Stuart Turner Monsoon Extra S3.0 bar Single User Manual
Page 4
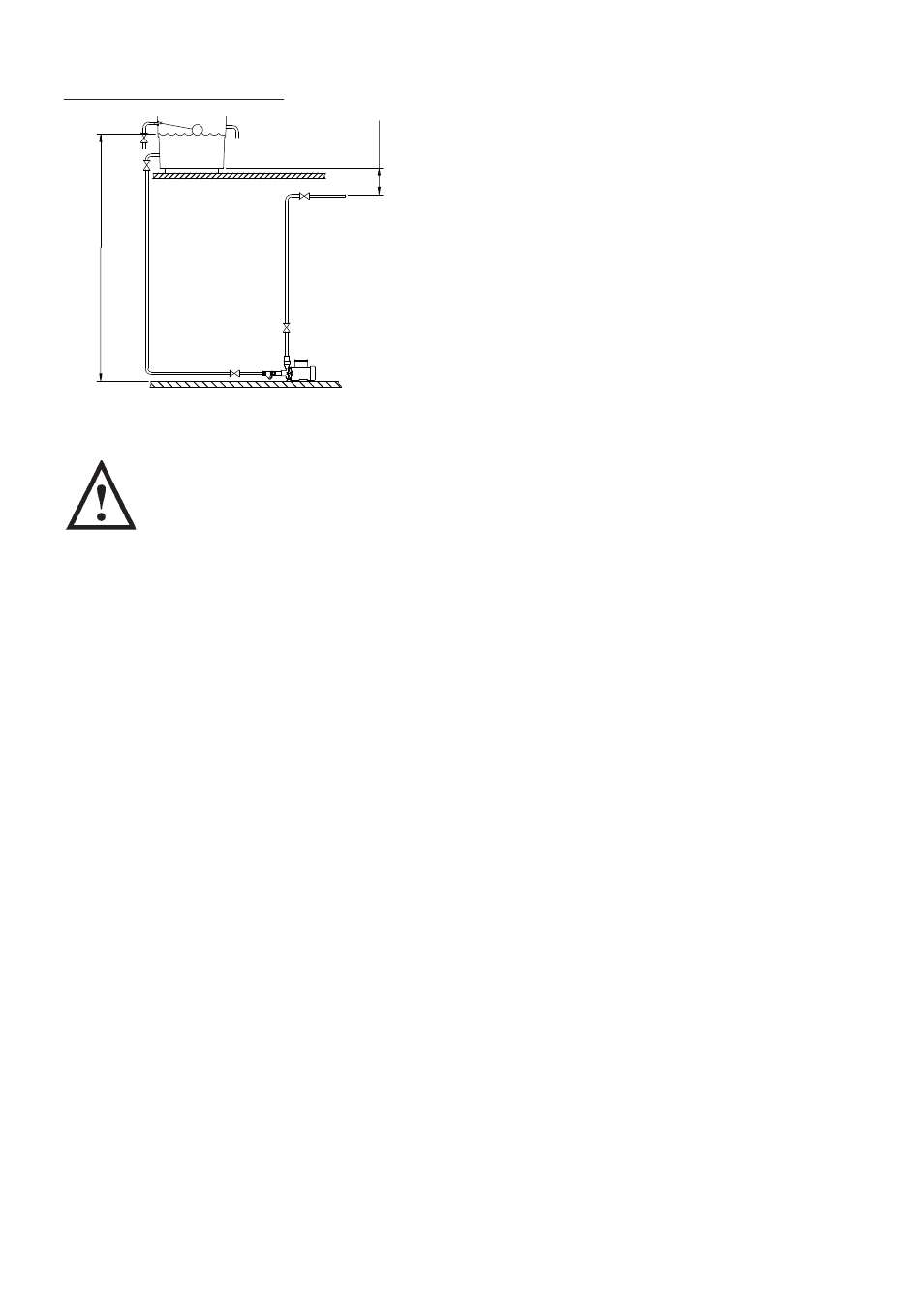
- 4 -
Diagram showing typical cold
water boosting installation.
Cold Water Installation
STEP 2 PIPEWORK CONNECTIONS (General)
WARNINGS:
Ensure pipework to and from pump is independently supported to
prevent forces being transferred to inlet and outlet branches of pump.
Do not introduce solder flux to pumps or pump parts manufactured
from plastic. All solder joints should be completed and flux residues
removed prior to pump connection.
Do not allow contact with oil or cellulose based paints, paint thinners
or strippers, acid based descalents or aggressive cleaning agents.
Always install isolating valves to both suction and delivery pipework.
Do not install a non-return valve, or devices
which contain non-return valves, in the
suction (inlet) pipework to the pump. The
pump must be free to vent to the supply
tanks at all times.
It must be ensured that the water storage capacity is sufficient to meet the flow rates
required by the pump and any other water using fittings and appliances, which may be
operated simultaneously.
As a rule of thumb: assuming a cold water temperature of 10°C and a hot water
temperature of 65°C.
A 6-minute shower using 10 litres/min will consume 40 litres of hot water and 20 litres
of cold. This means the total quantity of water used from the cold water storage tank
will be 60 litres (40 + 20).
A 10-minute shower using 15 litres/min will consume 100 litres of hot water and
50 litres of cold. This means the total quantity of water used from the cold water
storage tank will be 150 litres (100 + 50).
On installations where there are high flow requirements e.g. multiple showers or body
jets.
A 10-minute shower using 45 litres/min will consume 300 litres of hot water and
150 litres of cold. This means the total quantity of water used from the cold water
storage tank will be 450 litres (300 + 150).
Fig. 4
10
metres max
1
metre min
100
mm
min
