Booster pumps, Operating procedures sec ii- 7, Follow the maintenance and inspection procedures – Hale 2CBP User Manual
Page 19
Operating Procedures
Sec II- 7
Booster Pumps
cause cavitation.
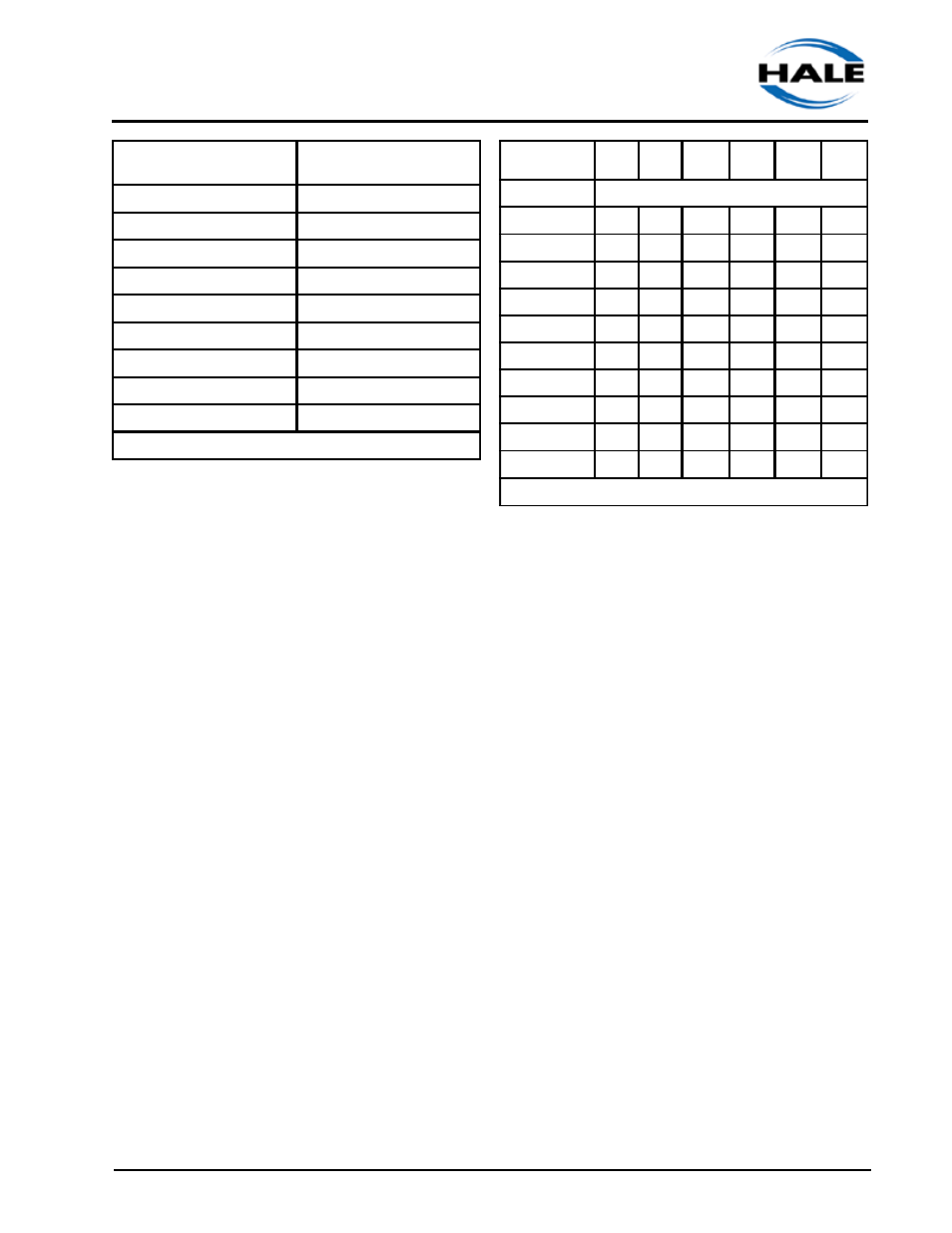
o Consider the size of the suction hose: Table
2-4 shows the NFPA pre-selected hose
sizes for each pump-rating capacity. Using
the appropriate-sized hose will minimize the
occurrence of cavitation.
o
Consider the piping within the truck: Further
suction losses may result from additional
suction piping added to the fire pump during
assembly by the manufacturer.
o
Follow the maintenance and inspection
procedures.
o
Cavitation can occur with large nozzle tips.
Solve this problem by reducing flow.
o
Cavitation can also occur when air enters the
pump. The pump may be primed, however,
air leaks can cause rough operation and an
increase of engine speed without an in-
crease in pressure or flow. If an air leak is
suspected, discontinue pumping and refer to
Section IV.
Elevation
Feet (Meters)
Lift-Loss in Feet
(Meters)
2,000 (609)
NFPA Baseline
3,000 (914)
1.1 (0.33)
4,000 (1219)
2.2 (0.67)
5,000 (1524)
3.3 (1)
6,000 (1828)
4.4 (1.34)
7,000 (2133)
5.5 (1.67)
8,000 (2438)
6.6 (2.01)
9,000 (2743)
7.7 (2.35)
10,000 (3048)
8.8 (2.68)
Table 2-3: Lift Loss from Elevation
Hose
Diameters
(mm)
3"
(76)
4"
(102)
4 ½"
(114)
5"
(127)
6"
(152)
Dual
6"
FLOWS GPM
(LPM)
Lift Loss
250
5.2
(19.7)
350
2.5
(9.5)
500
5.0
(19)
3.6
(51.5)
750
11.4
(43)
8.0
(30)
4.7
(17.8)
1.9
(7.2)
1000
14.5
(55)
8.5
(32)
3.4
(12.9)
1250
13
(49)
5.2
(19.6)
1500
7.6
(28.7)
1.9
(7.2)
1750
10.4
(39.4)
2.6
(9.8)
2000
3.4
(12.9)
2500
5.2
(19.6)
Table 2-4: Hose Sizes for Pump-Rating Capacity
