Dwyer ULL User Manual
Page 17
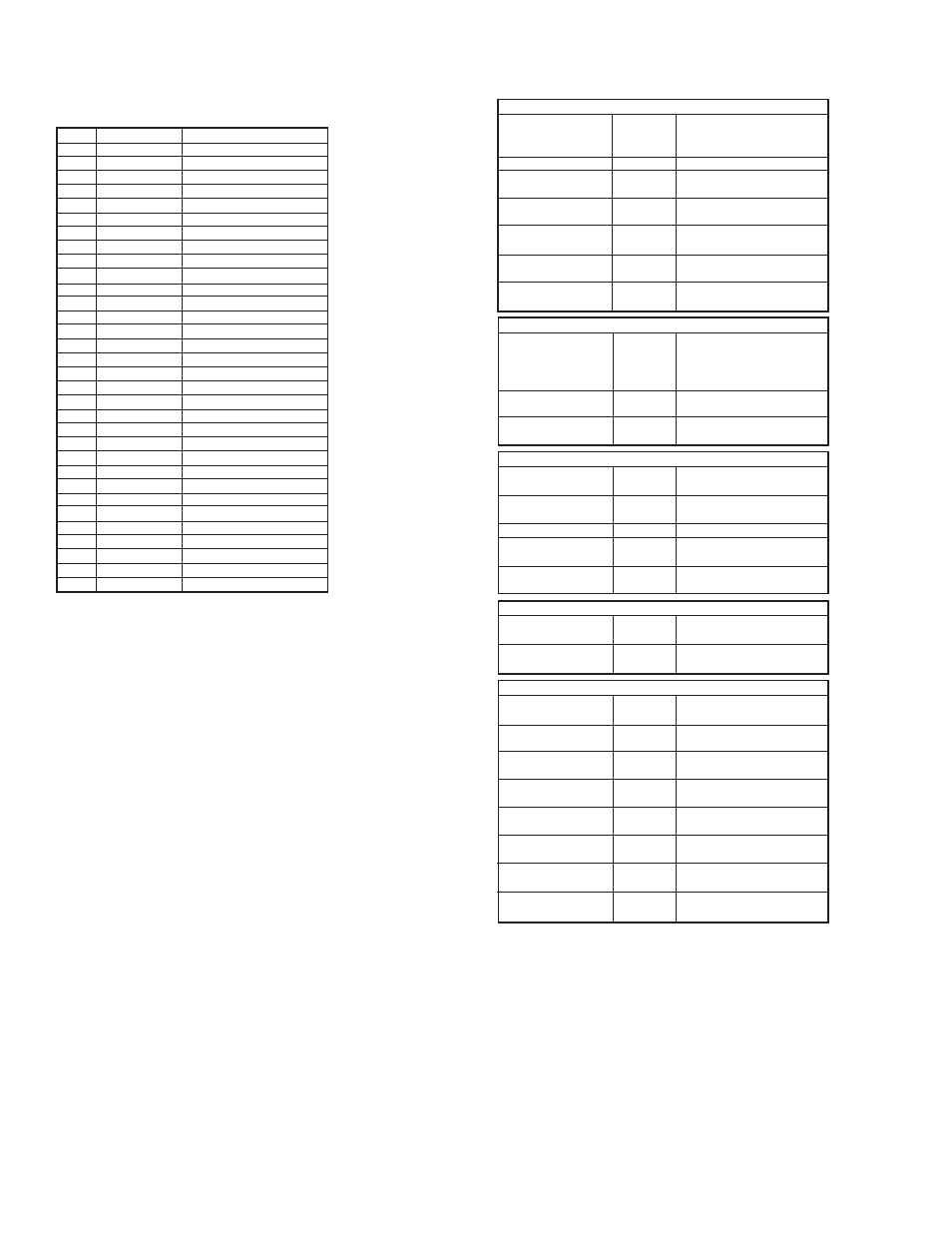
Appendix A
Gas Factor Table
The following table contains 32 different types of gasses and their factor for
compensating the sound velocity:
Appendix B
Installation Tips
Page 16
Distance to tank walls
Surface
Acoustic noises
Electrical interference
Tank installation
Tank installation
Sensor
Must Be
Must Be
Must Be
Must Be
Must Be
Must Be
Must Be
At least 19.69˝ (50 cm) from
walls + 3.94˝/3.28 ft (10 cm/1
m) range.
