Power loss (w) – JUMO 709050 IPC IGBT Power Converter Data Sheet User Manual
Page 3
JUMO GmbH & Co. KG • 36035 Fulda, Germany
2009-11-01/00389005
Data Sheet 70.9050
Seite 3/12
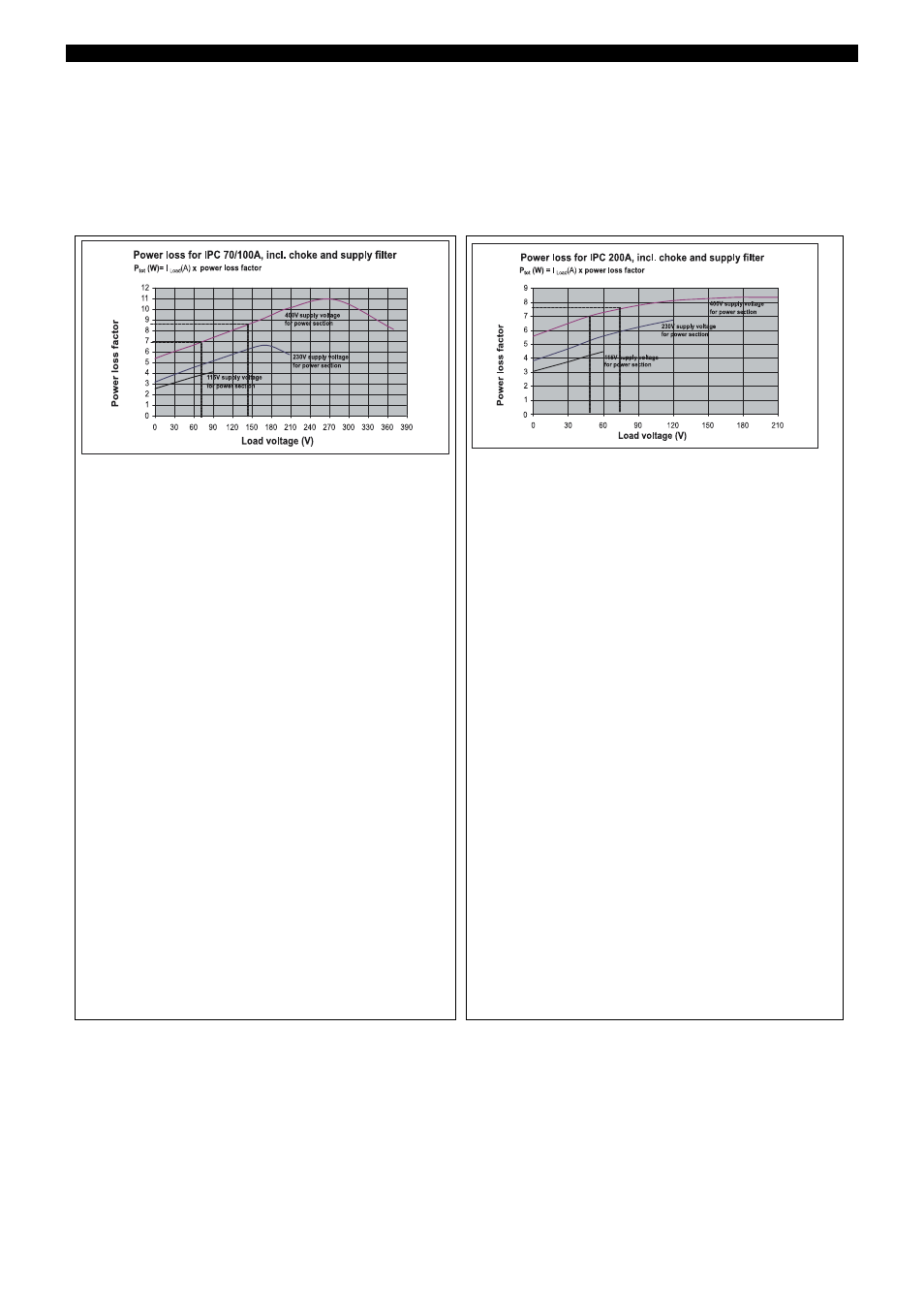
Power loss (W)
Note:
Power loss occurs in the form of thermal discharge at the cooling body of the power converter, at the EMC filter and choke. It
has to be be discharged from the point of installation (e.g. in the switch cabinet) according to the climatic conditions!
Type 709050/X1...and type 709050/X2...
Type 709050/82-12-400-150-100/252
Nominal data of the device: Load voltage = 150V; load current = 100A;
Voltage supply to the power section = 400V
Resistive loads and Molybdenum Disilicide heating elements:
Heating element data: Load voltage = 140V; load current = 90A
Determine the max. load voltage actually taken (e.g. 140 V) and find the point
intersecting with the curve for the voltage supply in the power section. The Y
axis shows the attendant power dissipation factor of, e.g., 8.5.
The power dissipation (W) is obtained by multiplying this power dissipation
factor by the load current (e.g. 90A)
that flows at max. load voltage (e.g. 140V) through the load resistor
Power loss = 90(A) x power dissipation factor
Power loss = 90(A) x 8.5 = 765W
___________________________________________________________________
Type 709050/92-12-400-150-100/252
Nominal data of the device: Load voltage = 150V; load current = 100A;
Voltage supply to the power section = 400V; P control, P = 6300W
SIC heating elements
SIC heating element data: new: 70V/90A, old 140V/45A; P = 6300W
Determine the maximum load voltage actually taken (e.g. 70V) of the new SIC
heating element and find the point intersecting with the curve for the voltage
supply in the power section. The Y axis shows the attendant power dissipa-
tion factor of, e.g., 6.8.
The power dissipation (W) is obtained by multiplying this power dissipation
factor by the load current (e.g. 90A)
that flows at max. load voltage (e.g. 70V) through the new SIC heating ele-
ment
Power loss = 90(A) x power dissipation factor
Power loss = 90(A) x 6.8 = 612W
Type 709050/83-12-400-90-200/252
Nominal data of the device: Load voltage = 90V; load current = 200A;
Voltage supply to the power section = 400V
Resistive loads and Molybdenum Disilicide heating elements:
Heating element data: Load voltage = 75V; load current = 130A
Determine the max. load voltage actually taken (e.g. 75V) and find the point
intersecting with the curve for the voltage supply in the power section. The Y
axis shows the attendant power dissipation factor of, e.g., 7.5.
The power dissipation (W) is obtained by multiplying this power dissipation
factor by the load current (e.g. 130A) that flows through the load resistor at
max. load voltage (e.g. 75V)
Power loss = 130 (A) x power loss factor
Power loss = 130 (A) x 7.5 = 975W
___________________________________________________________________
Type 709050/93-12-400-90-200/252
Nominal data of the device: Load voltage = 90V; load current = 200A; voltage
supply to the power section = 400V; P control, P=9000W
SIC heating elements
SIC heating element data: new: 45V/200A, old 90V/100A; P = 9000W
Determine the maximum load voltage actually taken (e.g. 45V) of the new SIC
heating element and find the point intersecting with the curve for the voltage
supply in the power section. The Y axis shows the attendant power dissipa-
tion factor of, e.g., 6.8.
The power dissipation (W) is obtained by multiplying this power dissipation
factor by the load current (e.g. 200A) that flows at max. load voltage (e.g. 45V)
through the new SIC heating element
Power loss = 200(A) x power loss factor
Power loss = 200(A) x 6.8 = 1360W
