Flight optimisation, Groundspeed (speed over ground), Wind direction and wind strength – Flytec 6015 * User Manual
Page 27: Glide ratio (= l/d ratio), Operation manual flytec 6015, 5 flight optimisation
Operation Manual Flytec 6015
25
3.5 Flight
optimisation
3.5.1 Groundspeed (speed over ground)
The GPS-Receiver calculates its new position once every second. Speed over Ground is
derived from the distance between these positions. It is possible to reach conclusions about
the wind’s influence from the difference between flying speed (Airspeed) and the speed over
ground.
3.5.2 Wind direction and Wind strength
It is very important to know the wind in direction and
strength, especially in
case of an out landing.
The wind strength can be selected within the user
defined fields.
For this purpose it is however necessary to fly one or two
complete circles at similar speed as possibly can be done.
Duration time for
one full circle should at least be 16 seconds,
some more time would be
better.
Whilst circling, the 6015-GPS
determines the direction of least
speed over ground, and checks also synchronously if in opposite direction
there might be the fastest speed over ground.
The calculation of wind speed and wind strength is the result hereof.
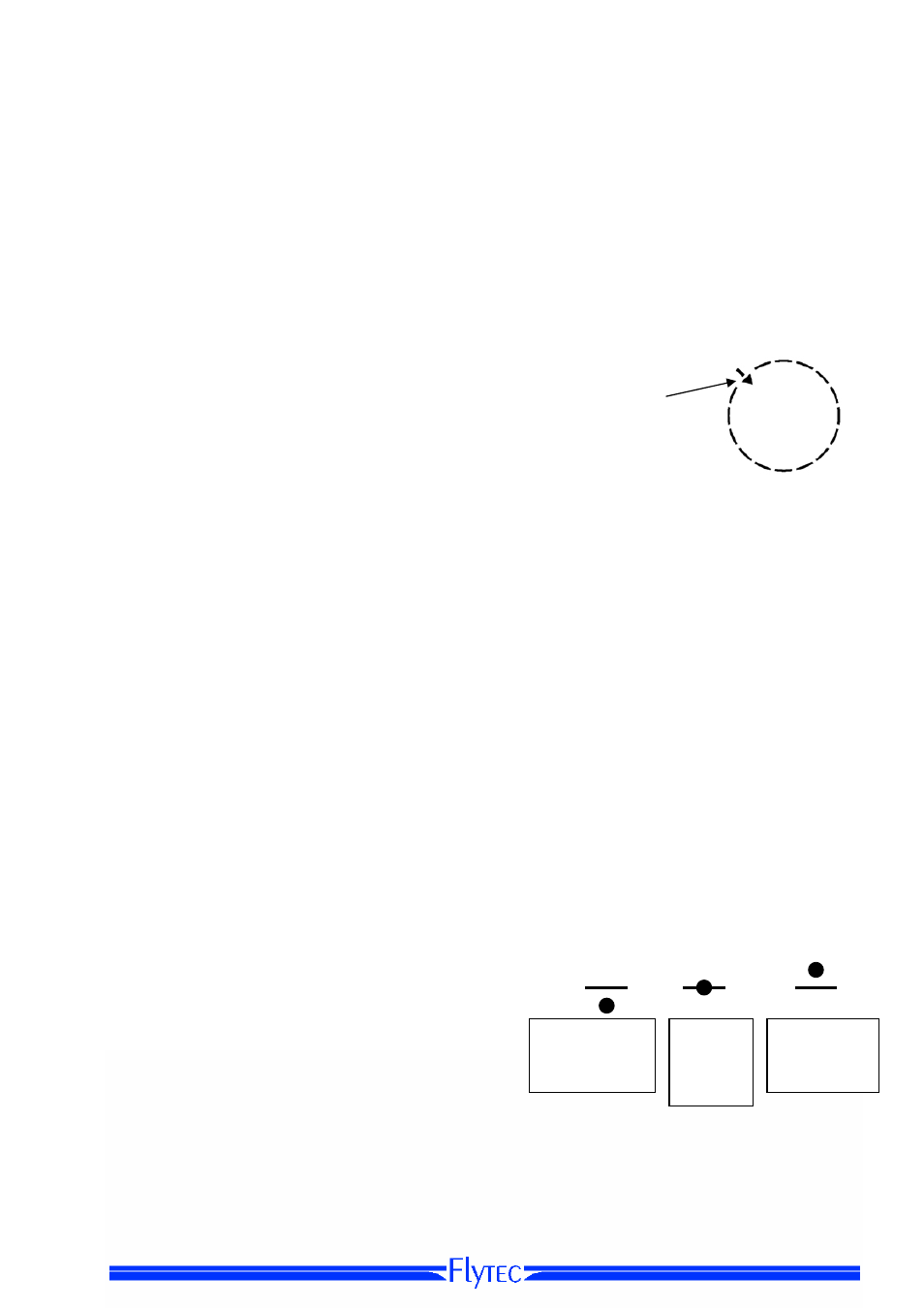
Wind direction is shown in the compass rose at the position from where the wind is blowing
by a small, inwardly pointing arrow. It indicates from where the wind is blowing.
in die Kompassrose an der Stelle, aus welcher der Wind weht, ein kleiner, nach innen zeigender
Pfeil eingeblendet.
During the landing approach this symbol should always be at the top.
3.5.3 Glide ratio (= L/D ratio)
By definition, the glide ratio is calculated by taking the horizontal distance traveled and
dividing it by the height which was lost. If instead of the horizontal speed the speed through
the air is accounted for, the error is 2% at glide ratio 5 and just only 0,5% at glide ratio 10.
This small inaccuracy may be disregarded.
3.5.4 Glide ratio (= L/D ratio)
Again, by definition, the glide ratio is calculated by taking the horizontal distance travelled and
dividing it by the height which was lost on the way.
Glide ratio over Ground :
(L/D)G display page 3)
(L/D)G
= Speed over Ground divided by sink rate
(L/D)Req to the next Waypoint:
(L/D)Req = display page 3 and 4)
Required Glide ratio (L/D) over Ground to reach the
selected WP from the momentary position.
(L/D)Req = Distance to WP/Altitude Difference to WP
ACTUAL L/D
inferior to
(L/D)Req
Actual
and Req
equal
(+/- 0,5)
ACTUAL
L/D better
than Req.