Fixed on a horizontal surface.
Far away from acoustic
noises and vibrations.
Shielded away from power
and sensor cables.
Far away from tank inlets,
outlets, physical obstacles.
Far away from tank inlets,
outlets, physical obstacles.
Exactly perpendicular to the
surface of the target.
1) Choosing Location
Extension pipes (1)
Extension pipes (2)
Extension pipes (3)
Must Be
Must Be
Must Be
At least 3˝ (7.62 cm) internal
diameter and 19.69˝ (50 cm)
long (from sensor low edge to
pipe low edge).
With completely smooth
interior surface.
Installed with a flange/not
protruding into the tank.
2) Handling Dead Zone
Voltage
A battery
Ripple and noise
Type
Rechargeable supply
Must Be
Must Be
Must Be
Must Be
Must Be
At least 12 VDC on unit
terminals.
Rated higher than 12 volts
due to normal voltage drop.
Not exceeding 100 mV.
Preferably regulated switching
PS (avoid rectified PS).
Non operational when
switched to recharge.
3) Power Source
PLC Connections
Barrier
Must Be
Must Be
As specified in the user
manual, preferably grounded.
Connected in EX zones,
grounded.
4) 2-Wire Interface
Tank Height,
Level/Distance
4 to 20 settings
5 cm margin
Scan distance (1)
Scan distance (2)
Scan distance (3)
SBD (1)
SBD (2)
Must Be
Must Be
Must Be
Must Be
Must Be
Must Be
Must Be
Must Be
Configured correctly.
Defined (consider the
extension pipe).
Kept between pipe low edge
and full level.
Preferably be executed in all
applications.
Executed when the tank is
empty.
Performed after the old stored
data is cleared.
Set up in flange and
extension pipe installations.
At least 1.97˝ (5 cm) before
the pipe edge.
5) Configuration
Factor
0.62
0.63
0.74
0.54
0.99
1.26
0.92
0.53
0.41
0.37
0.56
0.77
1.01
0.38
0.68
0.71
0.90
0.71
0.95
2.93
3.79
0.89
0.62
1.29
0.71
1.30
1.01
0.63
1.02
0.72
0.61
0.57
Symbol
C
2
h
4
o
2
C
3
h
6
o
C
2
h
4
o
C
2
h
3
c
1
o
C
2
h
2
H
3
n
Ar
C
6
H
6
Br
2
Cbrclf
2
CH
3
COCH
2
CH
3
CO
2
CO
CCI
4
Cl
2
C
2
h
6
o
C
2
h
6
C
2
h
6
o
C
2
h
4
He
H
2
H
2
S
C
3
h
8
o
CH
4
Ch
6
n
2
Ne
N
2
CH
3
NO
2
O
2
C
3
H
8
C
3
H
8
O
C
4
H
8
O
Gas
Acetic Acid
Acetone
Acetaldehyde
Acetyl Chloride
Acetylene
Ammonia
Argon
Benzene
Bromine
Bromochlorodifluoromrthane
Butanone
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon Monoxide
Carbon Tetrachloride
Chlorine
Dimethyl Ether
Ethane
Ethanol
Ethylene
Helium
Hydrogen
Hydrogen Sulfide
Isopropyl Alcohol
Methane
Methyl Hydrazine
Neon
Nitrogen
Nitromethane
Oxygen
Propane
Propanol
Tetrahydrofuran
