Drive speeds, Motion warning alarm, Gradeability – Snorkel AB80J User Manual
Page 55: Warning
Chapter 8 – Operation
AB80J/AB85J – 0420453
51
• Use mid range (four wheel drive) when traveling
across soft surfaces or those with small inclines.
Mid range can only be activated when the booms
are stowed. Mid range is for medium speed, high
torque operation.
• Use low range (four wheel drive) for driving on
loading ramps or other steep grades and when
safety considerations demand slow deliberate
machine movement. Low range is for low speed,
high torque operation.
2. Determine the desired steer mode for the specific
driving conditions. Place the switch in the four wheel
coordinated, two wheel, or crab steer mode position
to achieve the desired machine movement. Refer to
Figure 8.5
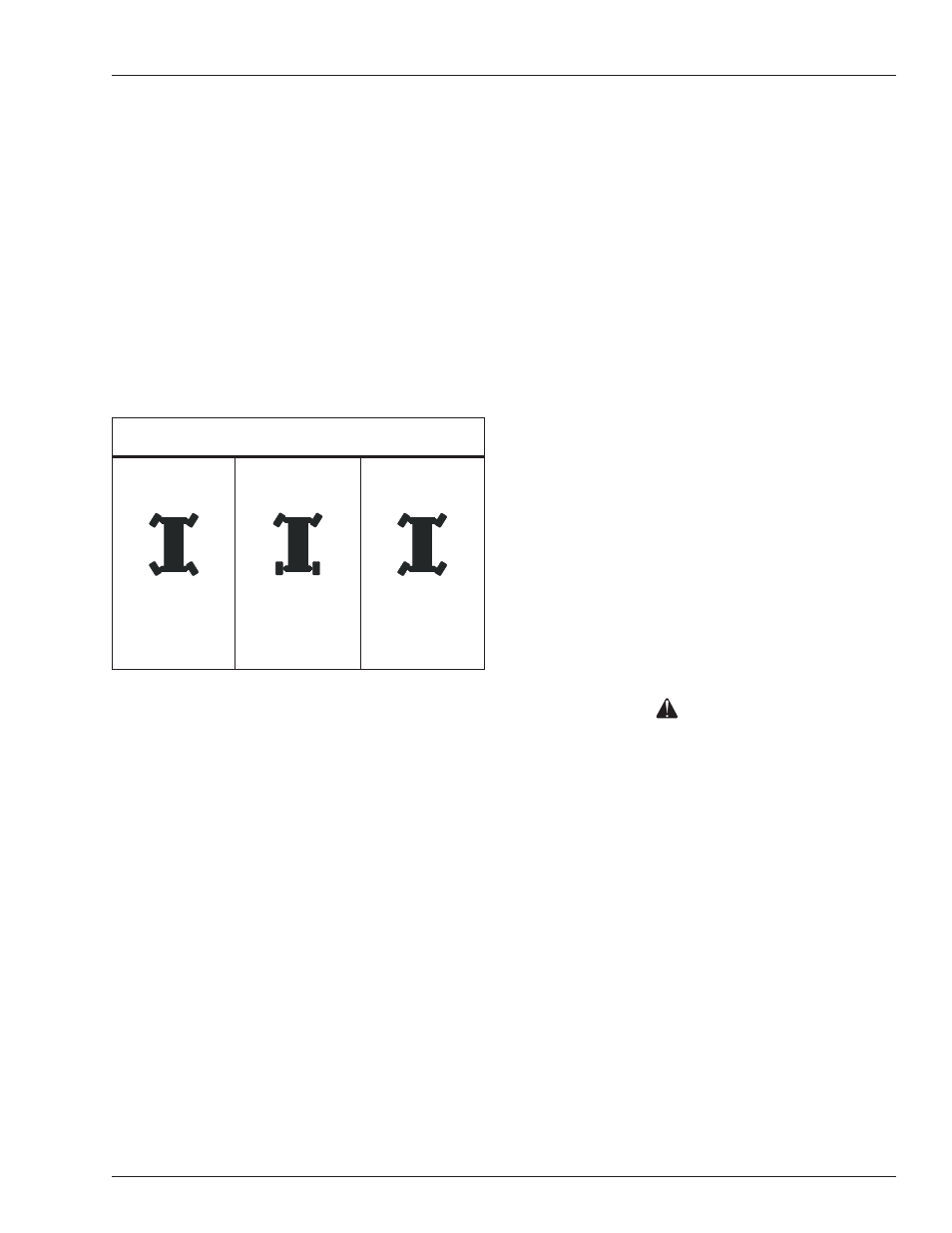
Figure 8.5 – Steer Modes
• Use two wheel steer for most machine operation
such as travel between jobs and to position the
machine near the job location.
• Use four wheel coordinated steer when a tight turn-
ing radius is desired for positioning the machine.
• Use crab steer to travel in a diagonal motion in the
direction of the wheels.
Note
The steering wheels are not self-centering. Set the steer-
ing wheels straight ahead after completing a turn and
before switching from one steer mode to another.
3. Step down on the platform foot switch.
4. Push the drive joystick forward to move the chas-
sis forward, the direction of the blue arrow. Pull the
joystick backward to move the chassis backward,
the direction of the yellow arrow. The drive speed is
proportional to the joystick position.
5. To stop drive motion, return the joystick to neutral.
6. Push the drive joystick to the right to steer to the right,
the direction of the yellow arrow. Push the joystick
to the left to steer to the left, the direction of the blue
arrow. The wheels will steer only when the drive
joystick is in the forward or reverse drive position, or
when the booms are stowed.
Note
The steering wheels are not self-centering. Set the steer-
ing wheels straight ahead after completing a turn.
7. After driving to the desired location, release the foot
switch, or push the emergency stop button to apply
the parking brakes.
Drive Speeds
The drive speed is proportional to the joystick position.
The farther the joystick is moved, the faster the travel
speed.
Always slow down and shift the drive system to low
range before traveling over rough terrain or any sloped
surface.
Drive speed ranges are interlocked through limit switches
that sense the main and riser boom position. When either
boom is elevated or extended, only the slowest drive
speed will work regardless of the drive range switch posi-
tion. To avoid a sudden speed change from high to low
elevated boom speed, always bring the machine to a stop
before raising the booms from the stowed position.
Warning
The potential for an accident increases when safety
devices do not function properly. Death or serious
injury can result from such accidents. Do not alter,
disable, or override any safety device.
Do not use the aerial platform if it drives faster than 0.6
miles per hour (26 feet in 30 seconds) when any of the
booms are out of the stowed position.
Motion Warning Alarm
The motion warning alarm sounds loud intermittent beeps
when the drive joystick is in the forward or reverse posi-
tion.
Gradeability
Machine gradeability refers to the maximum slope that
the aerial platform is capable of travel under practical
conditions. It is based on mathematical calculation, but
it also takes into account the practical application.
At any given moment when driving the machine on a
slope, at least one, if not all, of the factors contributing
to achieving theoretical gradeabilty will not be at optimal
performance. For example, tire contact may not be the
same at each drive wheel or the slope conditions may not
be optimal, which would then allow for loss of traction.
Steer Modes
Crab
• Front and rear
wheels turn in
steer direction
Four Wheel
Coordinated
• Front wheels turn
in steer direction
• Rear wheels turn
in the opposite
direction
Two Wheel
• Front wheels turn
in steer direction
• Rear wheels do
not turn
