KB Electronics KBWA-23D User Manual
Page 27
27
11
HIGH VOLTAGE DIELECTRIC WITHSTAND TEST (HI-POT TEST)
DESCRIPTION
Testing agencies such as UL, CSA, etc., usually require that equipment undergo an
AC Hi-Pot Test. In order to prevent catastrophic damage to the drive, which has been
installed in the equipment, the following procedure is recommended. A typical Hi-Pot
Test Setup is shown in Figure 16, on page 28.
All drives have been factory hi-pot tested in accordance with UL requirements.
DC Hi-Pot Test Voltage = ((Line Voltage X 2) + 1000) X 1.41
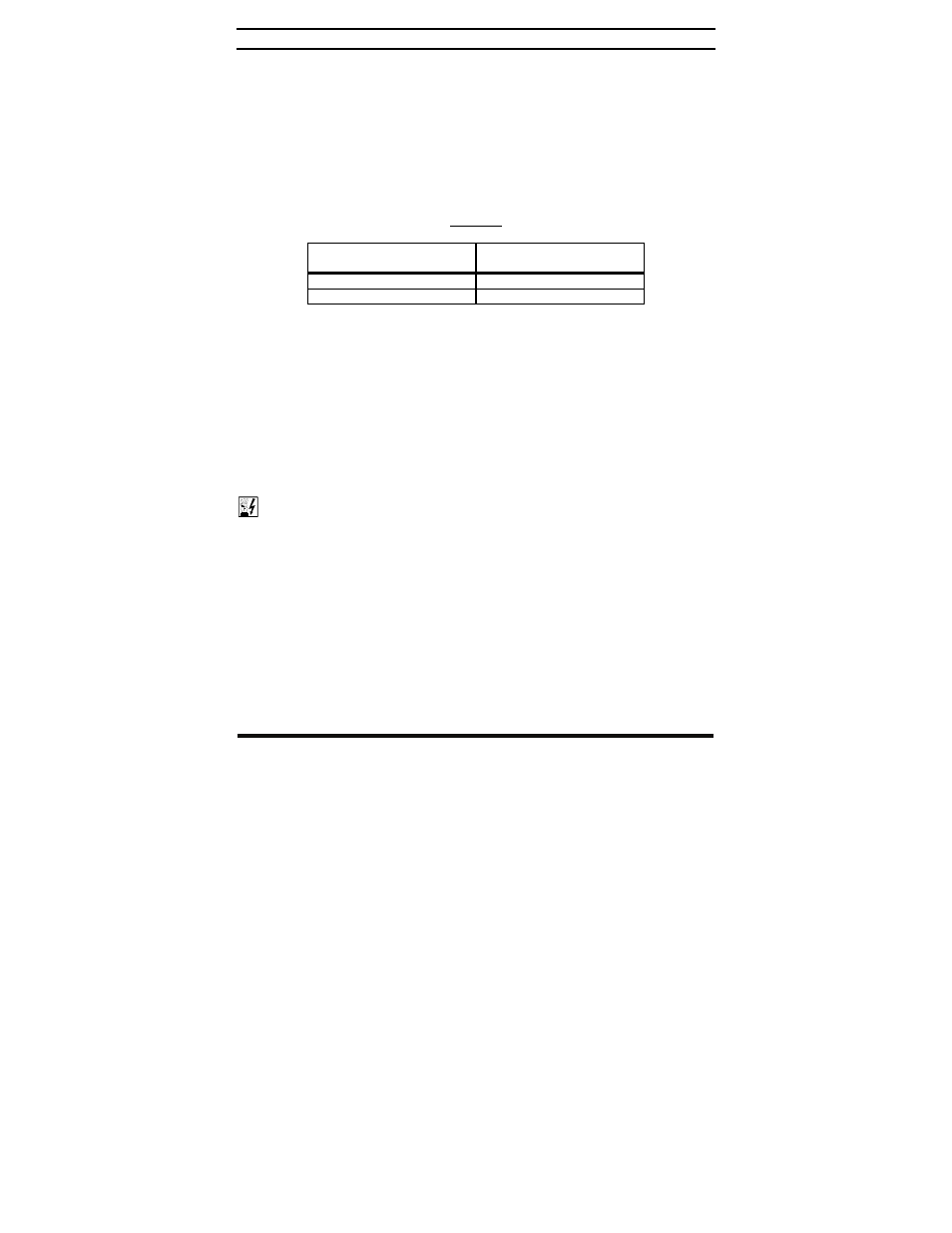
TABLE 5
DC HI-POT TESTER SETUP INFORMATION
Input Line Voltage
(Volts AC)
Hi-Pot Test Voltage
(Volts DC)
115 1800
208/230 2100
EQUIPMENT
A ramp-up type AC Hi-Pot Tester must be used. A suggested Hi-Pot Tester is
Slaughter Model 2550, or equivalent.
Note: If the Hi-Pot Tester does not have automatic ramping, then the hi-pot output
must be manually increased to the test voltage and then manually reduced to zero.
PROCEDURE
Warning! All equipment AC line inputs must be disconnected from the AC
power before performing the Hi-Pot Test.
1. Set the Hi-pot Tester to the appropriate voltage, as shown in Table 5, above.
2. Connect all equipment AC power input lines together and connect them to the H.V.
lead of the Hi-Pot Tester.
3. Connect the RETURN of the Hi-Pot Tester to the frame on which the drive and
other auxiliary equipment are mounted. The Hi-Pot Tester must have an automatic
ramp-up to the test voltage and an automatic ramp-down to zero voltage.
CAUTION! Instantly applying the hi-pot voltage will cause irreversible damage to
the drive, which will void the warranty.
