5 operation, 1 applications, 1 nucleic acid quantification – Eppendorf G0.5 µPlate User Manual
Page 10: 2 preparing measurements, 1 defining the blank value procedure, 2 average blanking, Operation 5.1, Applications 5.1.1, Nucleic acid quantification, Preparing measurements 5.2.1
Operation
Eppendorf
®
μPlate G0.5
English (EN)
10
5
Operation
5.1
Applications
5.1.1
Nucleic acid quantification
For the quantification procedure in the μPlate G0.5, a sample volume of 2 μL is sufficient
in order to achieve accurate results. The absorbance of the nucleic acid samples is
measured at 260 nm. The optical path length of the μPlate G0.5 is 0.5 mm. To assess the
purity of the nucleic acid, an additional measurement is conducted at 280 nm to display
any proteins that may be present in the sample. A 260/280 ratio between 1.8 and 1.9 is
acceptable for pure nucleic acids. A ratio < 1.8 may show that the sample contains
proteins or other impurities. If this is the case, additional purification steps are
recommended.
5.2
Preparing measurements
5.2.1
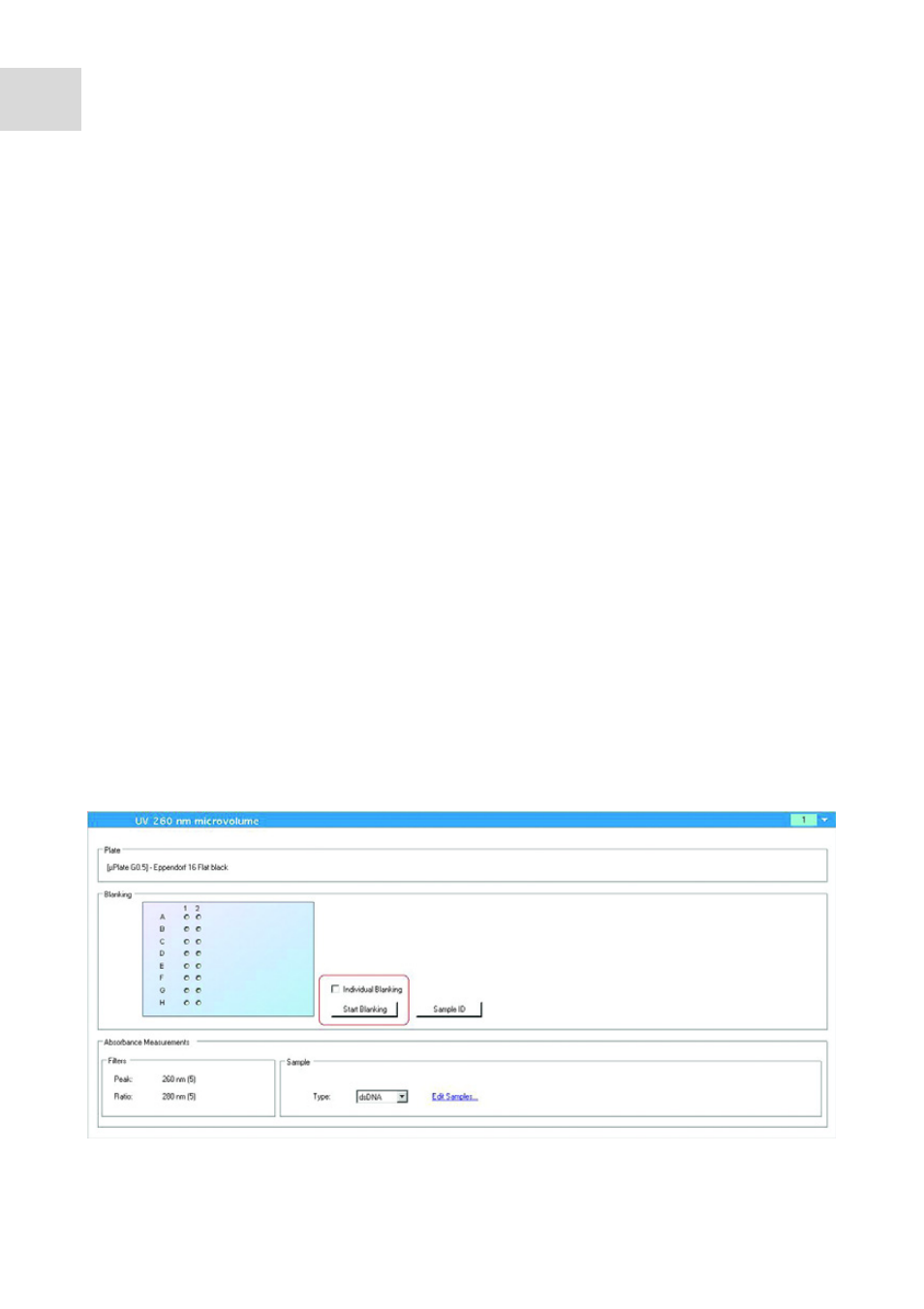
Defining the blank value procedure
The user can select from two options: determining the average blank value ("average
blanking") and determining the individual blank values ("individual blanking", set as
default).
5.2.2
Average blanking
To determine the average blank value, select the wells to be used for blanking. To do so,
drag a border around the corresponding sample positions in the plate preview. We
generally recommend carrying out the blank measurement with all 16 sample positions.
However, at least two wells are required to calculate an average value which will then be
used for the blank value correction of all measured samples.
To ensure reliable measuring results, the OD results measured must have a CV of < 10%
(CV= Coefficient of variation).
Abb. 5-1:"Start Blanking" button
Fig. 5-1:
"Start Blanking" button
