Appendix b. rf401 to md485 network, B.1 connection using a ps100 with a100 – Campbell Scientific MD485 RS-485 Multidrop Interface User Manual
Page 29
Appendix B. RF401 to MD485 Network
Where an RF401 to MD485 network is desired, the following configurations
will provide access to an MD485 network via RF401s.
The connection between the remote RF401 and the base MD485 can be made
in two different ways. 1) Using a Campbell Scientific PS100 Power Supply
with A100 Null Modem Adapter. The PS100 provides 5 and 12 volts for
system operation and the A100 performs the function of a null modem (the
RF401 and MD485 are both "modem" devices). 2) Using a null modem cable
and transformers to provide power to the RF401 and the MD485.
The following sections will describe how to set-up the RF401 to MD485
network using each of these two methods for each communication mode.
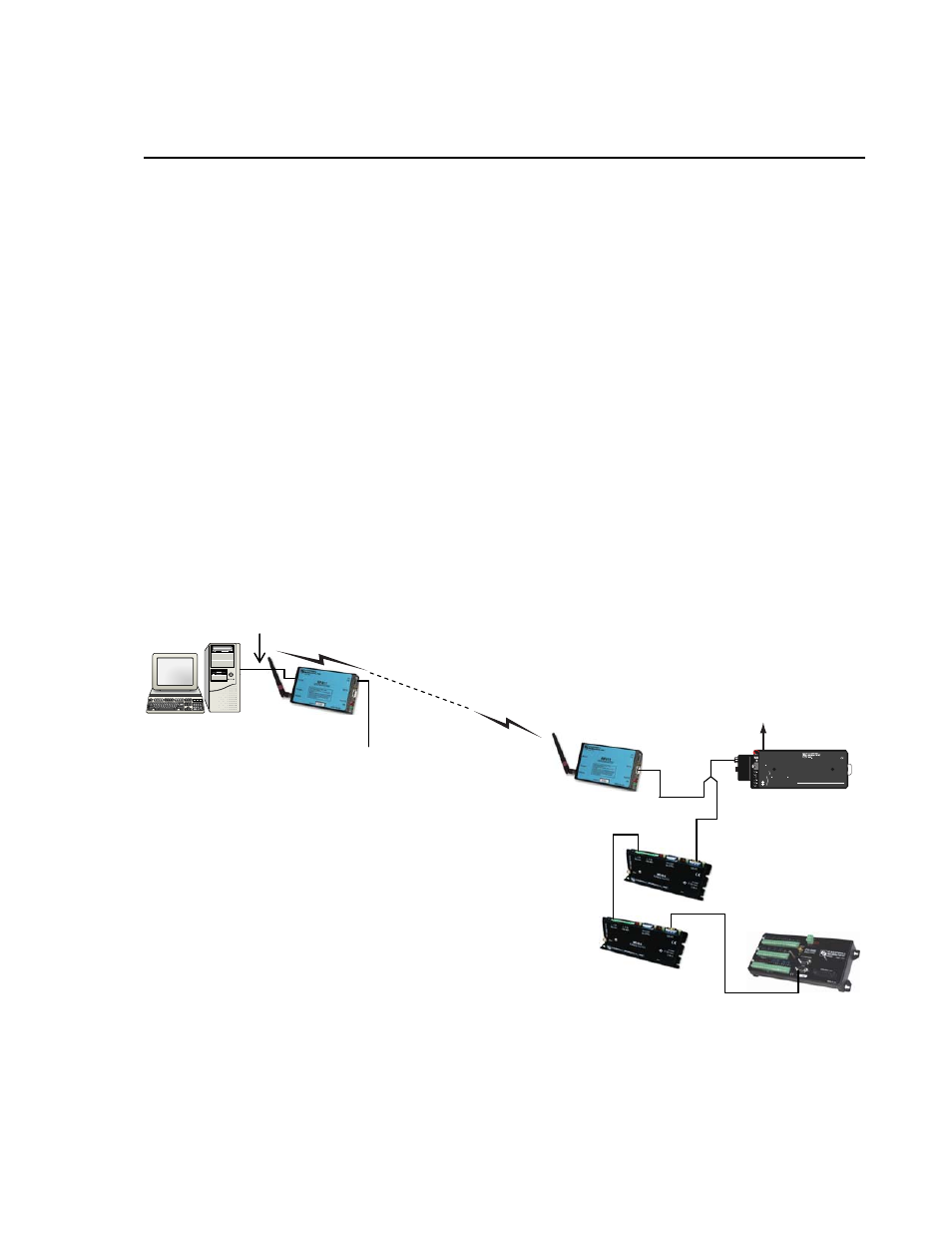
B.1 Connection using a PS100 with A100
Figure B-1 shows an RF401 to MD485 network using a PS100 with A100.
The following configurations will provide communications in transparent mode
or with MD9 emulation. Connection to a single PakBus datalogger is possible
with transparent communication. PakBus Networking is not possible using the
PS100/A100, but can be done using a datalogger in place of the PS100/A100
for routing.
+12V
PS100 12V POWER SUPPLY
A100
Null Modem Port
Adapter
WITH CHARGING REGULATOR
MADE IN USA
WARNING:
PERMANENT DAMAGE TO
RECHARGEABLE CELLS MAY
RESULT IF DISCHARGED
BELOW 10.5 VOLTS
+12V
BATTERY - INTERNAL (12V 7 AMP HOUR)
LIFT TO
REMOVE
BATTERY - EXTERNAL RECHARGEABLE BATTERY
CHARGE - CHARGING VOLTAGE PRESENT
OFF ON - POWER TO 12V TERMINALS
CHARGE
CHARGE
FROM CHARGER OR SOLAR PANEL
16-28VDC OR 18VAC RMS
TO EITHER TERMINAL, TO OTHER
POWER TO DATALOGGERS
OR 12V PERIPHERALS
Logan, Utah
RS-232
To Wall Transformer
Power
CS I/O
CS I/O
CS I/O
RS-485
FIGURE B-1. RF401 to MD485 Conversion
B-1
