Removing links, Removing hard links – HP NonStop G-Series User Manual
Page 110
Removing Links
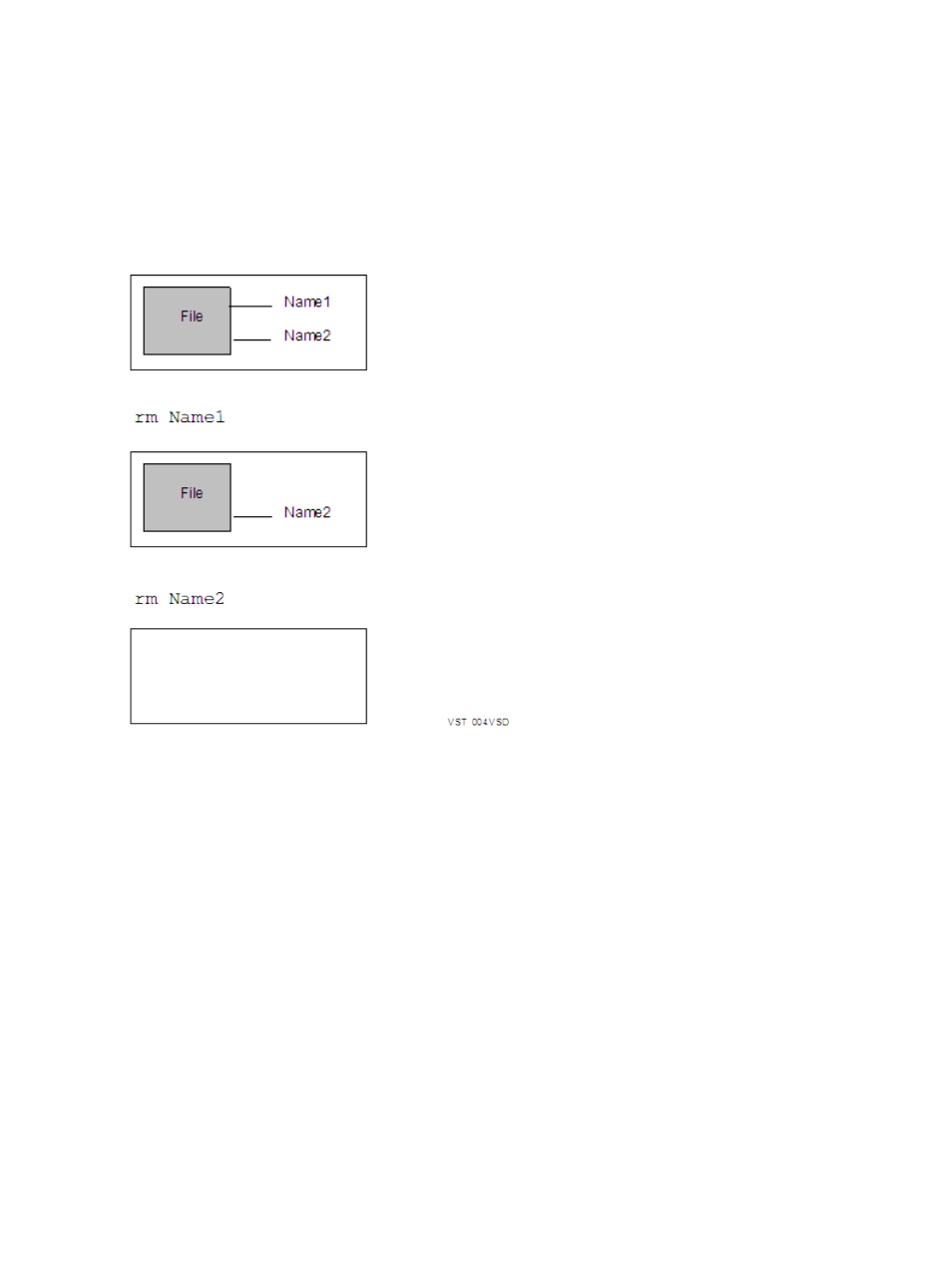
Files are removed (deleted) with the rm (remove file) command. When a file is linked to more than
one filename—that is, when several names refer to the same inode-number—the rm command
removes the link between the inode-number and that filename but leaves the physical file intact.
The rm command actually removes a physical file only after it has removed the last link between
that file and a filename, as shown in
.
For detailed information about the rm command, refer to
“Removing Files (rm)” (page 106)
.
Figure 5 Removing Hard Links
To display both the inode-numbers and the number of filenames linked to a particular i-number,
use the ls command with the -i (print inode-number) flag and the -l (long listing) flag, in the
following format:
ls -il
Now examine the links in your home directory. Remember that the inode-numbers displayed on
your screen will differ from those shown in the example and that your user name and your group’s
name will replace the larry and system entries.
$ ls -il
total 13
1079 -rw-r--r-- 2 larry system 65 Jun 5 10:06 checkfile
1077 -rw-r--r-- 1 larry system 101 Jun 5 10:03 file1
1078 -rw-r--r-- 1 larry system 75 Jun 5 10:03 file2
1079 -rw-r--r-- 2 larry system 65 Jun 5 10:06 file3
1080 drwxr-xr-x 2 larry system 32 Jun 5 10:07 project
Again, the first number in each entry shows the inode-number for that filename. The second element
in each line shows the file permissions, described in detail in
.
110
Managing Files
