An300, Modern chopper-stabilized amplifiers, Ac amp – Cirrus Logic AN300 REV1 User Manual
Page 4
4
AN300REV1
AN300
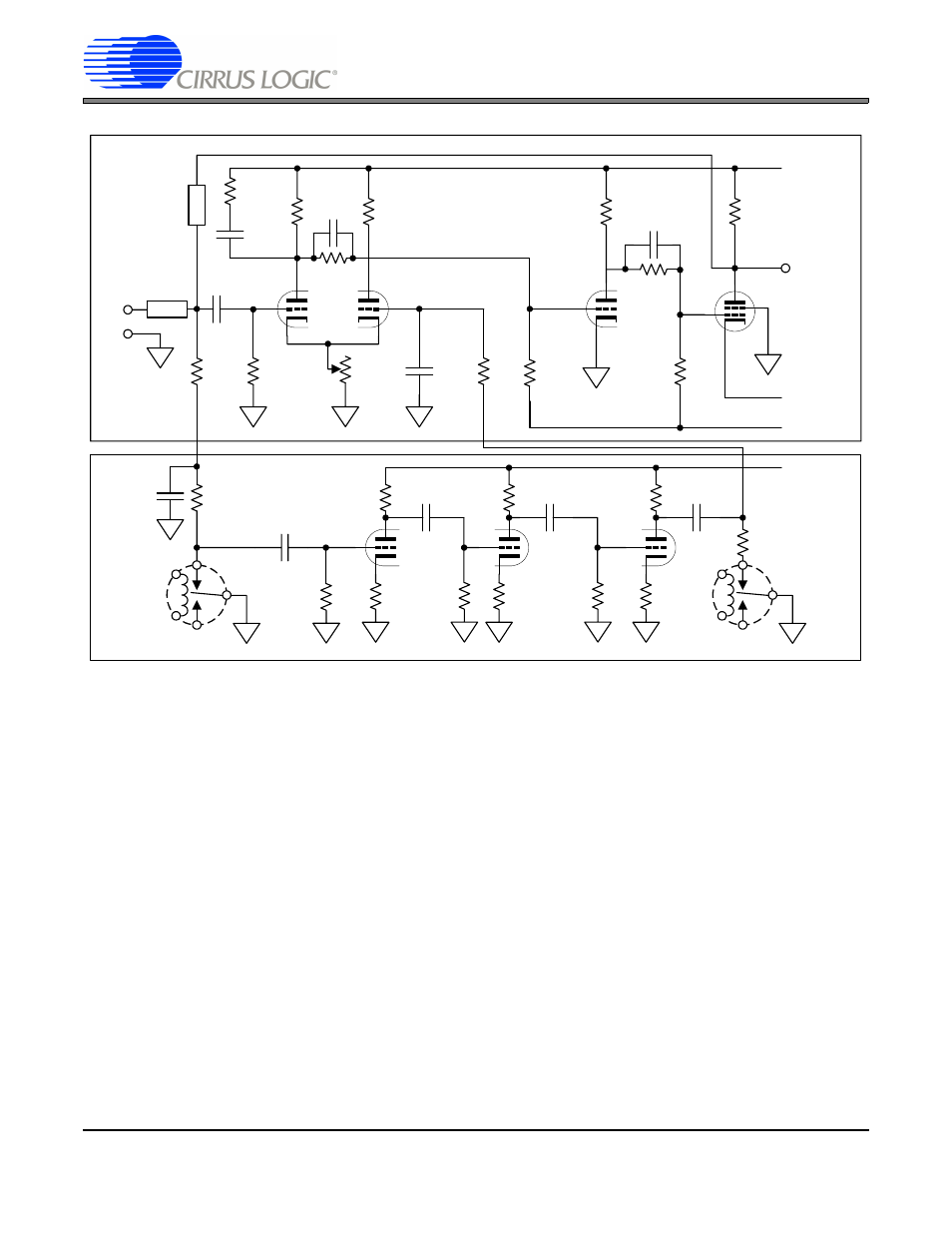
Figure 4. Chopper-stabilized Amplifier Using Electron Tubes and Mechanical Vibrating Switches
3. MODERN CHOPPER-STABILIZED AMPLIFIERS
Monolithic chopper-stabilized amplifiers became available in the late 1970s. Different chopping architectures have
been promoted by various vendors. The various architectures will not be examined in detail here. Before discuss-
ing the particulars of the Cirrus Logic chopper-stabilized amplifiers, it will be beneficial to understand some differ-
ences found in bipolar versus MOS transistors.
For many years bipolar transistors dominated monolithic amplifier designs. Bipolar transistors have some distinct
advantages over CMOS transistors for some performance parameters. The bipolar transistor provides higher
transconductance (I/V gain) for a specific value of operating current. The bipolar device, because of its construc-
tion, also provides lower noise than can easily be achieved in a MOS transistor, for devices of similar silicon area.
The wide band spot noise level is lower in the bipolar transistor. And a much lower 1/f noise corner can be
achieved in a bipolar transistor. Bipolar transistors can also be better matched when manufactured together on the
same silicon die.
Most recently, the most prominent semiconductor processes being developed to shrink the geometry size of
devices is being applied to CMOS technology. CMOS is favored because it can provide lower power consumption
for massive digital chips with millions of transistors. Smaller transistors mean the availability of more transistors in
a given area of silicon. This results in smaller device package sizes. In the last decade, more analog and mixed
signal devices have been designed to take advantage of the smaller geometry CMOS processes. This includes
monolithic amplifiers based upon CMOS processes.
AC Amp
220k
220k
680k
C2
350pF
R8
220k
100k
C4
3nF
R2
330
R7
1k
C1
2uF
Z
i
Z
f
5751
R3
10k
R1
10M
e
IN
C6
2uF
R4
10M
½ 5751
10k
2.2M
C3
10pF
760k
-400V
+300V
Output
+300V
½ 5751
0.1uF
1k
220k
0.1uF
220k
5751
0.1uF
-250V
1M
1M
1k
R6
2.2M
C7
0.01uF
1k
R5
2.2M
C5
0.01uF
1k
6AQ5
DC Amp
NOTE: 5751 = Ruggedized 12AX7.
2M
V2A
f
c
= 0.008 Hz
