3 voltage clamp circuit, 4 buck stage, 1 buck inductor model – Cirrus Logic CS1680 User Manual
Page 11: Figure 13 on, Cs1680
CS1680
DS1055F1
11
page 11). If the boost output voltage exceeds the
overvoltage protection threshold, a BOP fault signal is
generated. Boost overvoltage threshold V
BOP(th)
is
calculated using Equation 4:
For a nominal system design where resistor R
BST
equals 604k
and full-scale voltage V
BST(full)
equals
40V, this sets threshold voltage V
BOP(th)
to 37.4V.
The control logic continuously averages this BOP fault
signal, and if at any point in time the average exceeds a
set event threshold, the boost stage is disabled.
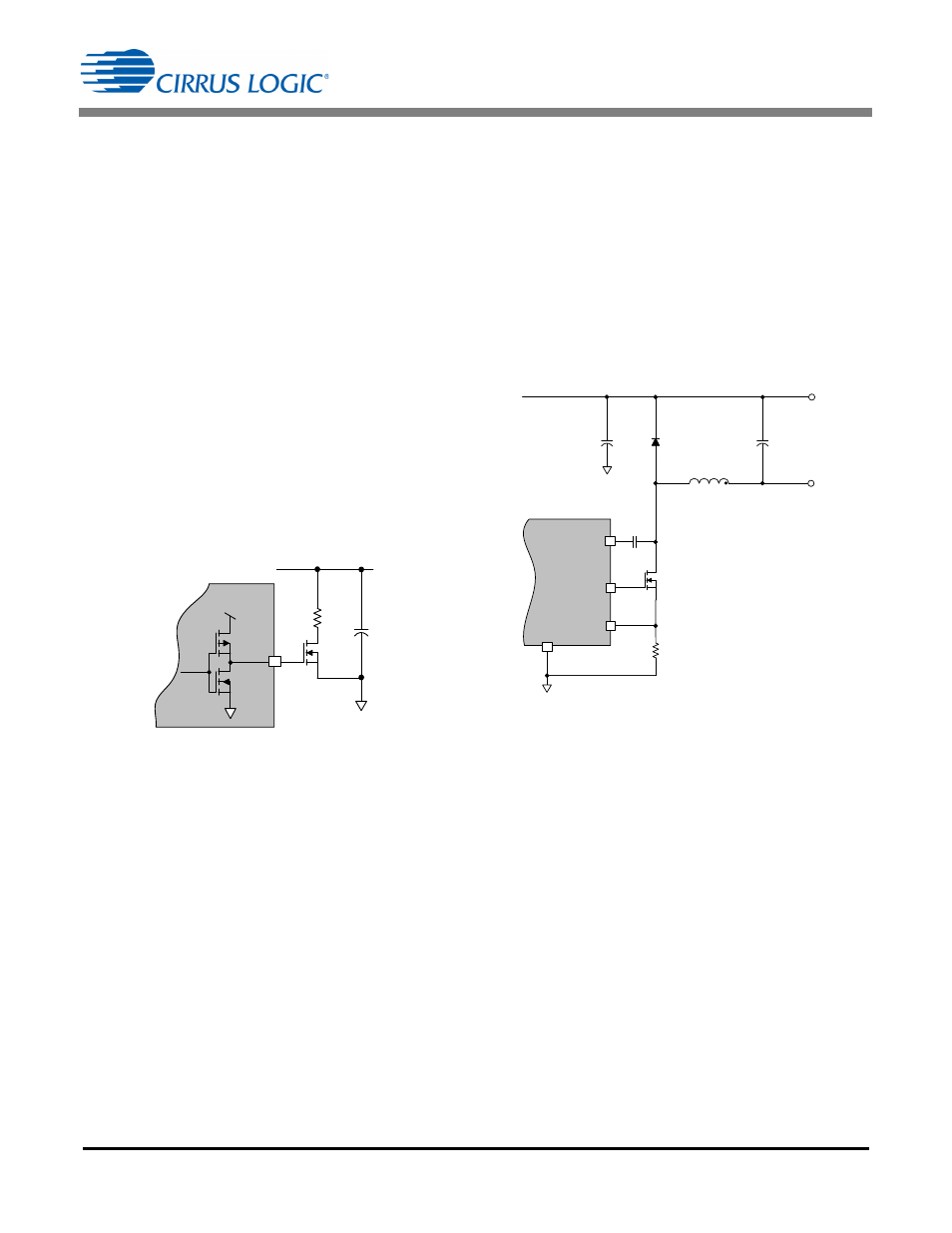
5.3.3 Voltage Clamp Circuit
During transient events and interactions with electronic
transformers, it is possible for the boost stage to
generate more power than is consumed by the second
stage. A clamping circuit is added to the system to
dissipate the excess power. The CS1680 provides
active clamp circuitry on pin CLAMP, as shown in
Figure 12.
The clamp circuit is enabled when boost output
voltage V
BST
exceeds the clamp turn-on threshold
voltage V
CLAMP(on)
. The clamp circuit will remain turned
on until boost output voltage V
BST
is lowered below the
clamp turn-off threshold voltage V
CLAMP(off)
. Threshold
voltage V
CLAMP(on)
is calculated using Equation 5
Threshold voltage V
CLAMP(off)
is calculated using
Clamp Overpower Protection
The CS1680 clamp overpower protection (COP) control
logic continuously monitors the turn-on time of the
clamp circuit. If the cumulative turn-on time exceeds
200ms during the internally generated 2-second
window time, a COP event is actuated, disabling the
boost and buck stages. The clamp circuitry is turned off
during the fault event.
5.4 Buck Stage
The second stage is a current-regulated buck converter,
delivering the highest possible efficiency at a constant
current while minimizing line frequency ripple. A buck
stage is illustrated in Figure 13. Primary-side control is
used to simplify system design and reduce system cost
and complexity.
When operating with a dimmer, the dimming signal is
extracted in the time domain and is proportional to the
conduction angle of the dimmer. A control variable is
passed to the second stage to achieve 5% to 100%
output currents.
The buck stage control parameters assures the LED
current remains constant despite a ±10% line voltage
variation (line regulation), and the LED current remains
constant over a ±20% variation in buck inductor
inductance.
5.4.1 Buck Inductor Model
The BUCKSENSE input is used to sense the buck
inductor current.
When the current reaches a certain
threshold, the gate drive turns off (output on pin
BUCKGD). The sensed current and internal calculation
are used to determine the switching period TT
BUCK
.
The zero-current detect input on pin BUCKZCD is used
to determine the buck inductor zero-crossing
V
BOP th
V
BST full
K
BOP
=
[Eq.4]
CLAMP
R
CLA MP
V
BST
CS1680
11
C
B S T
VDD
EXL
Core
Q
CLA MP
Figure 12. CLAMP Pin Model
V
CLAMP on
V
BST full
K
CLAMP on
=
[Eq.5]
V
CLAMP off
V
BST full
K
CLAMP off
=
[Eq.6]
GND
BUCKGD
BUCKSENSE
CS1680
R
B UCK(S ense)
Q
B UCK
LED +
LED -
V
B S T
C
B S T
D
B UCK
C
OUT
13
12
4
C4
BUCKZCD
9
L
B UCK
Figure 13. Buck Model
