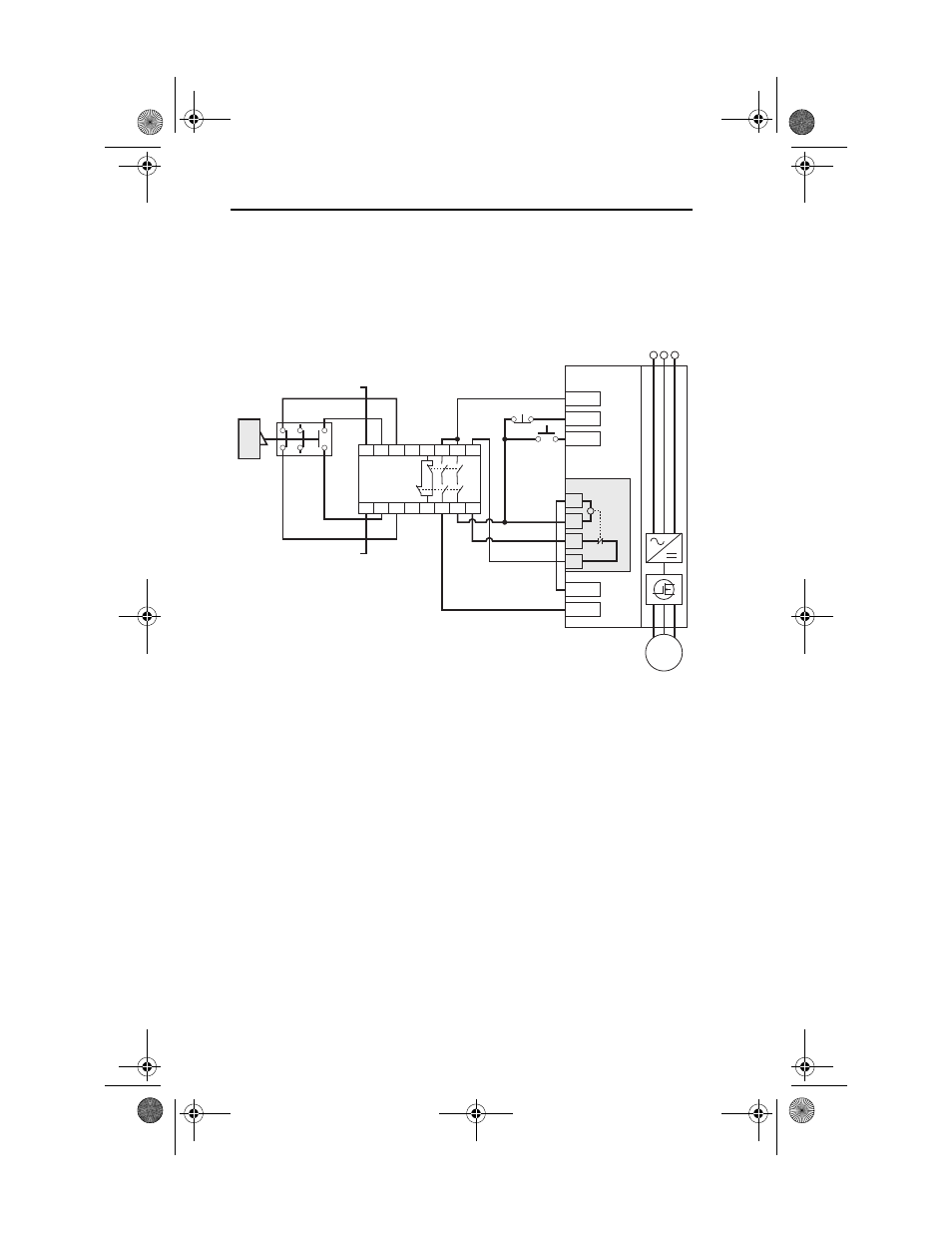
Connection Examples
Example 1 - Safe Torque Off Connection with Coast-to-Stop Action,
Dual Channel
Figure 10 - Stop Category 0 – Coast
Circuit Status
Circuit shown with guard door closed and system ready for normal drive
operation.
Operating Principle
This is a dual channel system with monitoring of the Safe Torque Off circuit
and drive. Opening the guard door will switch the input circuits (S13-S14 &
S21-S22) to the Minotaur monitoring safety relay unit. The output circuits
(13-14 & 23-24) will cause the Safe Torque Off option and drive Enable
circuit to trip and the motor will coast to stop. To restart the drive, the
Minotaur safety relay must first be reset followed by a valid start command to
the drive.
Fault Detection
A single fault detected on the Minotaur safety input circuits will result in the
lock-out of the system at the next operation and will not cause loss of the
safety function.
If the Safe Torque Off option sticks ON, the motor will stop on command
due to the enable input. The system cannot be reset when this fault condition
exists.
Stop
Start
A1 S21 S13
31 13 23 X1
A2
+24V DC
Common
+24V DC
S22 S14
32 14 24 X2
Minotaur
MSR9T
GuardMaster
Trojan
Gate
+24V DC
PowerFlex
AC Drive
Stop
Start
AC Line
Input Power
Common
Enable
*
M
1
2
3
4
Safe Off Option
*Important: The drive Enable digital
input is a solid state circuit. The safety
outputs on safety module must not be
configured for Pulsed/Safety Pulse Test.
PFLEX-UM003.fm Page 20 Wednesday, July 18, 2012 8:26 AM
